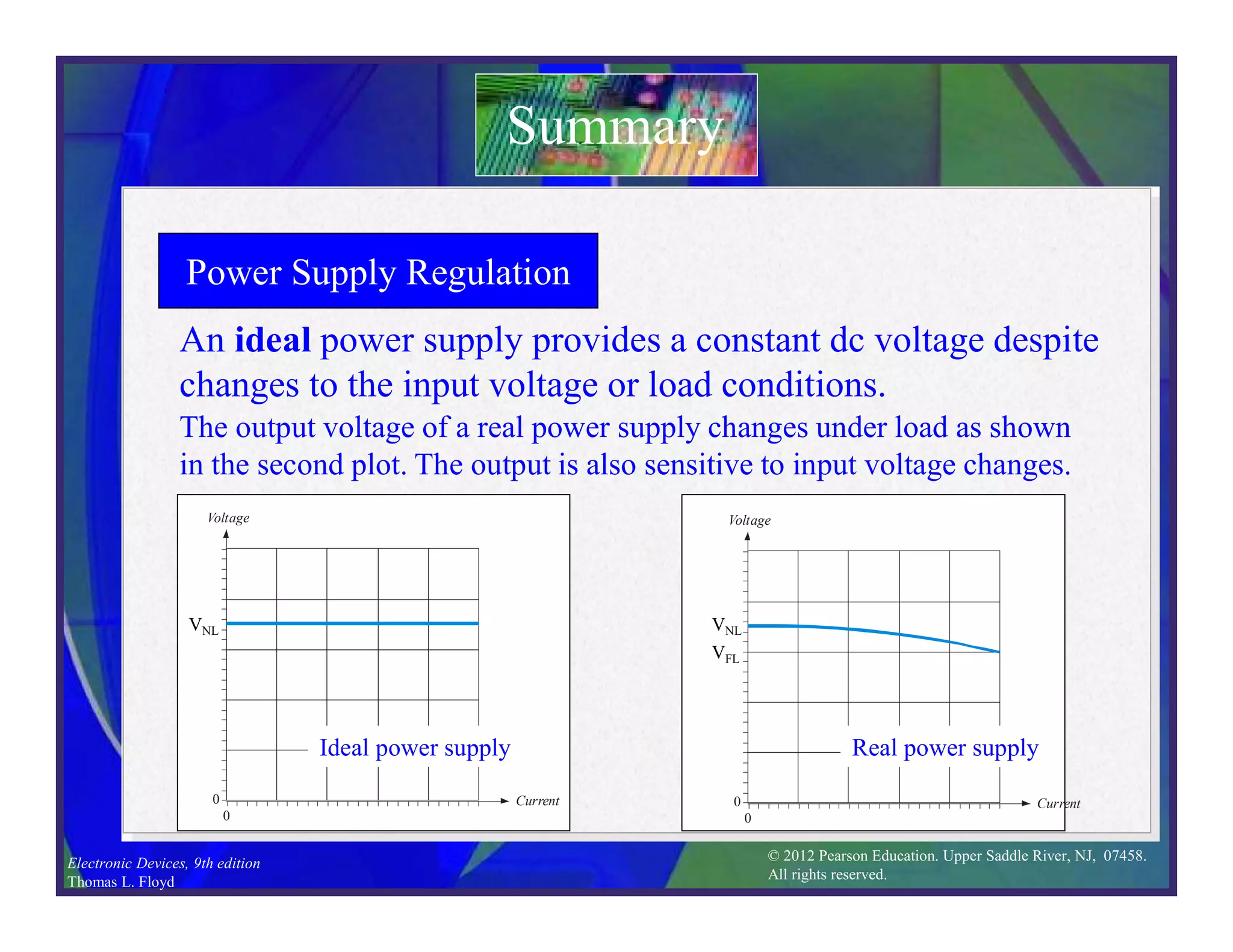
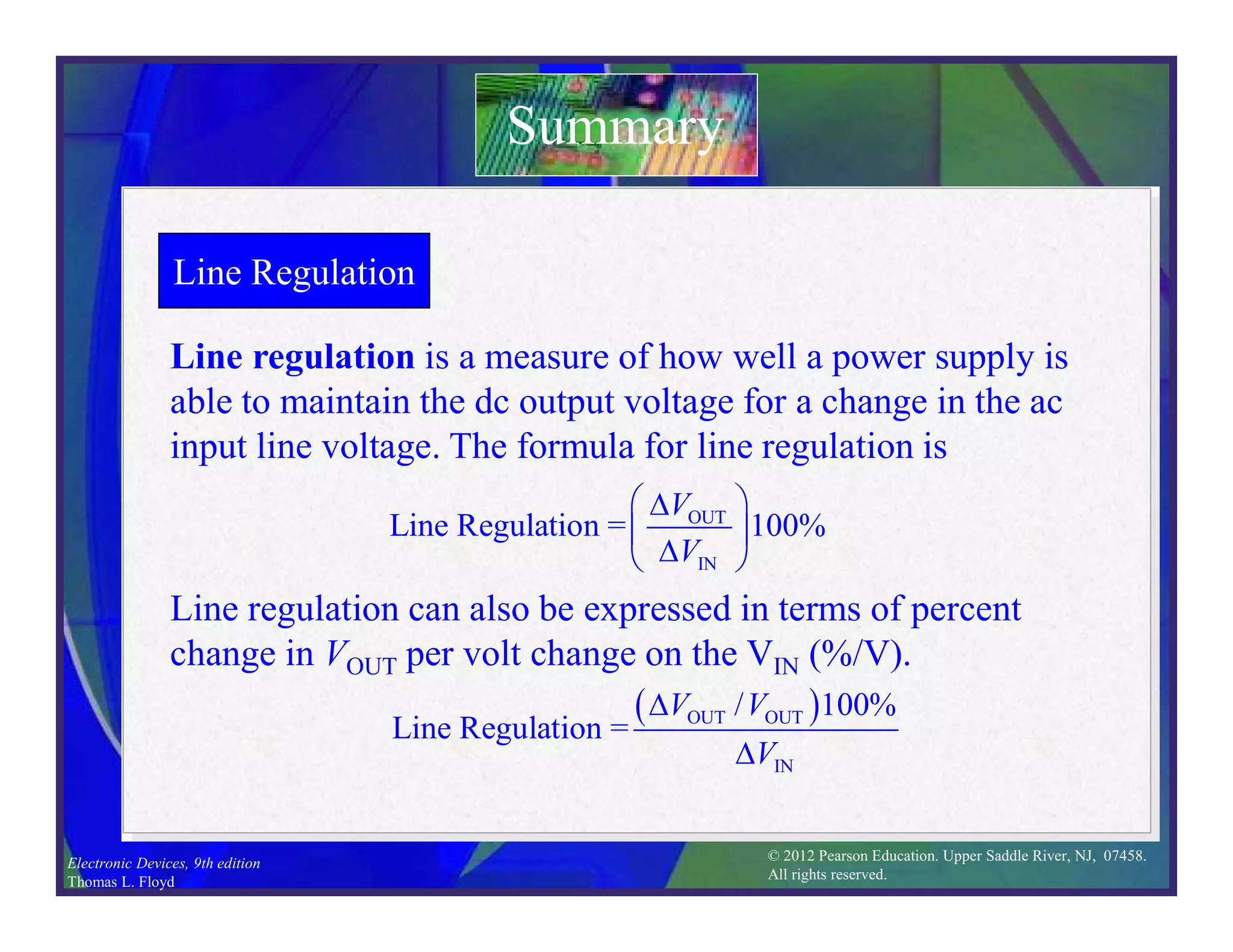
