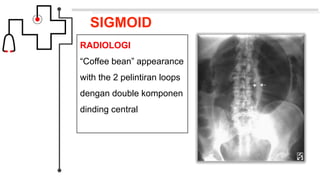
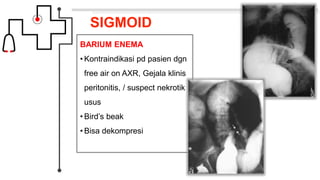
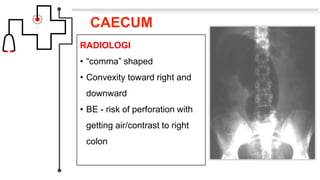
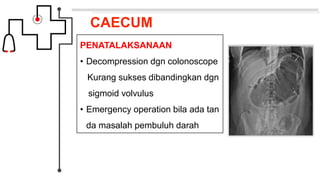
Volvulus adalah obstruksi usus yang disebabkan oleh terpelintirnya usus lebih dari 180 derajat pada sumbu mesenterium. Jenis volvulus yang paling umum adalah sigmoid volvulus yang melibatkan sigmoid colon (sekitar 65% kasus) dan cecal volvulus yang melibatkan cecum (sekitar 25% kasus). Gejala klinis meliputi nyeri perut, distensi, dan tidak ada flatus atau gerakan usus. Diagnosis dapat ditegakkan den