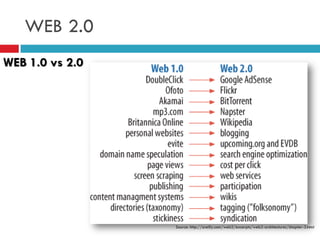
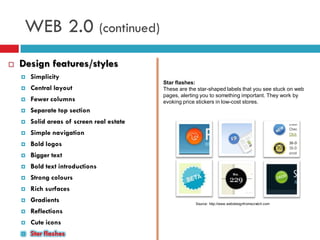
The document discusses the evolution of the web from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0. It defines Web 2.0 based on O'Reilly's definition as a business revolution caused by the move to the internet as a platform. It outlines some key differences between Web 1.0 and 2.0 technologies, including static vs. dynamic/user-generated content. The document also lists several common design patterns of Web 2.0 sites like collaborative tagging, synchronized web, and social networking that emphasize participation and sharing over proprietary platforms.























































![References
1. CASAREZ, V., CRIPE, B., SINI, J. and WECKERLE, P., 2009. Reshaping your business with WEB 2.0.
USA: McGraw-Gill
2. DIX, A. and COWEN L., BCS: HCI 2.0? Usability meets Web 2.0 [online]. Available:
http://www.bcs.org/upload/pdf/ewic_hc07_papaper1.pdf [accessed 20 Feb 2010].
3. Governor J., Hinchcliffe D. and Nickull D., 2009 WEB 2.0 Architectures. Canada: O‟Reilly Media,
Inc.
4. JONES, B. L., 2008. WEB 2.0 Heroes. Indianapolis: Wiley Publishing Inc.
5. O‟Reilly Media, 2010. Dissecting Web 2.0 Examples: Chapter 3 - Web 2.0 Architectures [online].
Available: http://oreilly.com/web2/excerpts/web2-architectures/chapter-3.html [accessed 21 Feb
2010].
6. O‟Reilly Media and TechWeb, 2010. Web2.0 Summit 2009 [online]. Available:
http://www.web2summit.com/web2009 [accessed 21 Feb 2010].
7. SANKAR, K. and Bouchard A. S., 2009. Enterprise Web 2.0 Fundamentals. Indianapolis: Cisco
Systems, Inc.
8. Scratchmedia Limited, 2009. Graphic Design for the web [online]. Available:
http://www.webdesignfromscratch.com/web-design/[accessed 21 Feb 2010].
9. SHUEN, A., 2008. Web 2.0: A Strategy Guide. Canada: O‟Reilly Media, Inc.
10. SITEBOAD, 2010. Creating a successful web 2.0 business [online]. Available:
http://siteboat.com/creating-a-successful-web-20-business/[accessed 21 Feb 2010].
11. SMITH, C., 2010. Web 2.0 (Videos/PPoints) [online]. Available:
http://web2videos.blogspot.com/[accessed 20 Feb 2010].
12. BLIP NETWORKS., 2010. Web2Expo [online]. Available: http://web2expo.blip.tv/[accessed 21
Feb 2010].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web2-0-110309185515-phpapp01/85/Web-2-0-63-320.jpg)