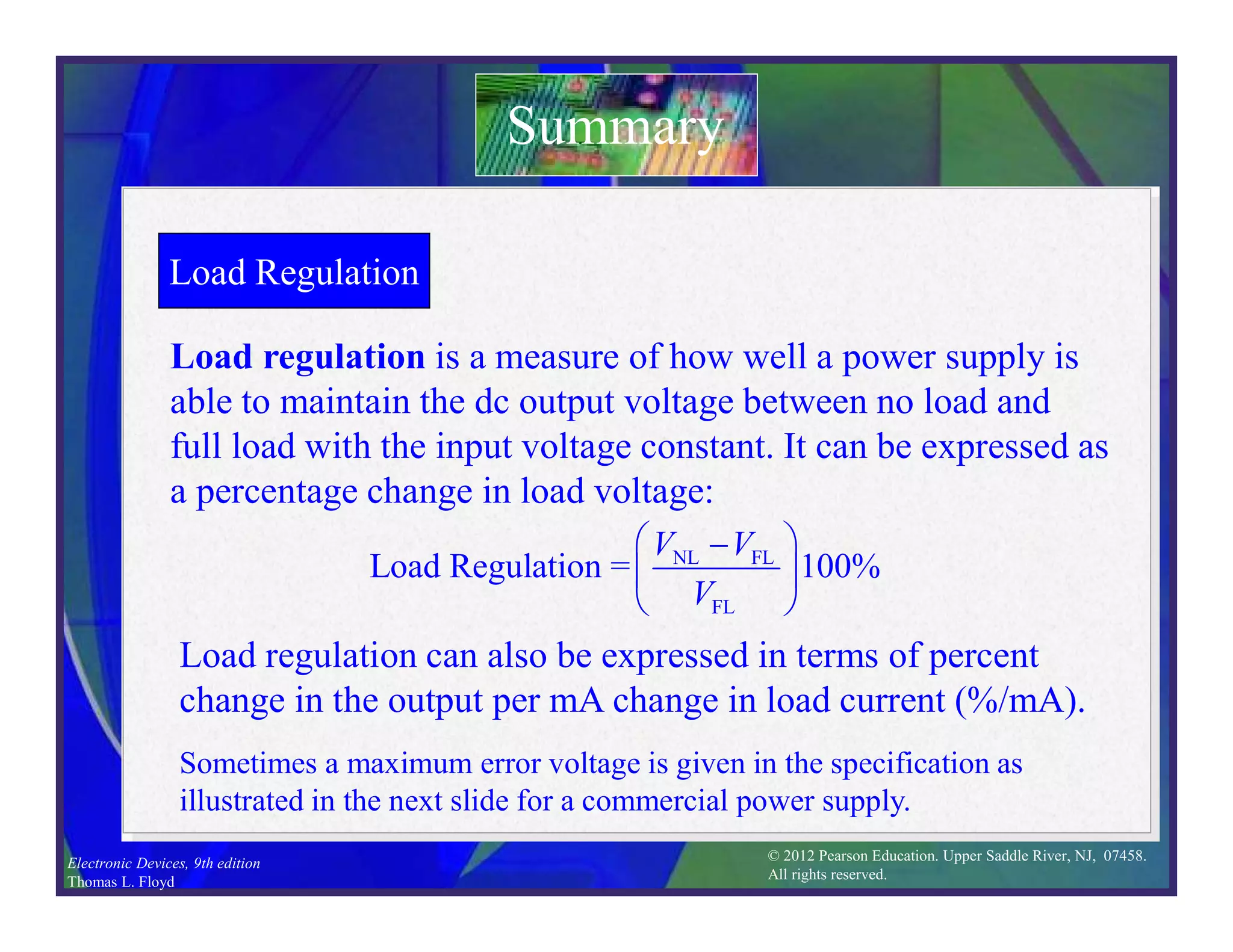
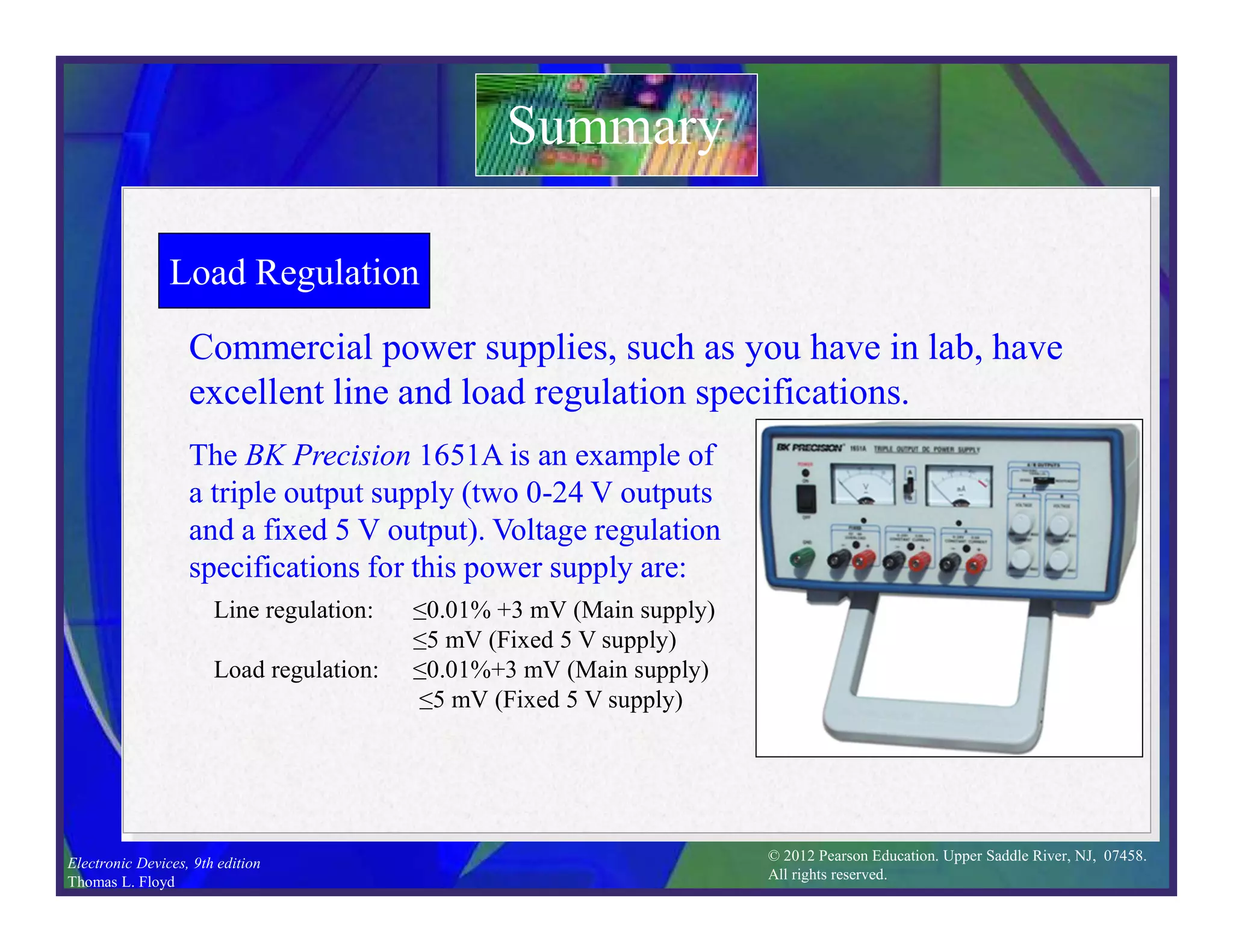
