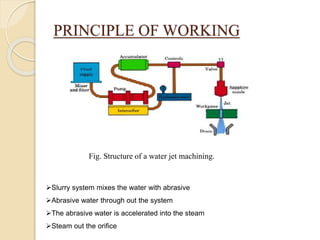
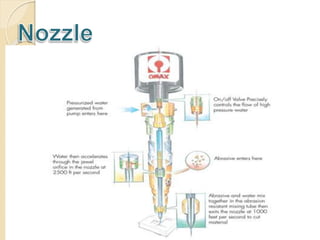
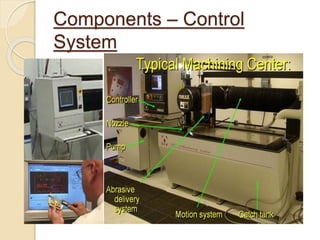
The presentation discusses water jet cutting as a versatile and environmentally friendly machining process that has evolved since the 1930s, now used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and food processing. It outlines the different types of water jets, their working principles, advantages, and disadvantages compared to other cutting technologies like lasers. The document concludes that as technology advances, water jet cutting will achieve faster rates, longer life, and tighter tolerances, positioning it to replace older manufacturing methods.