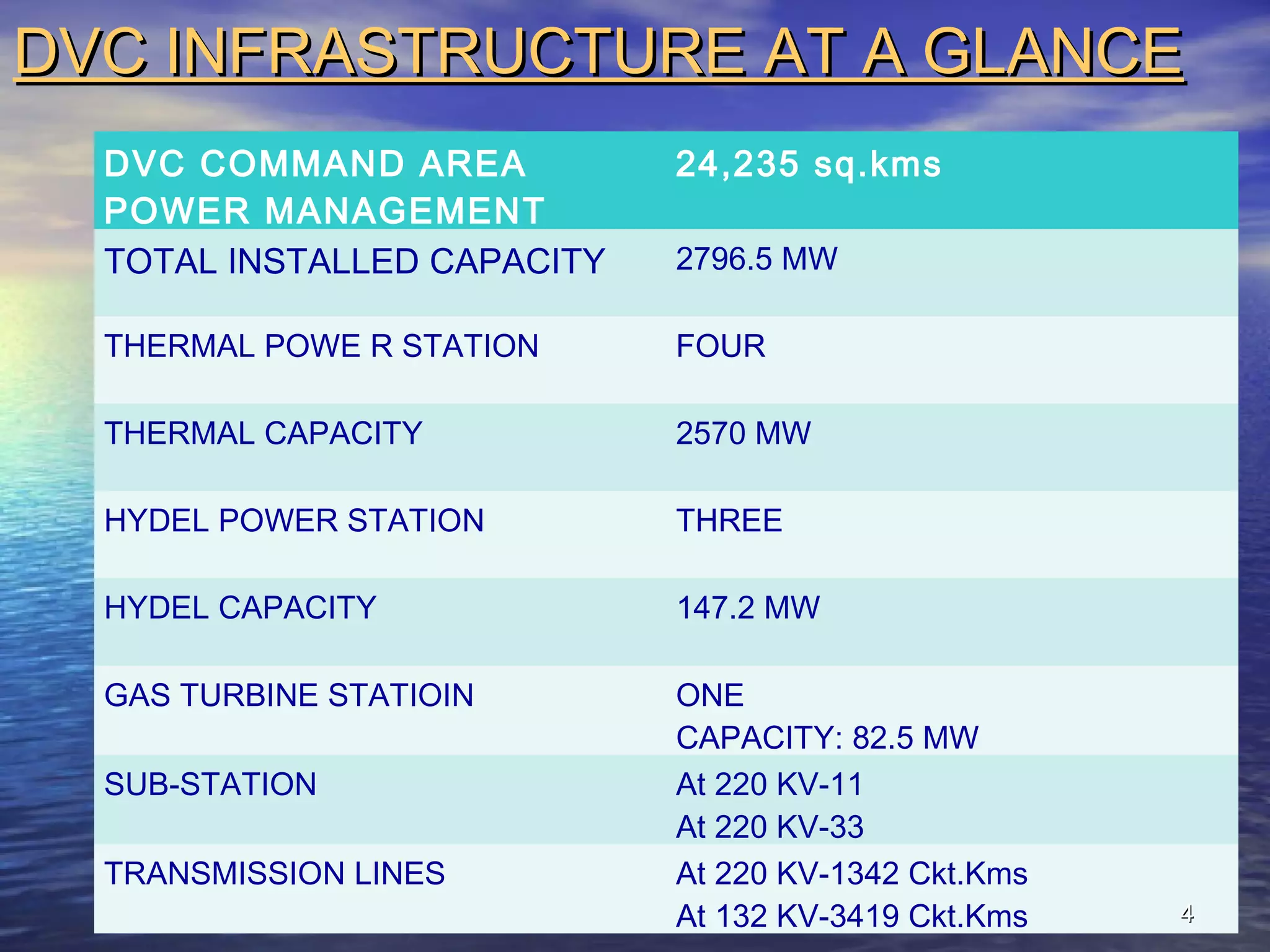
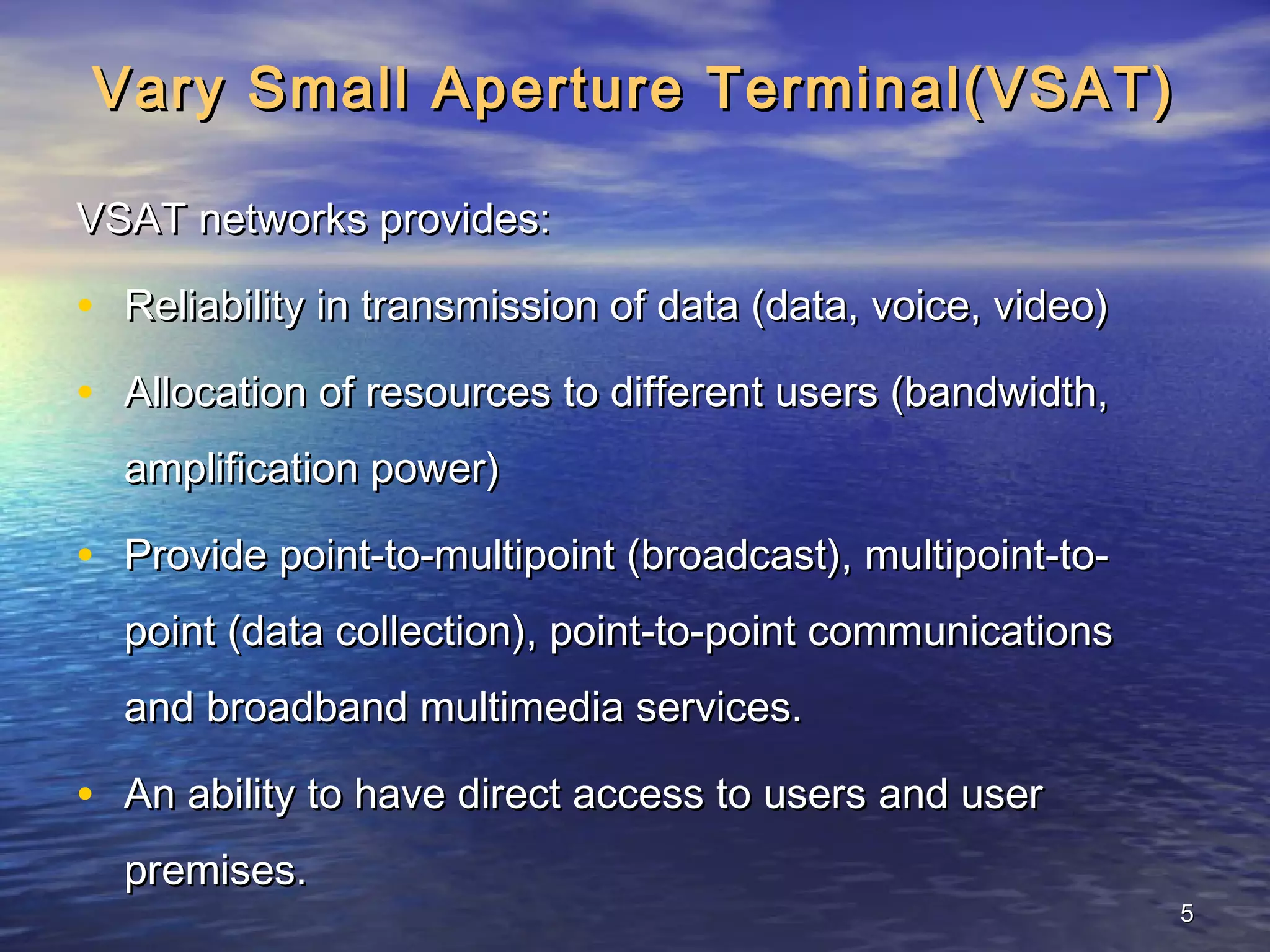
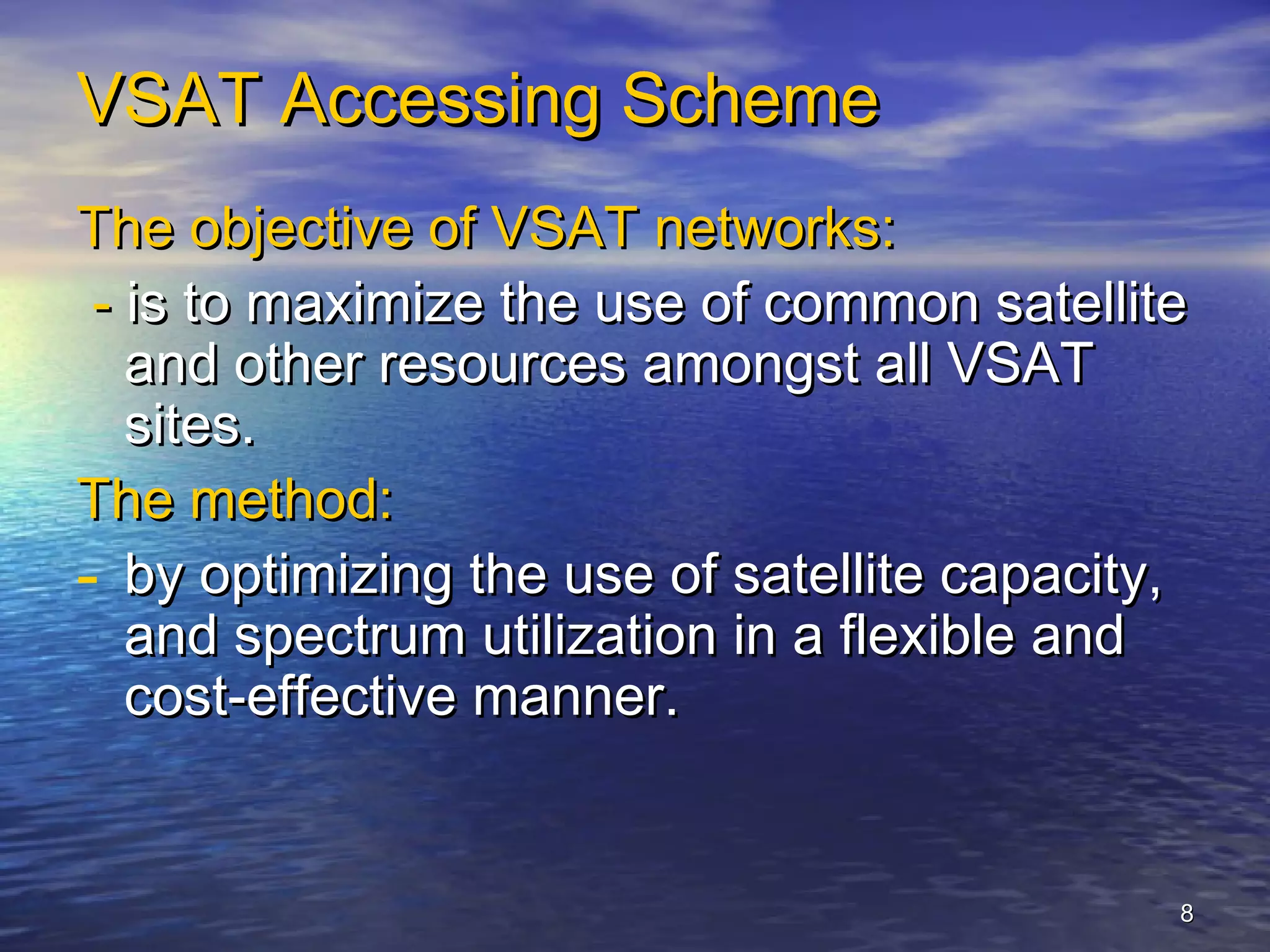