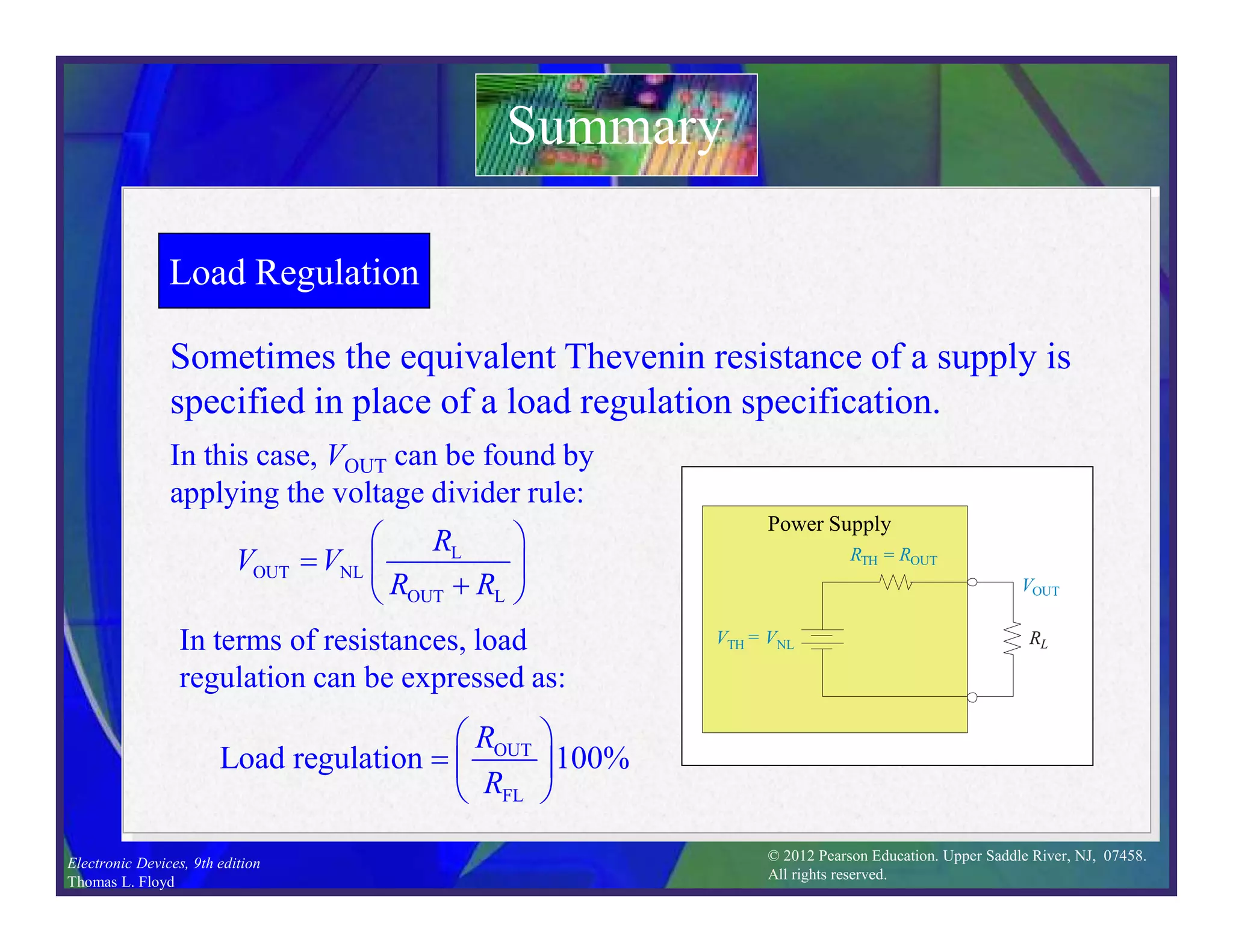
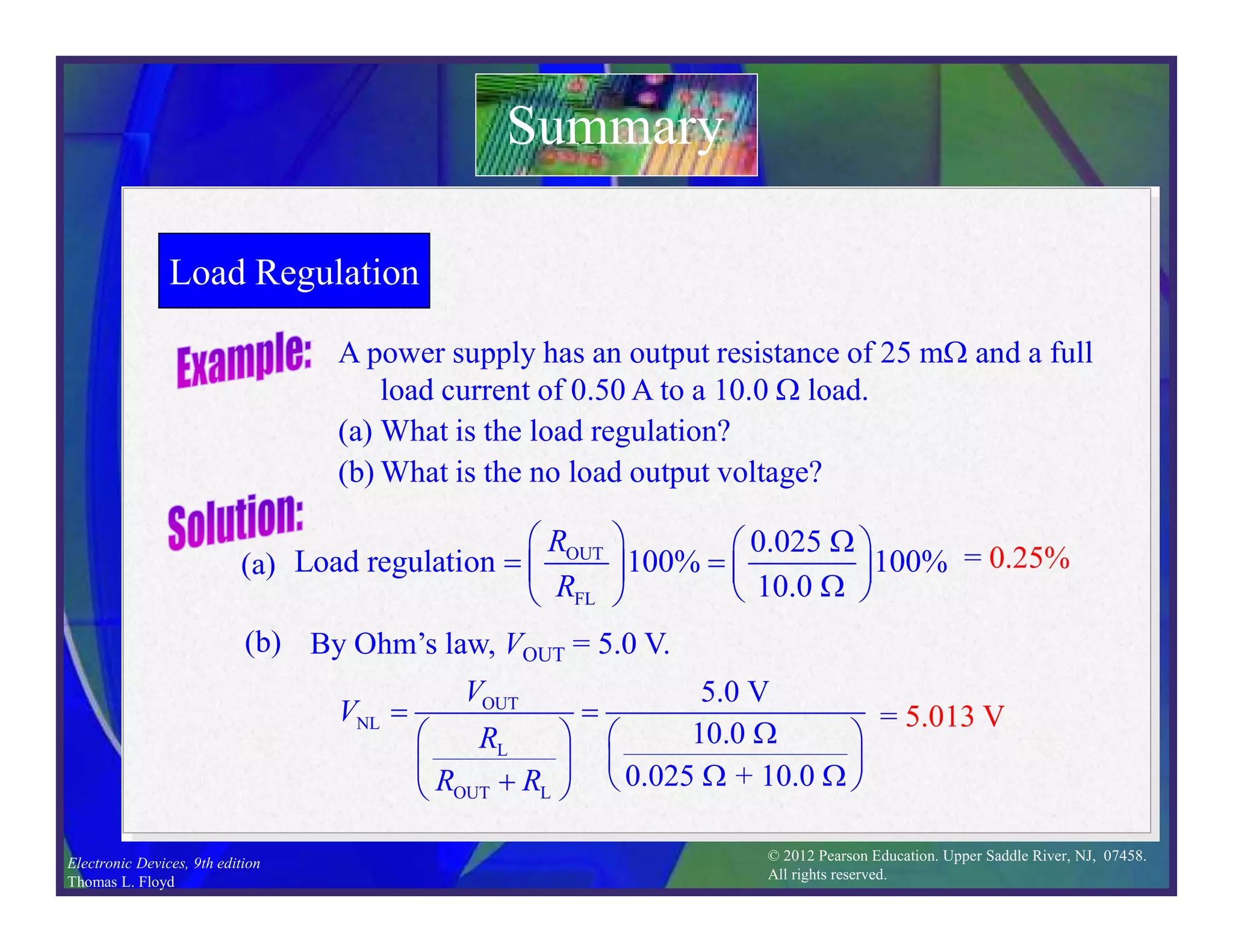
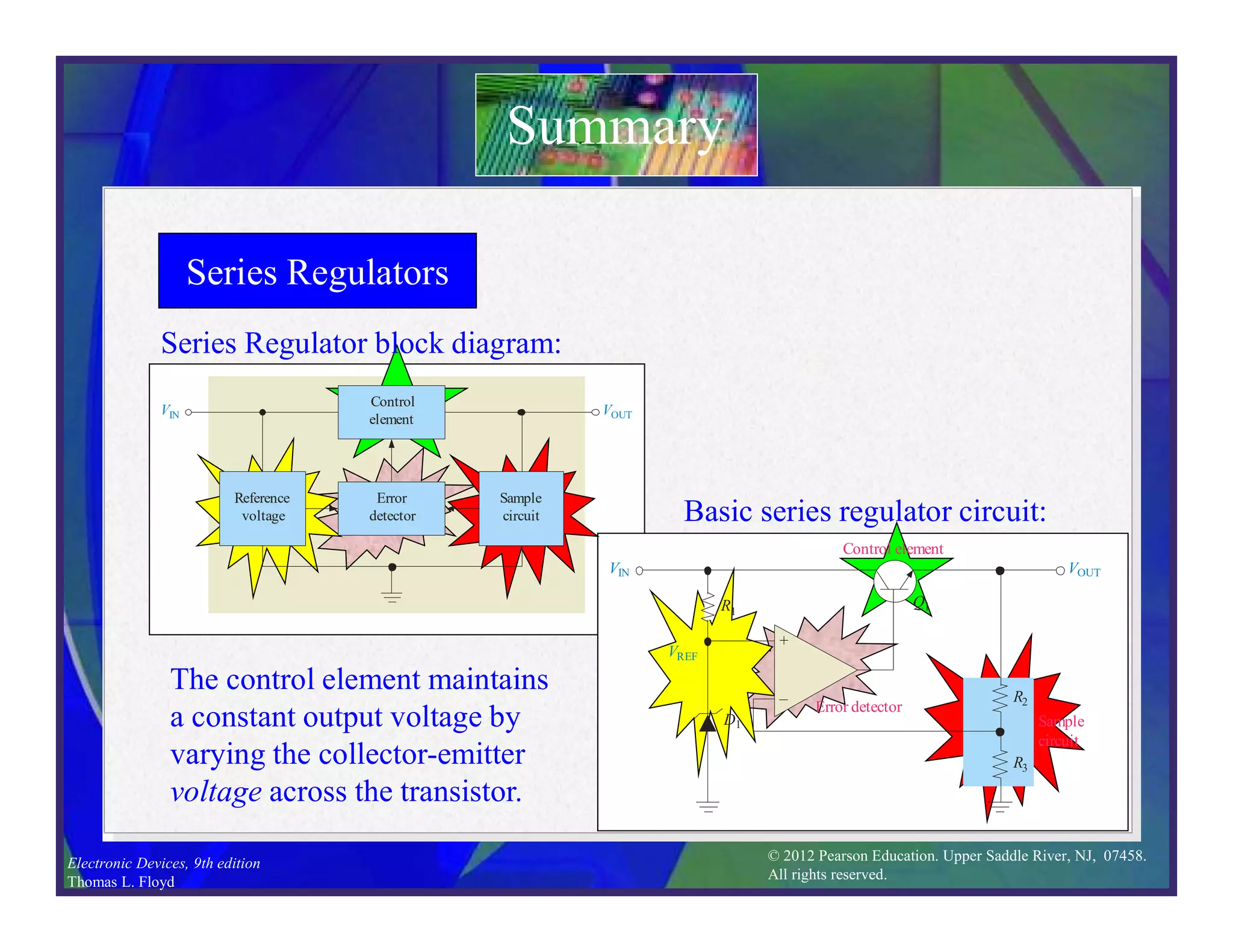
