Embed presentation
Downloaded 230 times

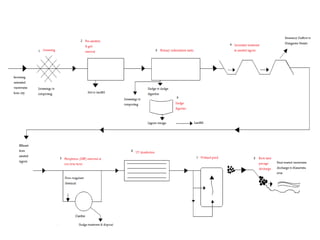








The wastewater treatment process involves screening debris, grit removal through aeration and settling, organic reduction through aerated lagoons, phosphorus removal by adding alum, UV disinfection to kill bacteria, sludge digestion to produce a stable sludge, and final dispersal through an outfall structure and wetland pond into a river.









