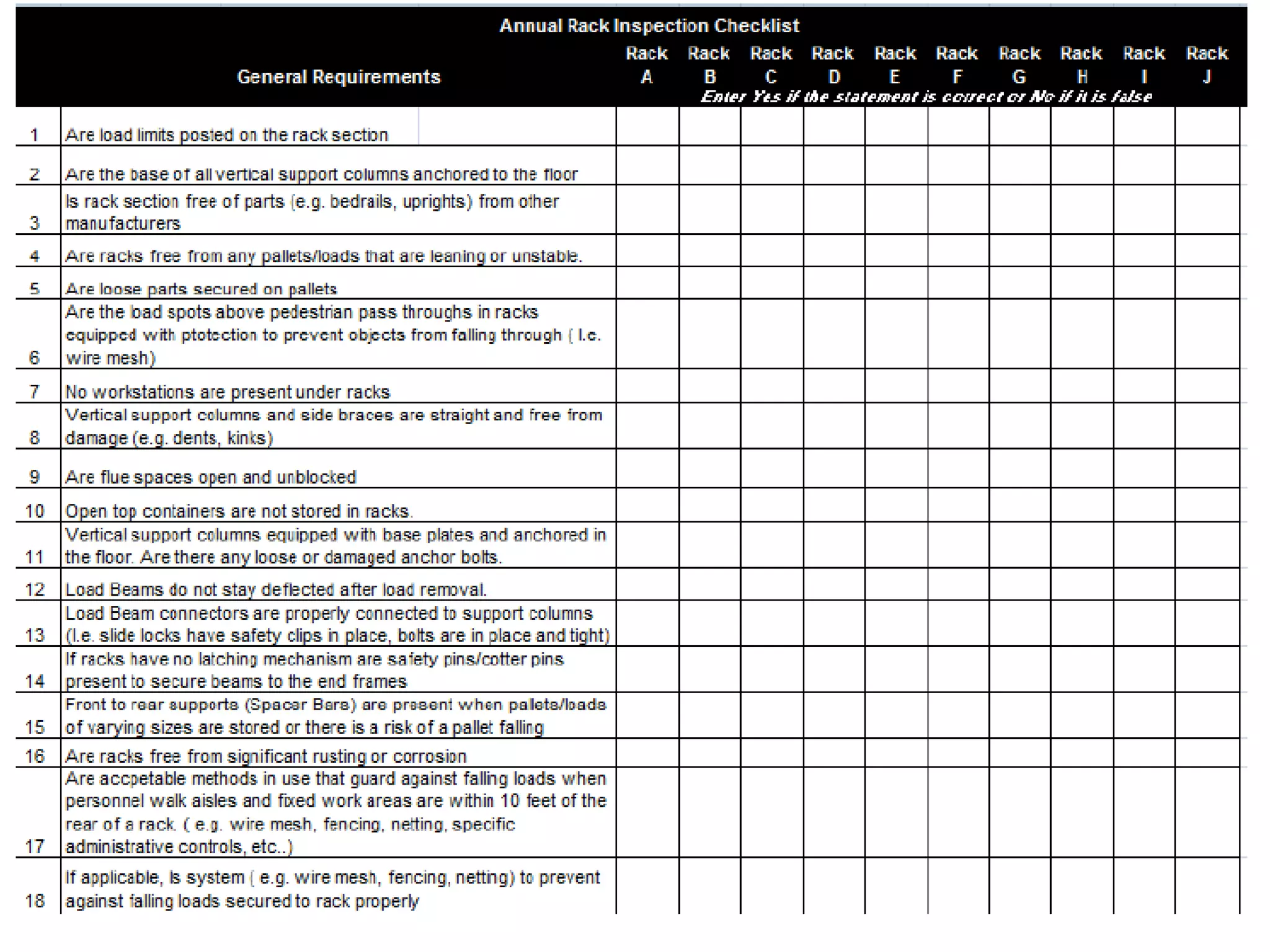
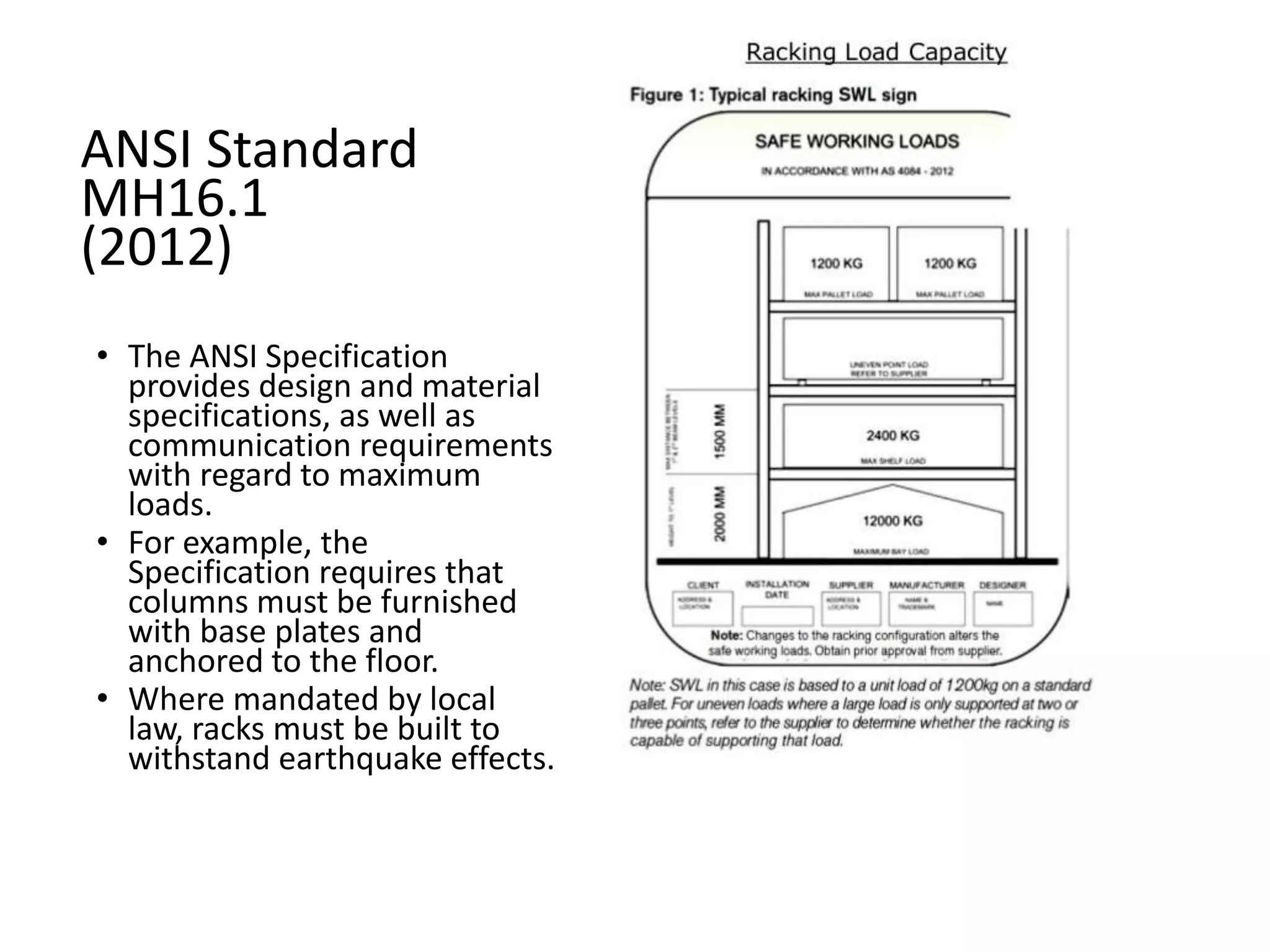
Improperly stored materials can fall and injure workers. Materials should be stacked evenly, with heavier loads on lower shelves. Aisles should be clear. Storage racks must be designed and inspected regularly to prevent materials from sliding or collapsing. The ANSI MH16.1 standard provides specifications for industrial storage racks regarding loads and inspections to ensure worker safety.