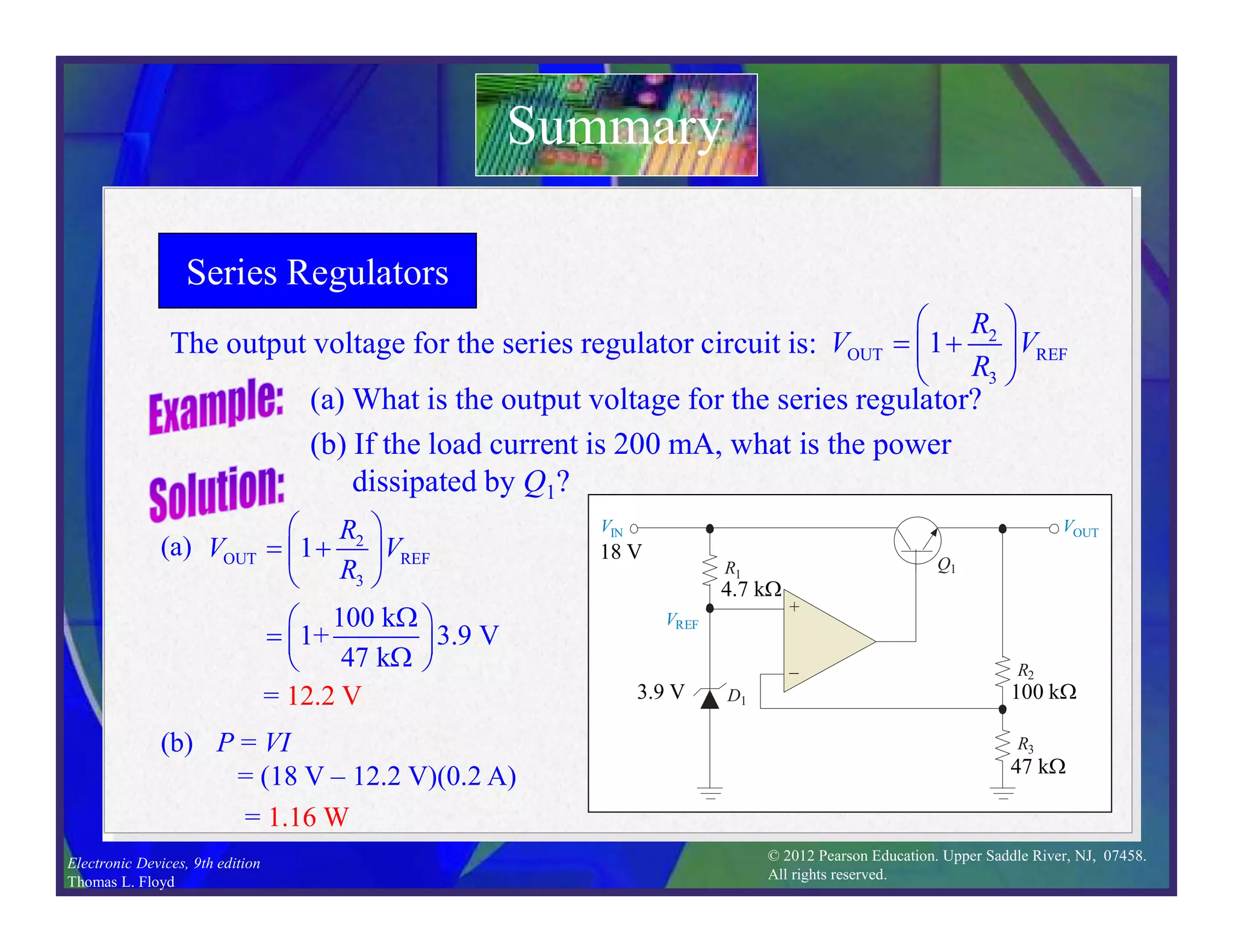
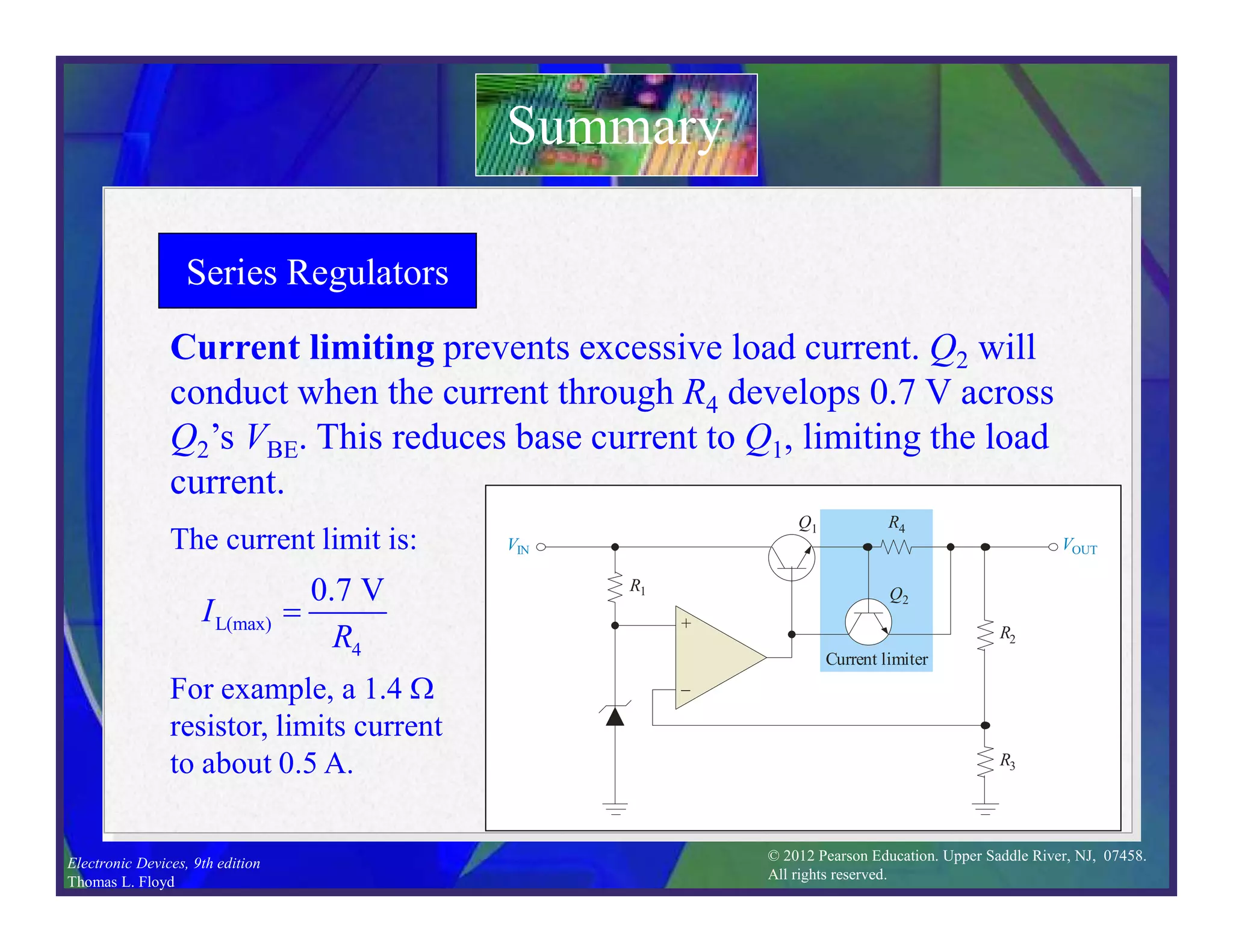