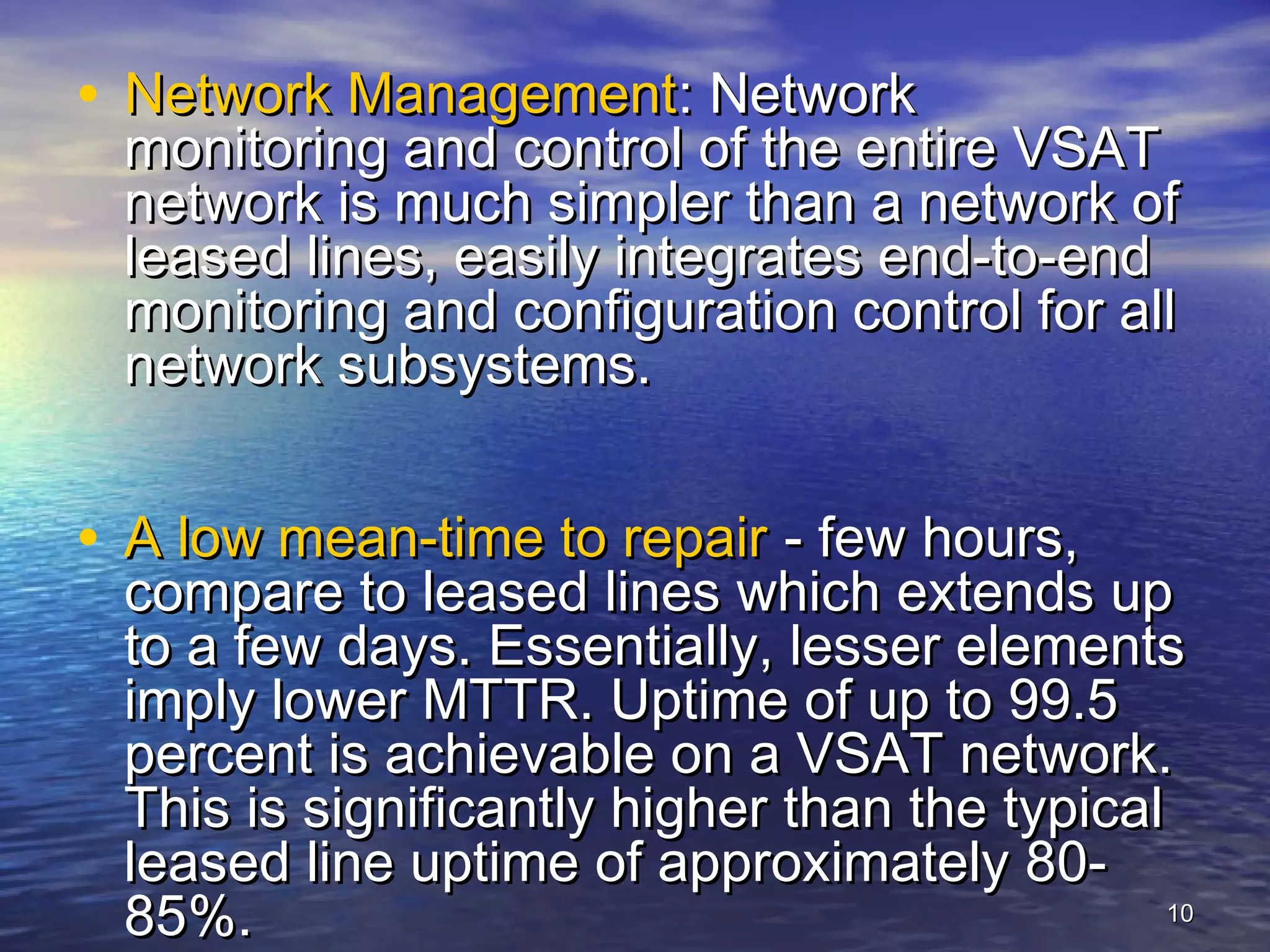
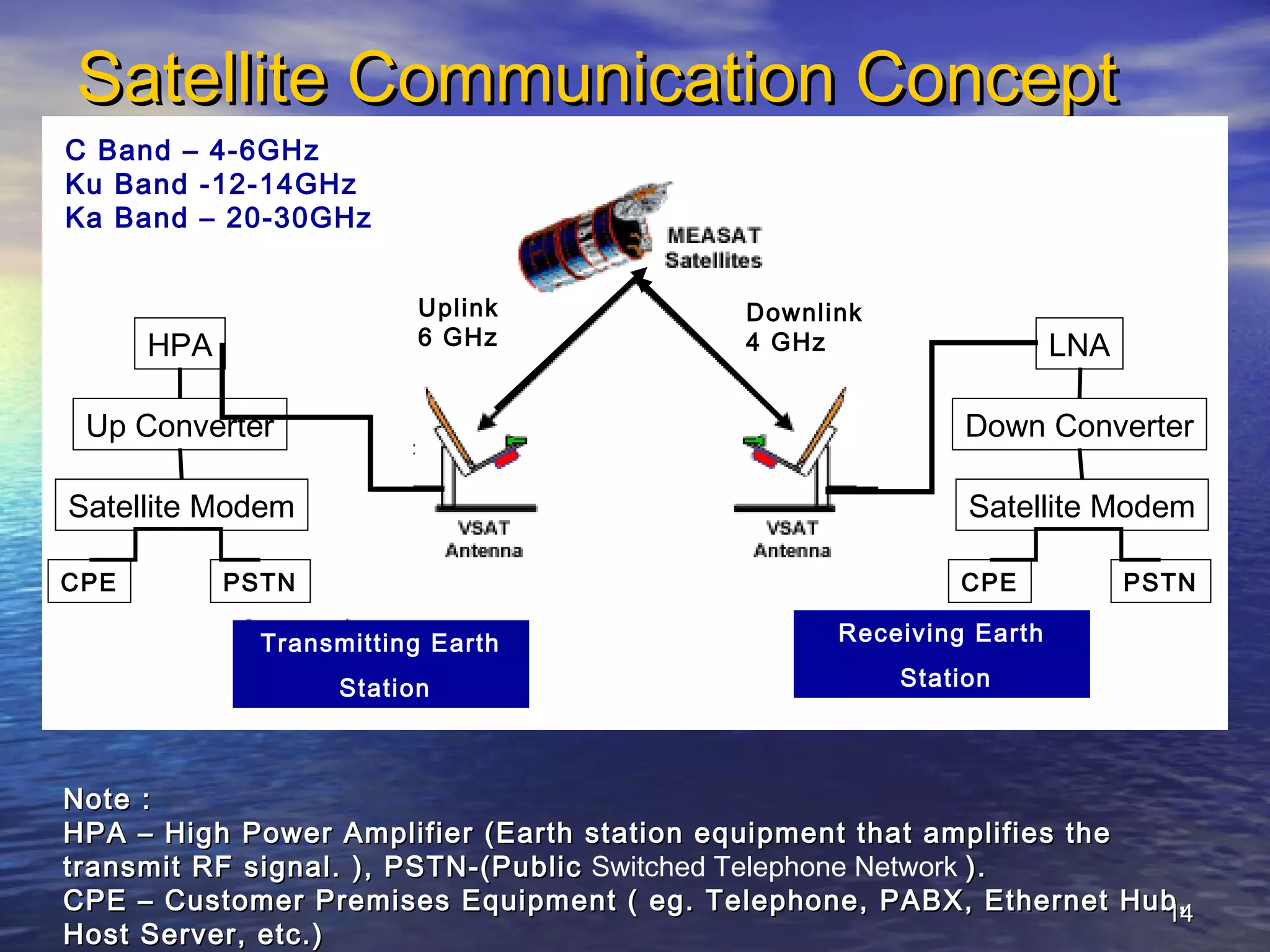
