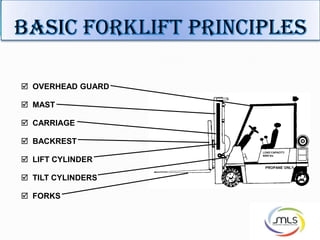
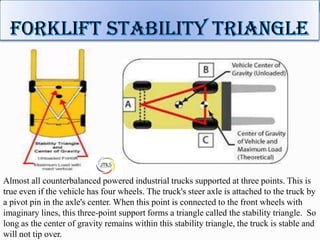
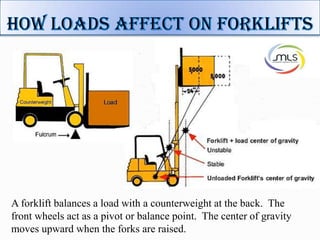
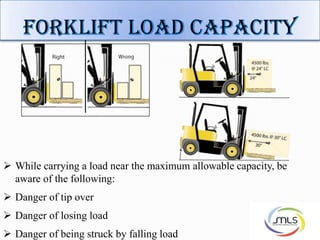
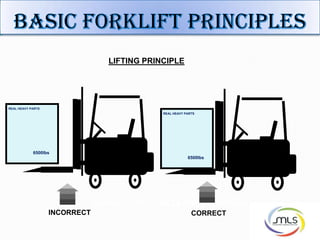
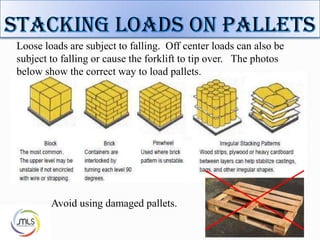
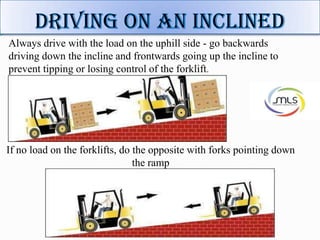
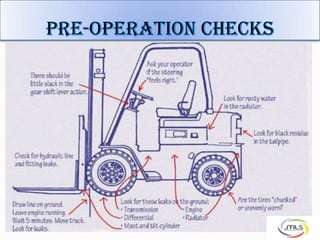
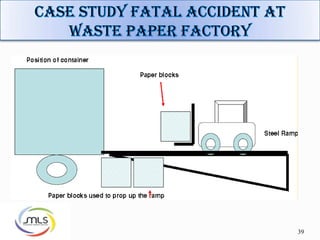
The document discusses forklift operation safety. It begins by describing how a forklift operates and some of its key components. It then discusses potential hazards of forklift operation, including workplace hazards, load hazards, and pedestrians. The document provides guidance on safely operating forklifts, such as only allowing trained operators, controlling forklift speed, ensuring stability of loads, and using caution around other workers. It emphasizes the importance of forklift inspections and maintenance to identify any issues.