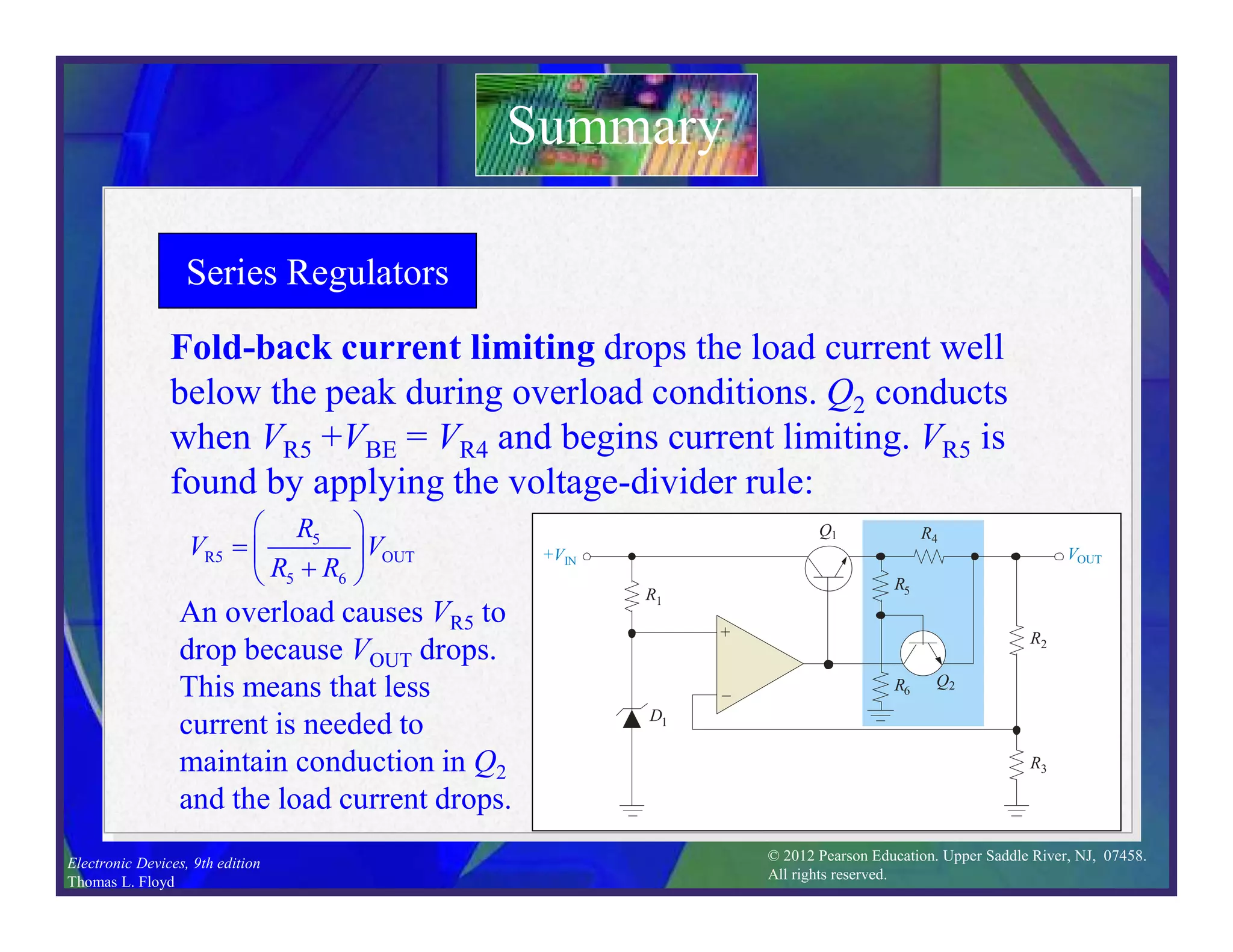
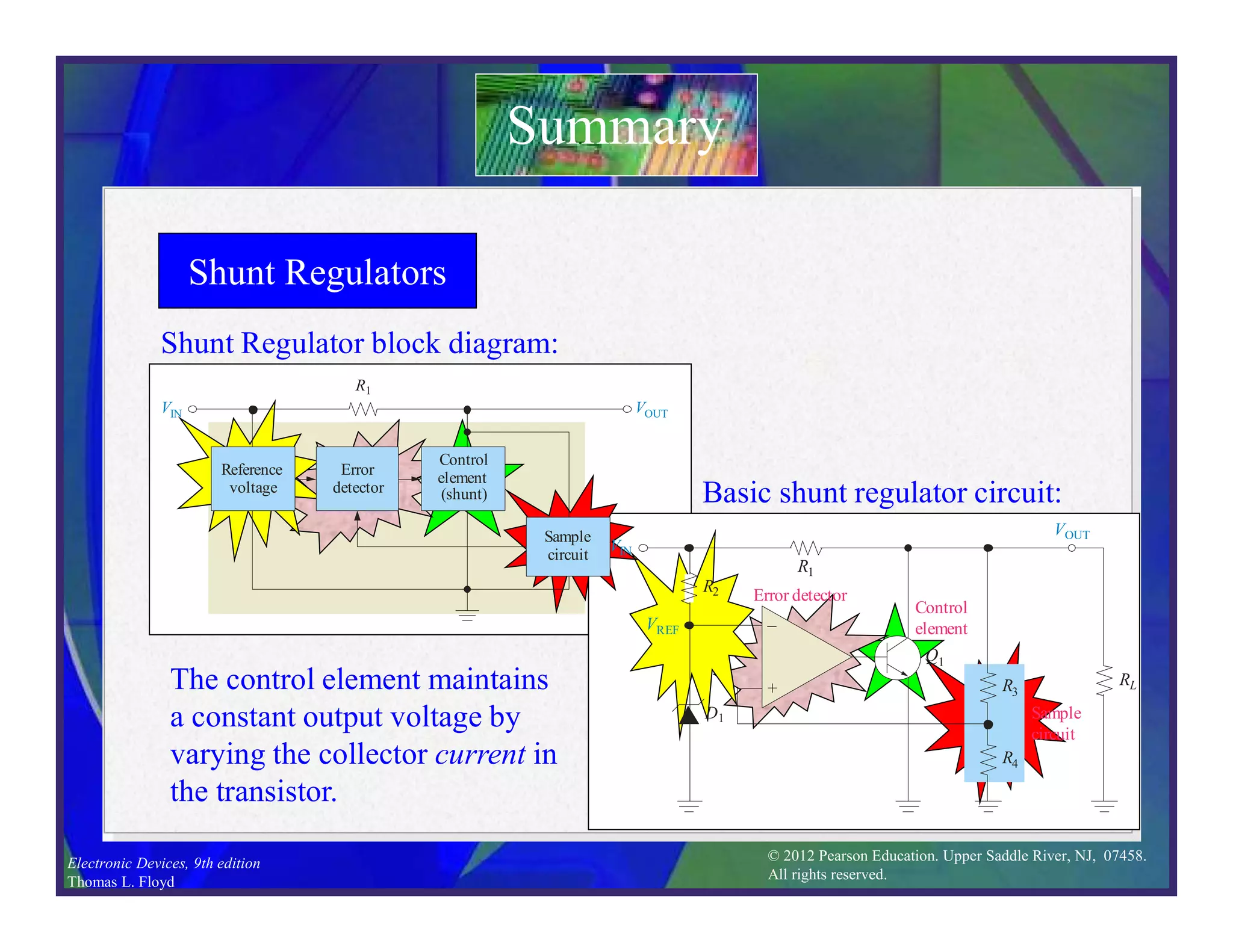
