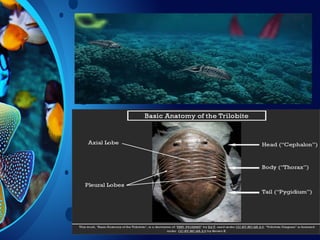
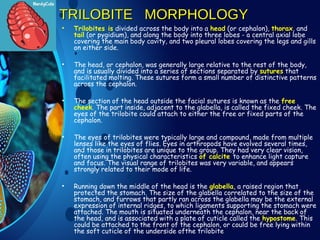
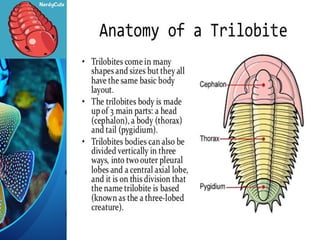
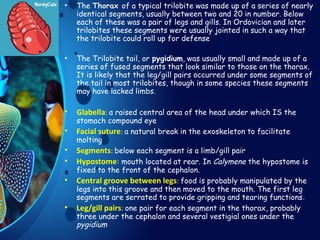
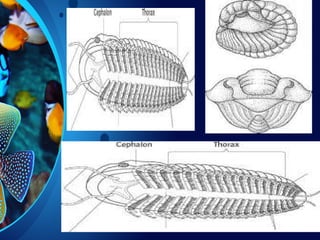
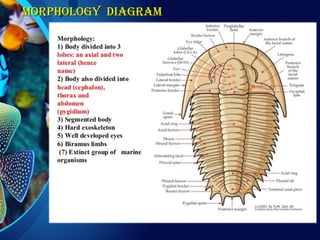
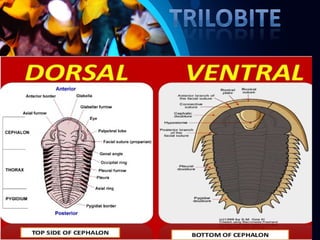
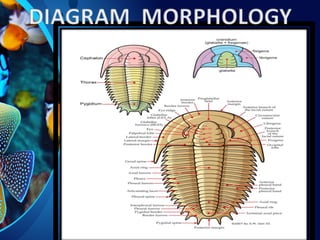
Trilobites are a diverse group of extinct marine arthropods that thrived from the lower Cambrian to the end of the Permian, existing for nearly 300 million years. Characterized by their hard shells, segmented bodies, and complex eyes, they include over 20,000 species, with sizes ranging from a millimeter to 70 centimeters. Trilobites serve as important fossil indicators in paleontological studies due to their distinct morphology and long geological presence.