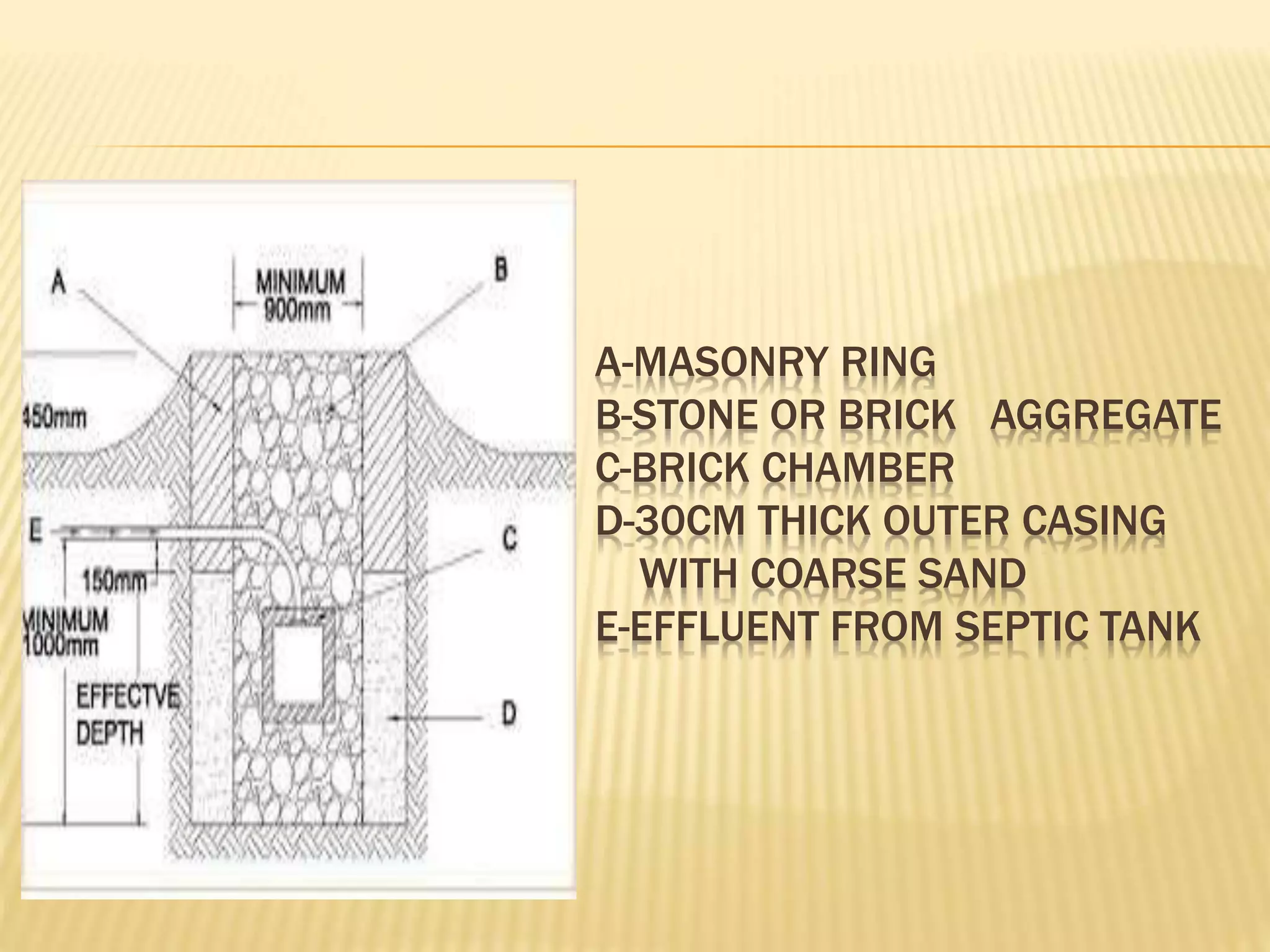
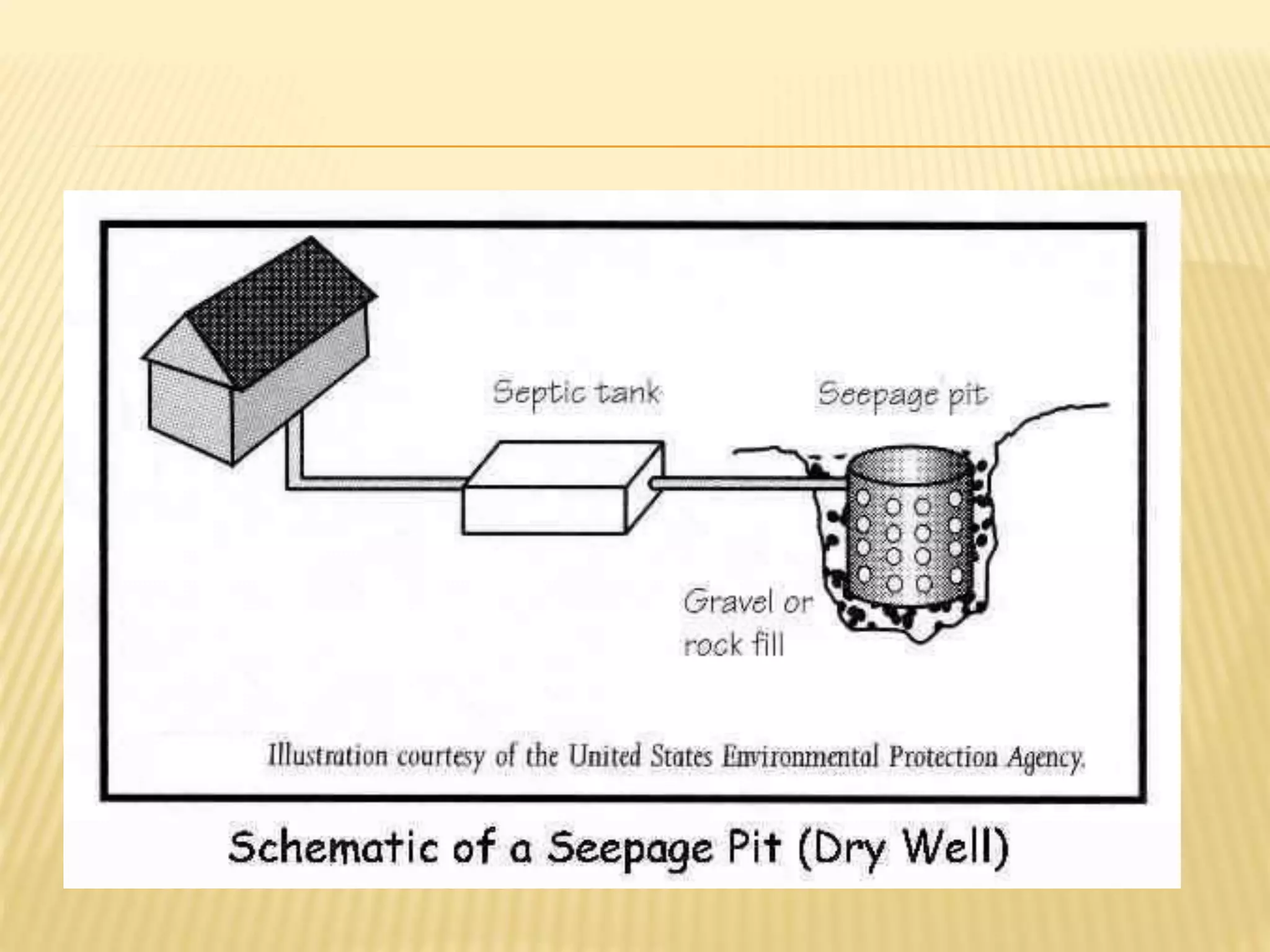
1) A soak pit is an underground chamber that allows pre-treated wastewater from a septic tank to slowly soak into the ground.
2) It is designed with a layer of sand and gravel at the bottom to disperse the flow and is typically 1.5-4m deep with a casing of coarse sand.
3) The wastewater percolates through the soil where small particles are filtered out and organics are digested, though eventual clogging of the pit is inevitable and requires cleaning.