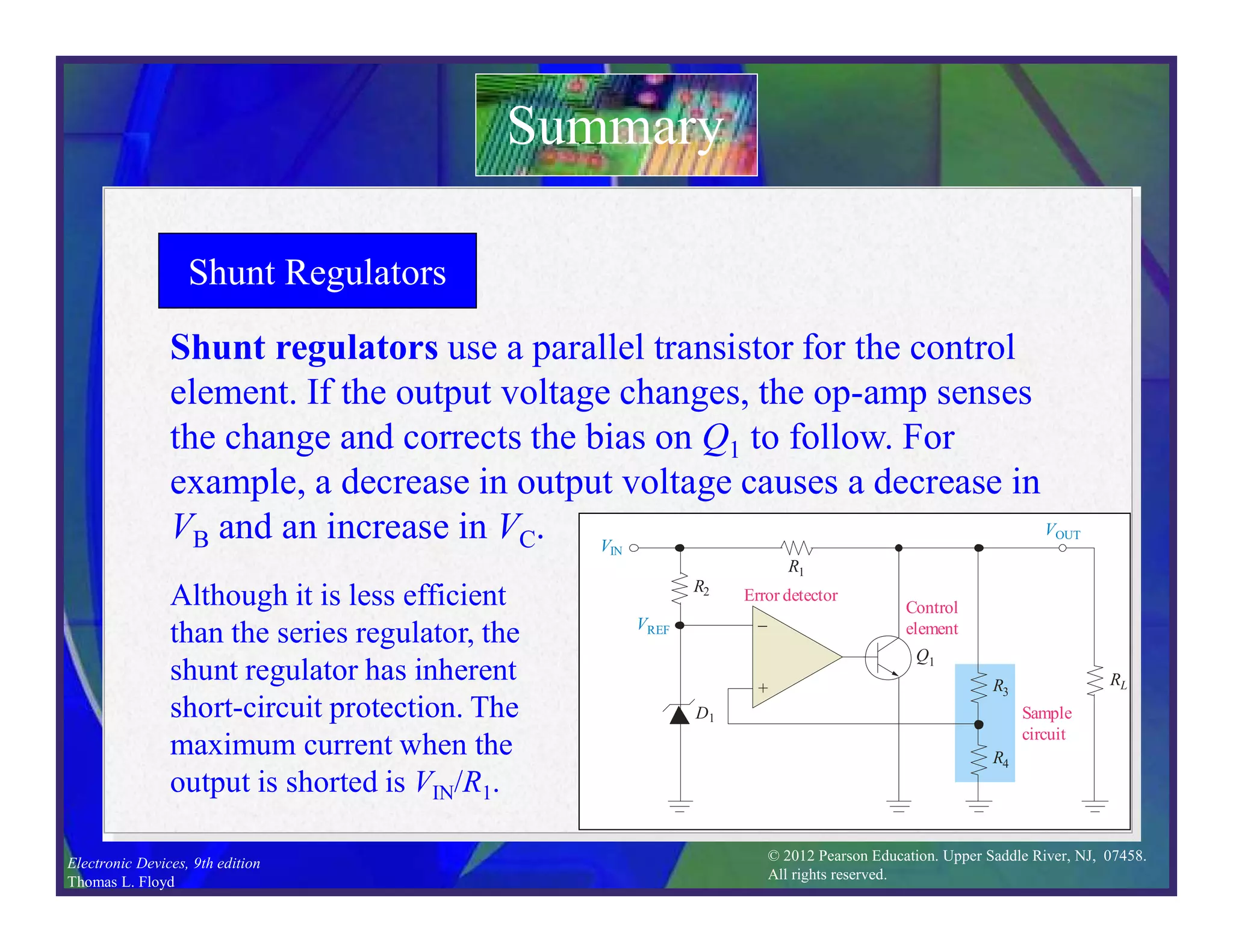
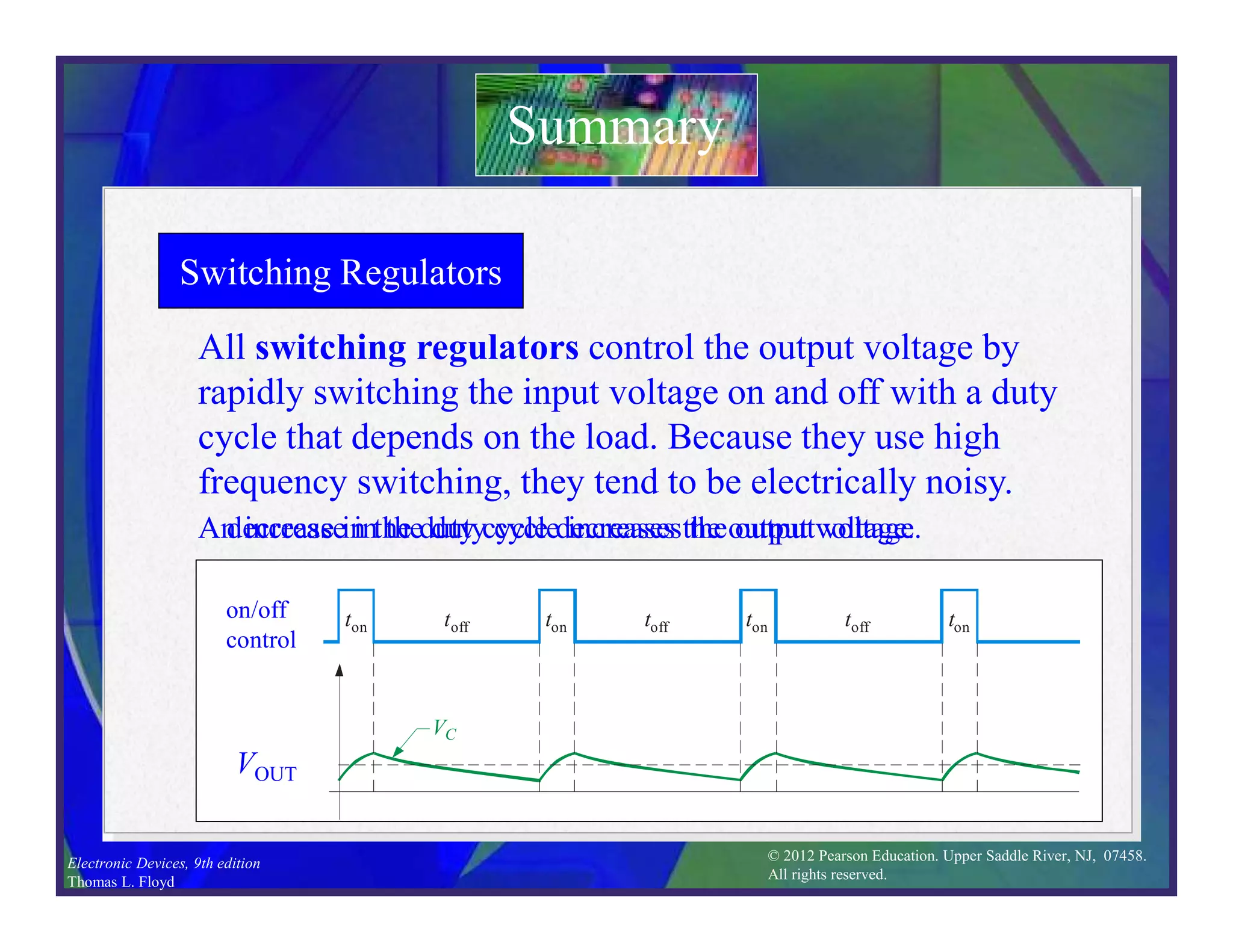
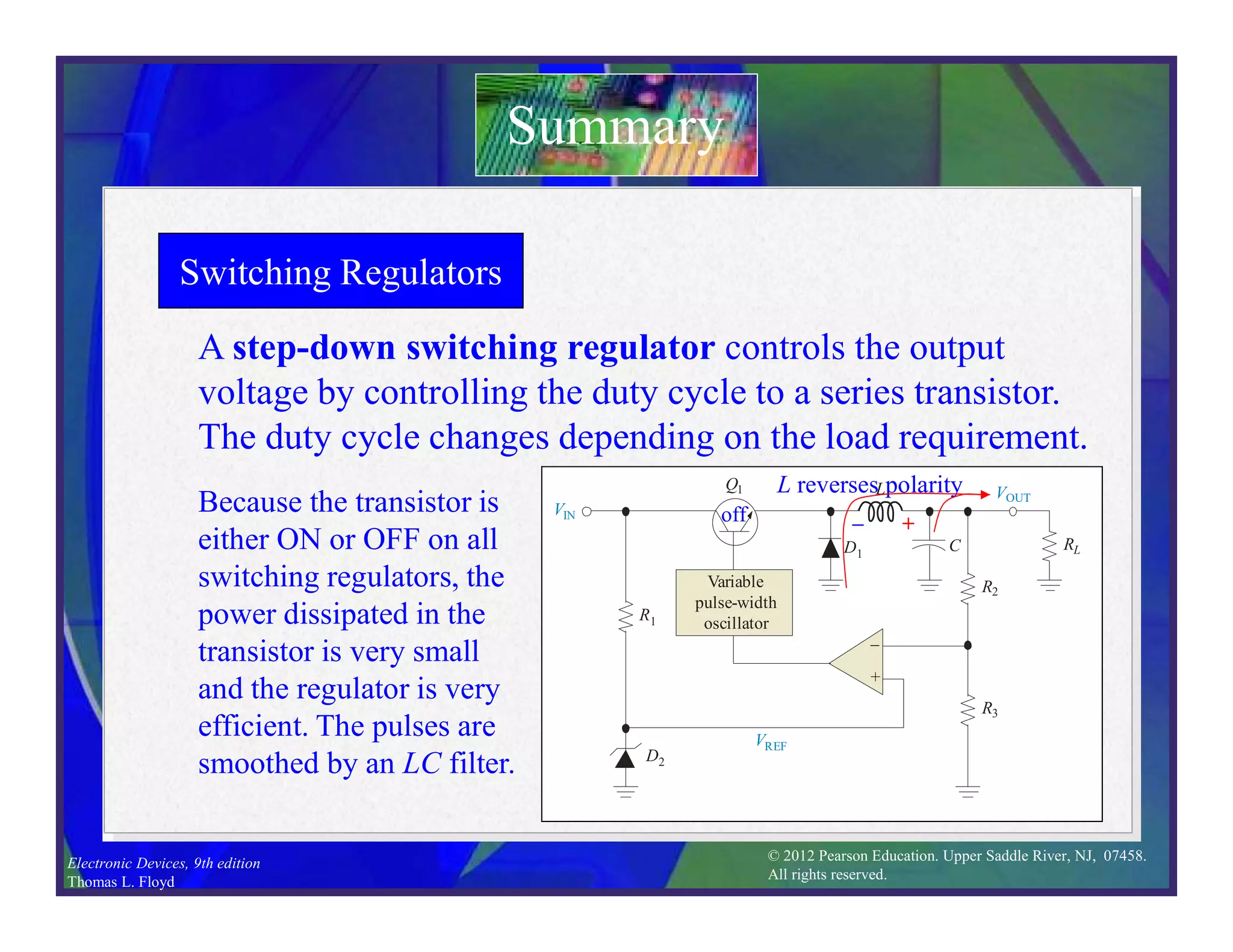
