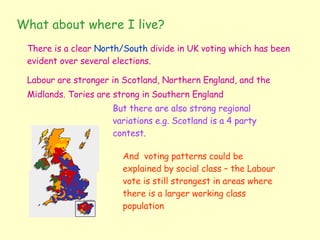
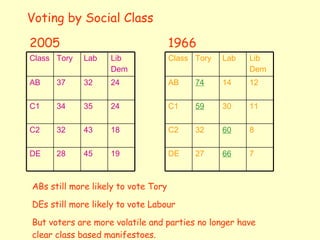
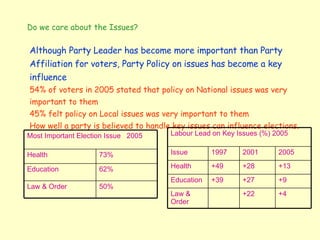
Social class is no longer the dominant factor in shaping political attitudes and voting behavior. While some residual class loyalty remains, factors like personality, policy issues, media influence, and regional differences now play a larger role in how people vote. Voters are also more volatile and willing to change their party alignments. With more floating voters, political parties must now appeal to a wider range of demographic groups and policy priorities to attract votes.