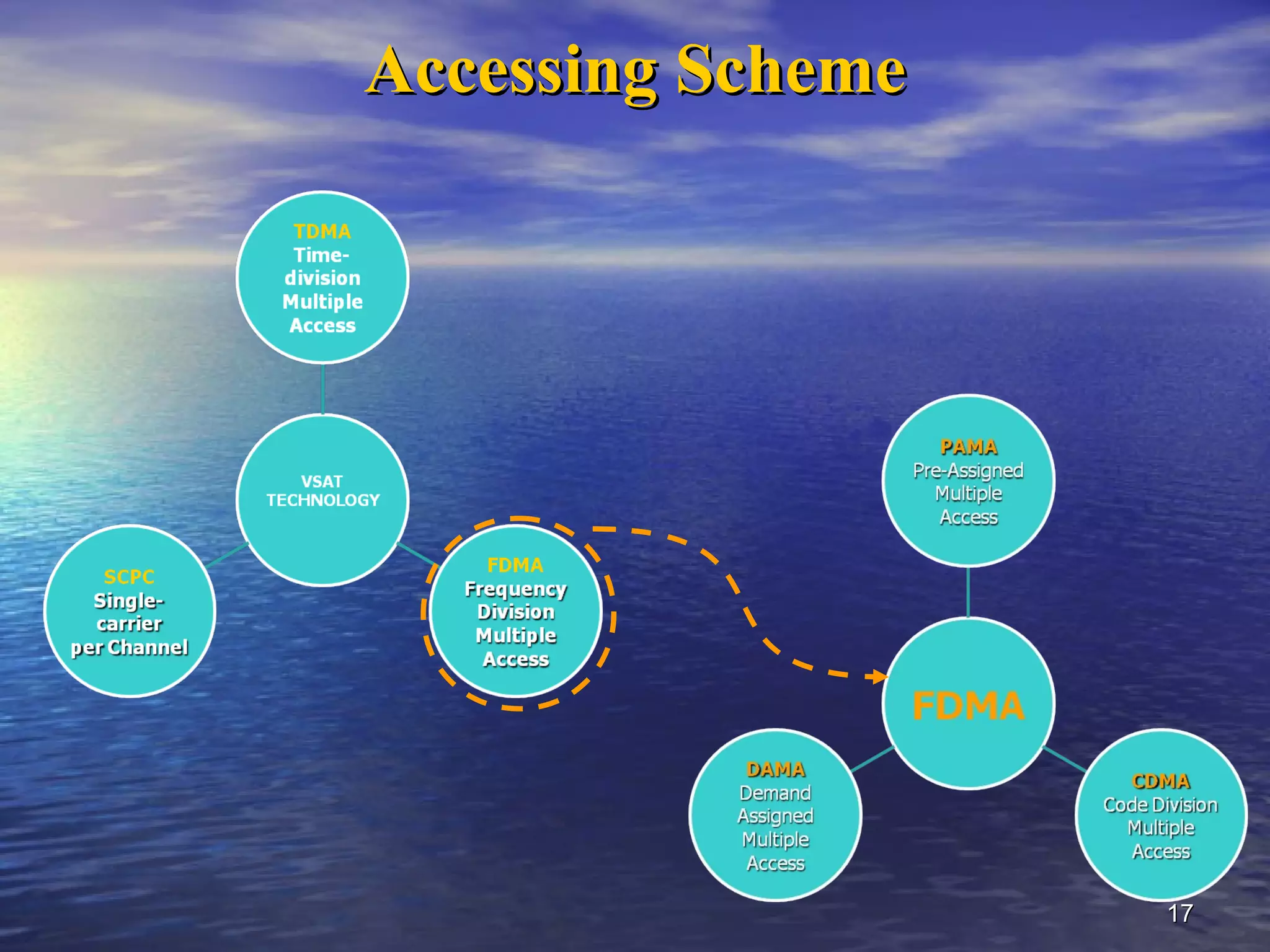
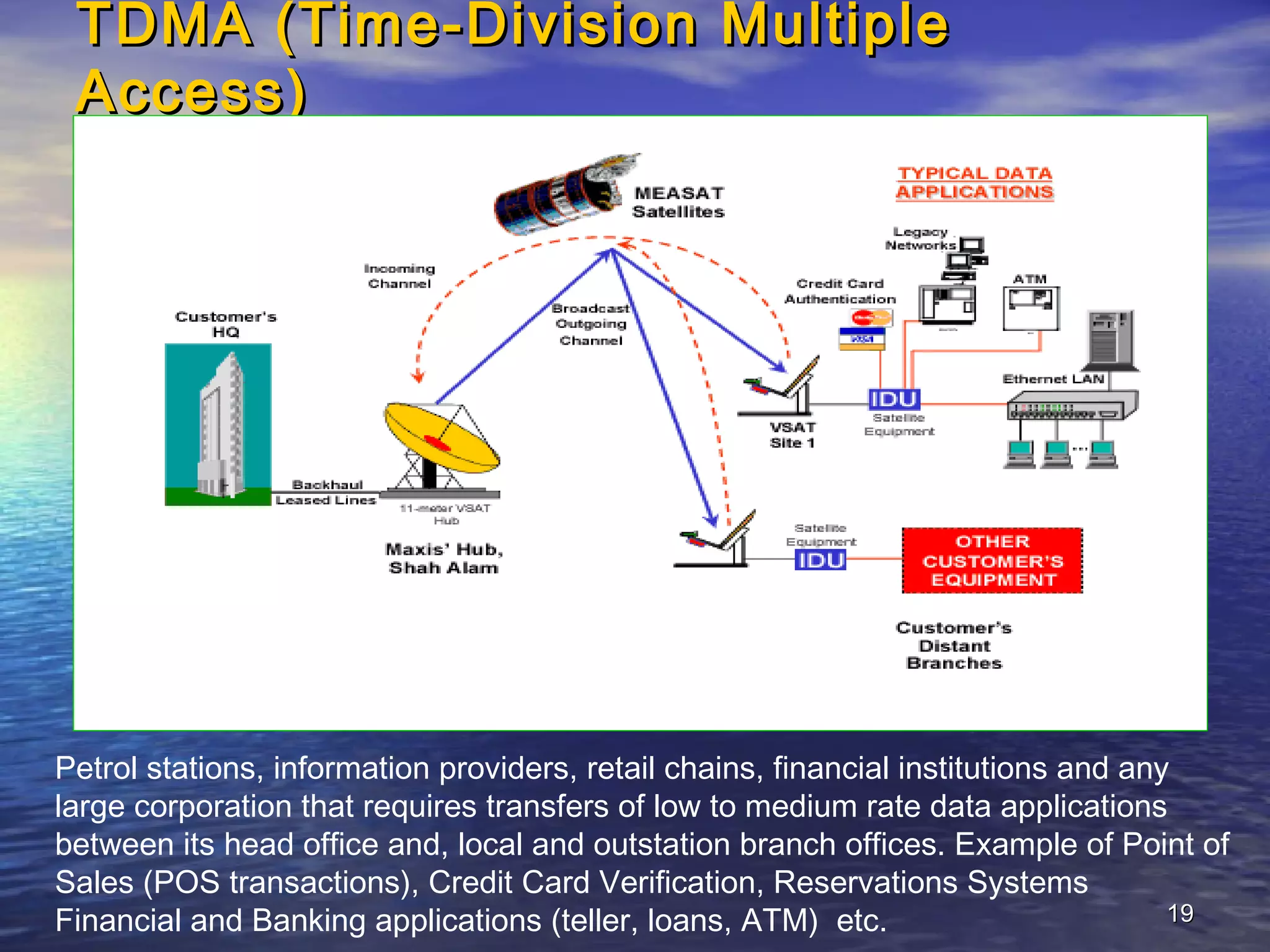
The document provides information about Damodar Valley Corporation (DVC), a river valley project in India. It discusses that DVC was the first multipurpose river valley project of independent India established in 1948. It generates, transmits and distributes electricity and facilitates irrigation and water supply. The document also provides details about DVC's infrastructure including its power generation capacity, transmission lines, and command area covered.