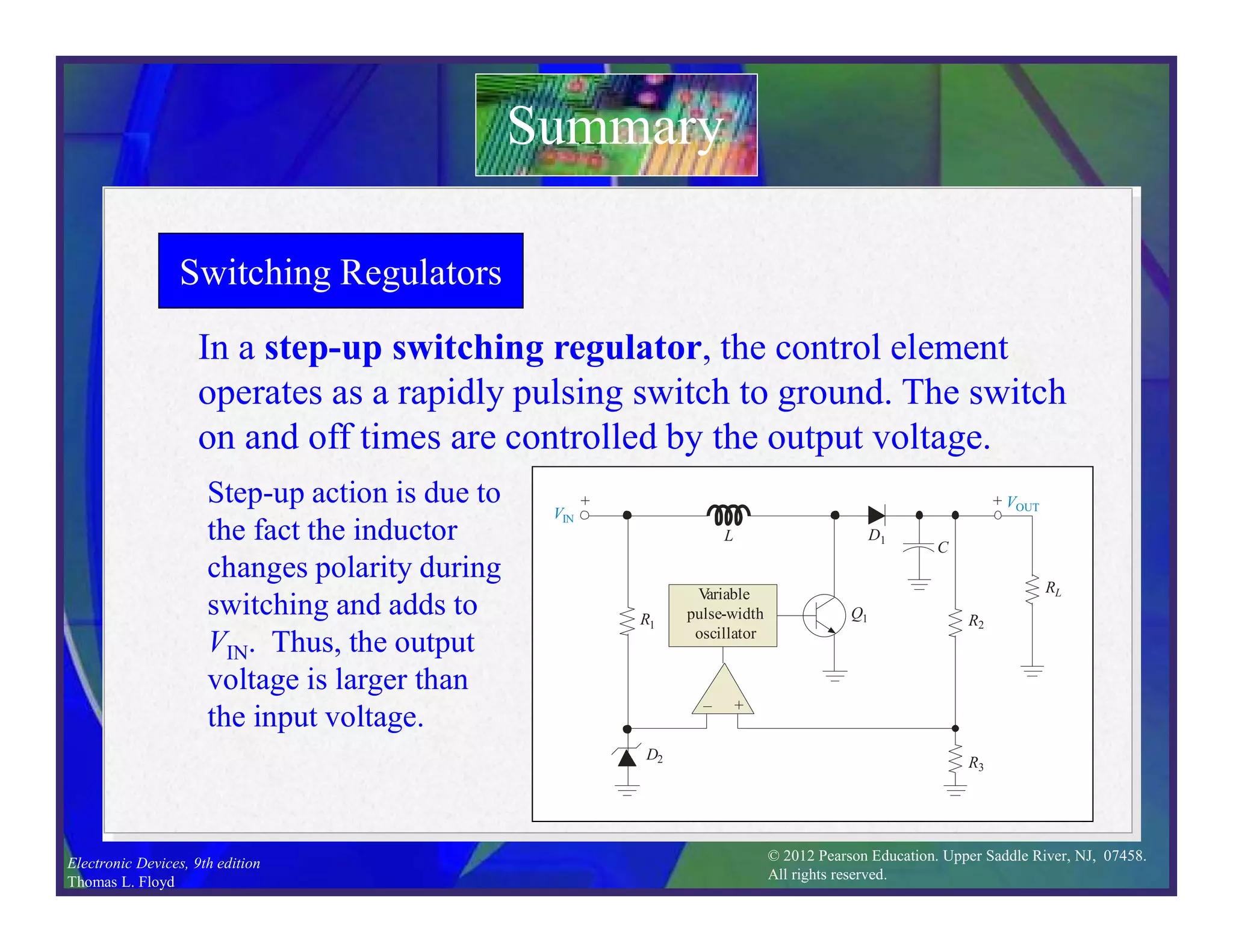
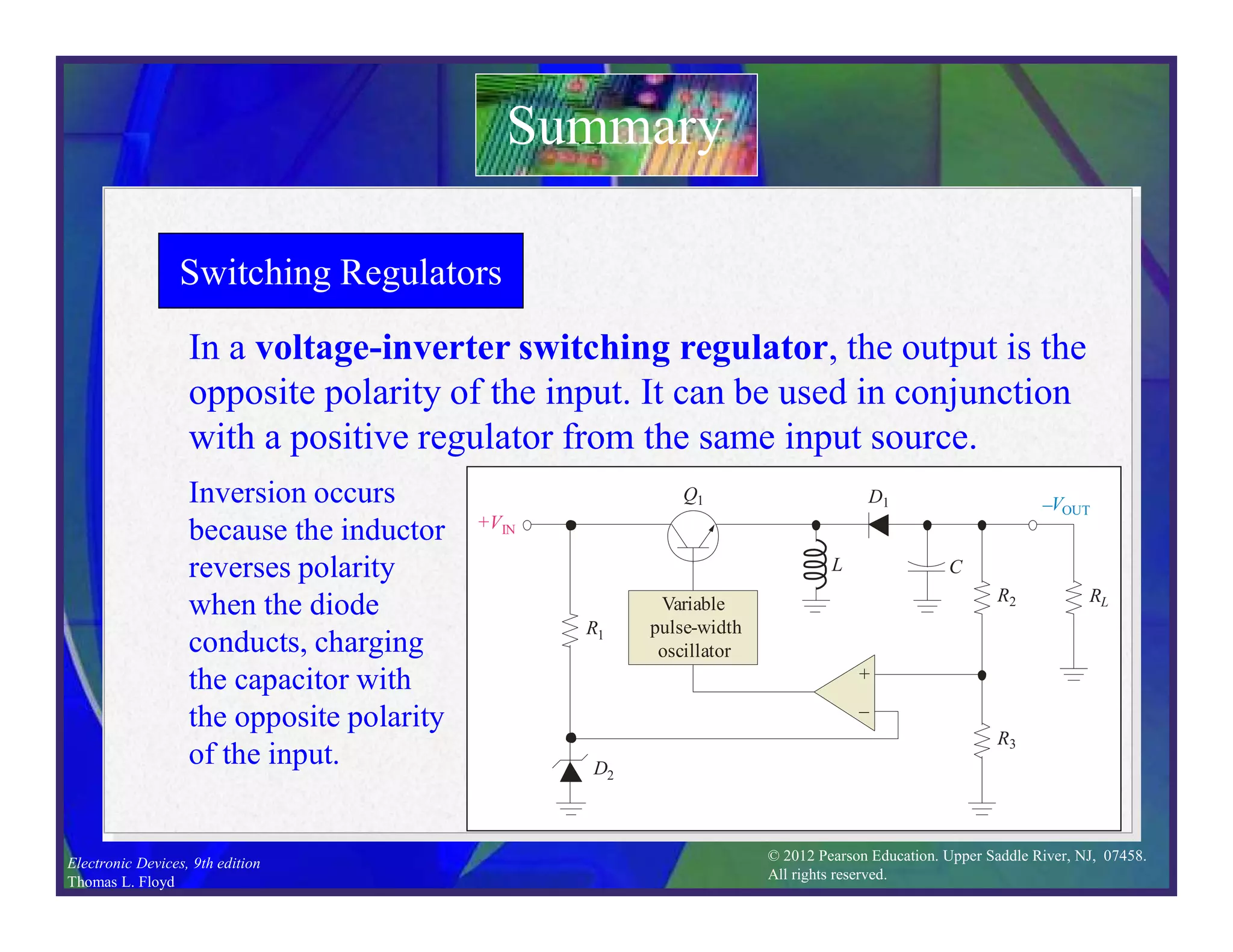
