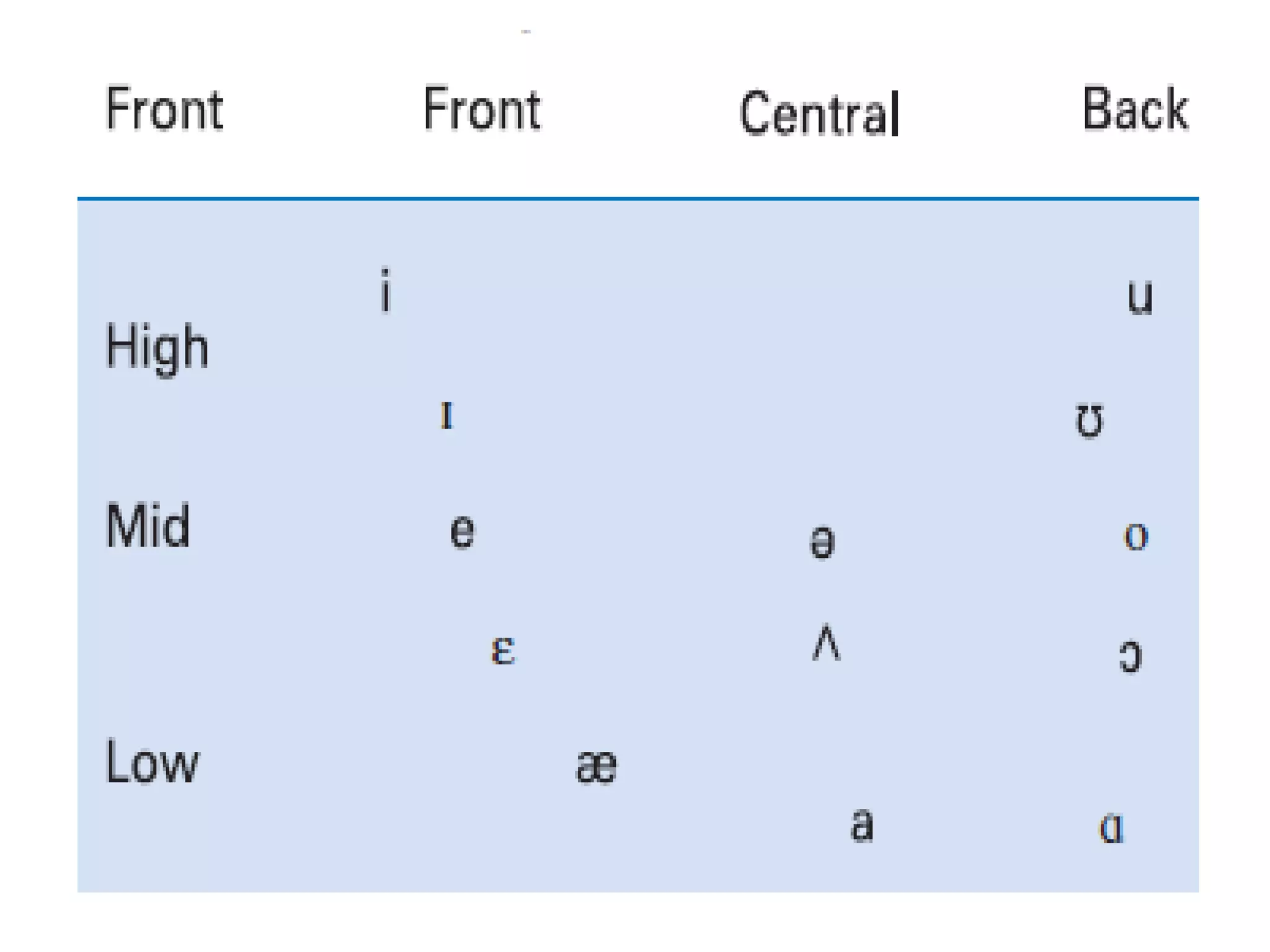
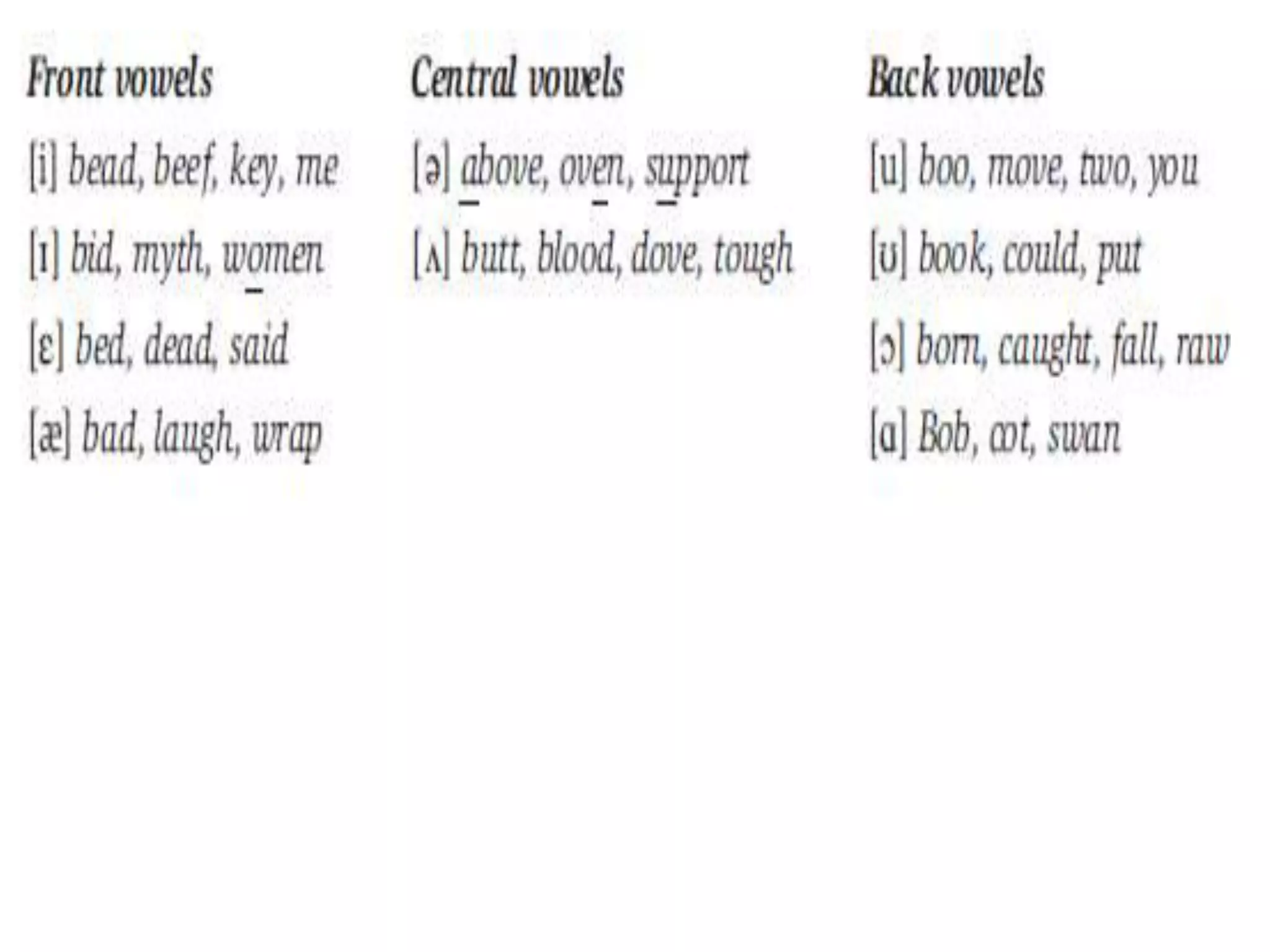
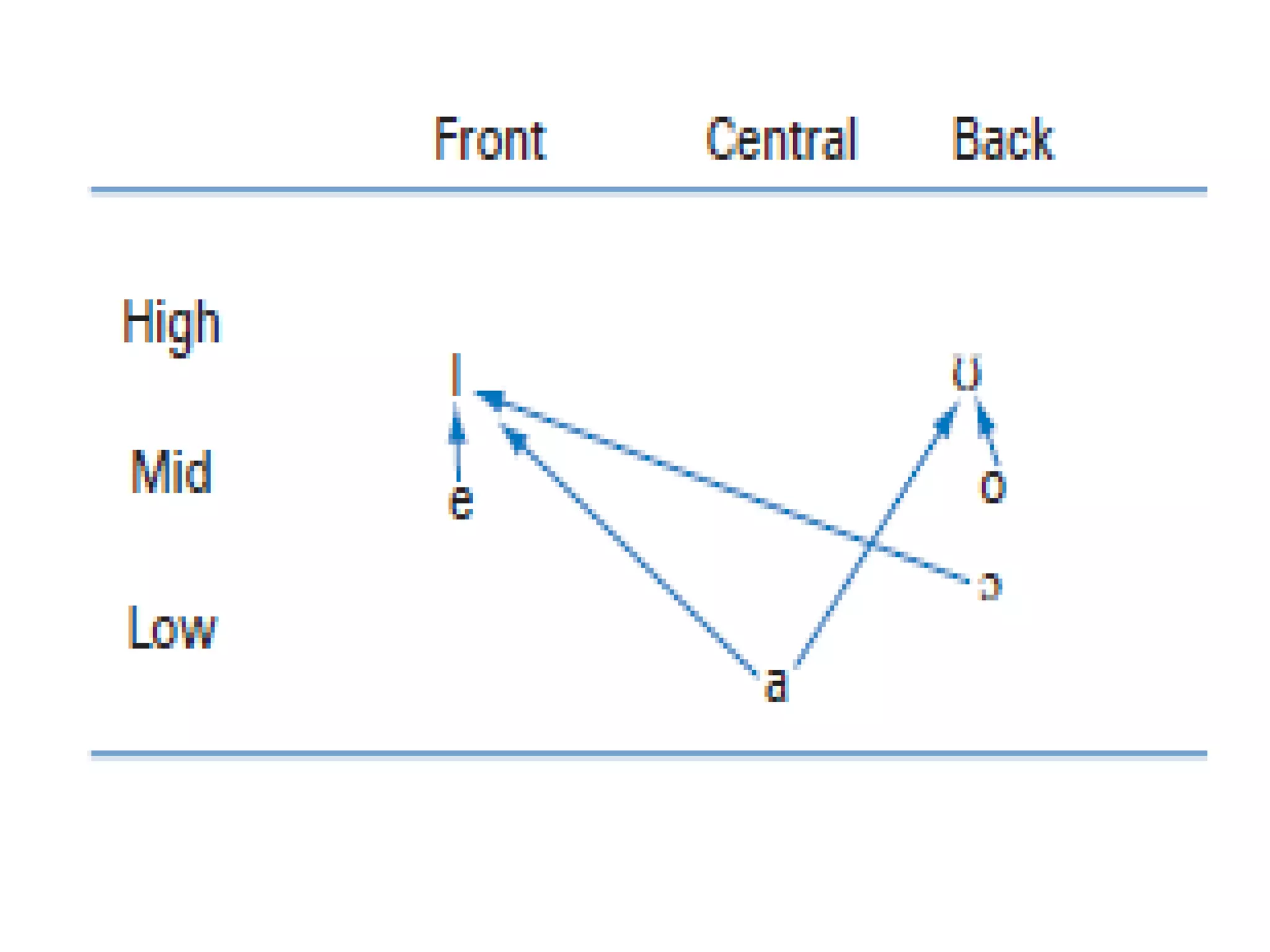
The document discusses vowels and diphthongs. It defines vowels as speech sounds produced without significant constriction in the vocal tract, and notes they do not have a place or manner of articulation. Vowels can be divided based on voicing, tongue position (front, central, back), tongue height (high, mid, low), rounding (rounded, unrounded), and length (long, short). Diphthongs are two-part vowels where the quality changes within a single syllable, like in "boy", while monophthongs have only one part. Diphthongs can be analyzed as a sequence of two vowels or a vowel glide. Semi-vowels are sounds like /j/ in