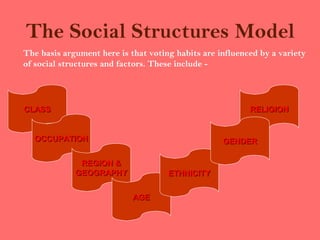
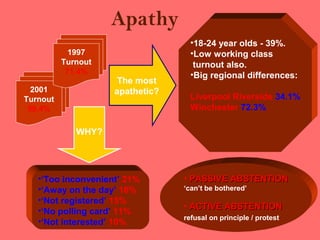
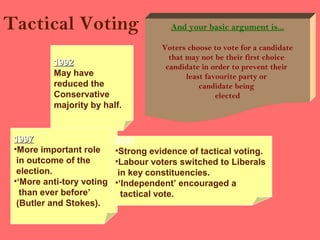
The document discusses various factors that influence voting behavior, including election campaigns, opinion polls, social class, and the role of the media. It examines different models of voting behavior, such as party identification, social structures, rational choice, and issue voting. Key influences on voting behavior are discussed, like election campaigns, opinion polls, the media, and voter apathy.