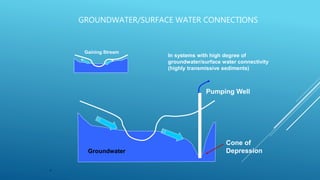
The document discusses various topics related to groundwater and surface water systems. It explains that groundwater and surface water are connected, with pumping wells able to cause interference between cones of depression. It notes that extraction should not exceed recharge to avoid water mining and subsidence, and that recharge zones need protection. The hyporheic zone of water exchange between surface and groundwater is also described. Rainwater harvesting and the water cycle are briefly covered.