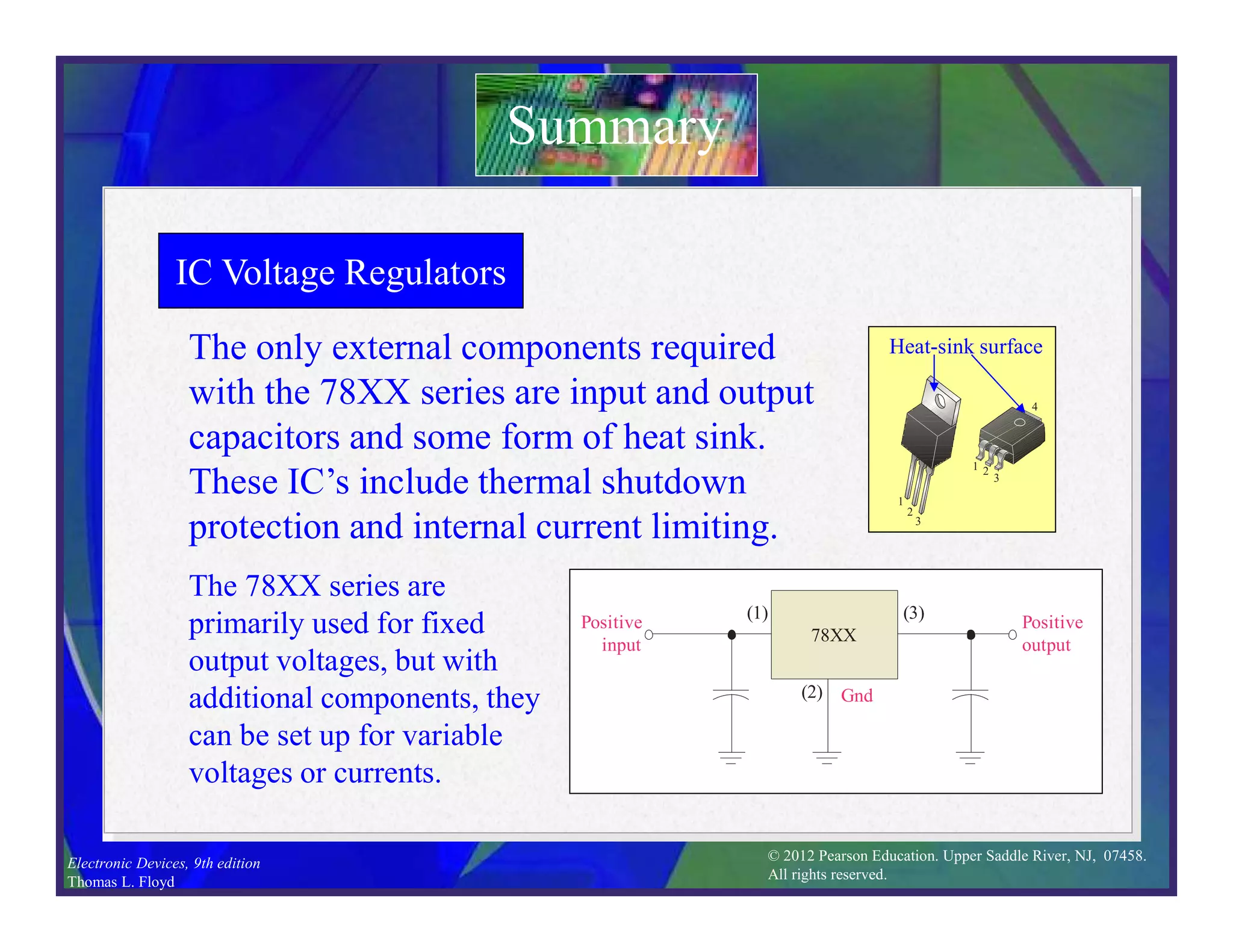
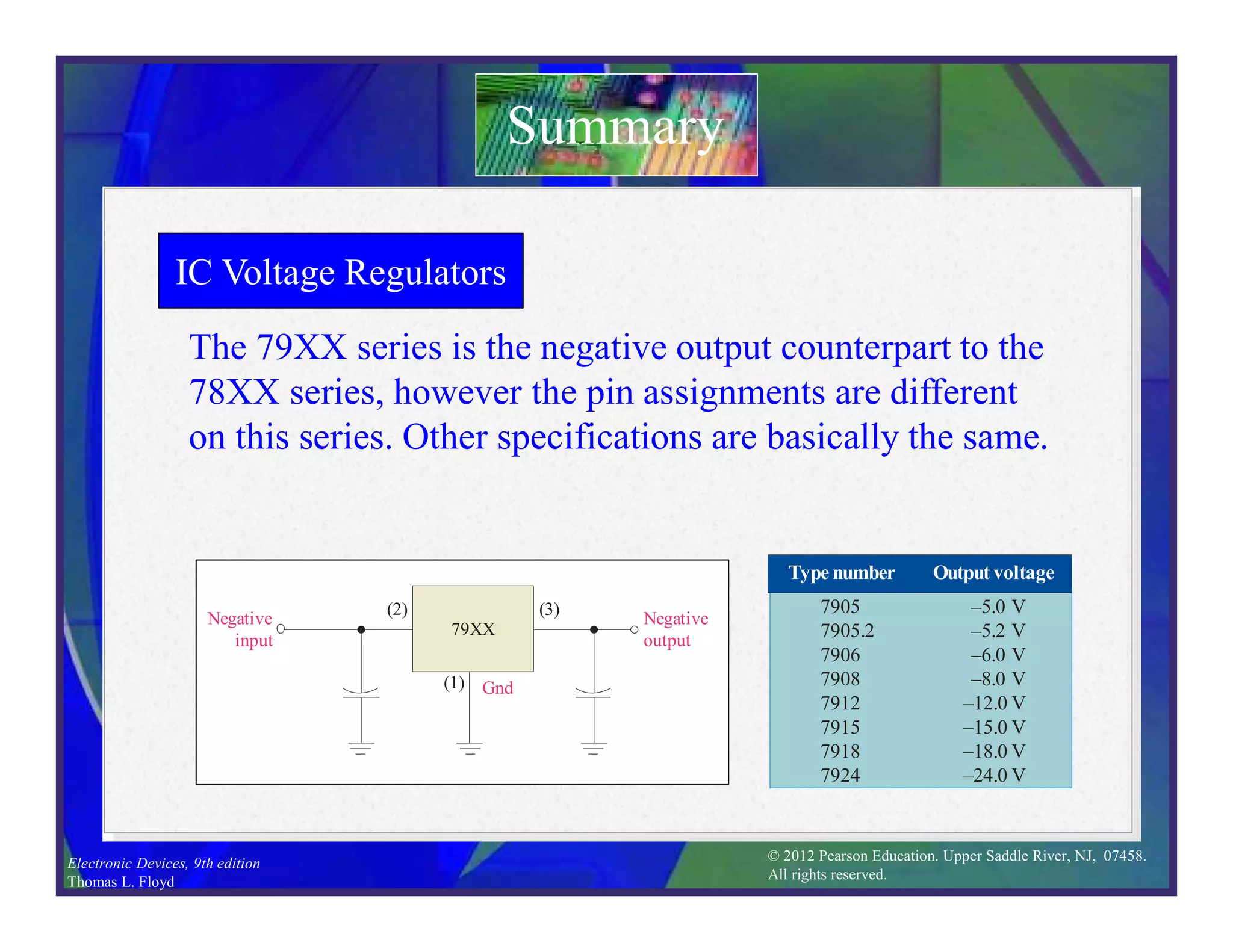
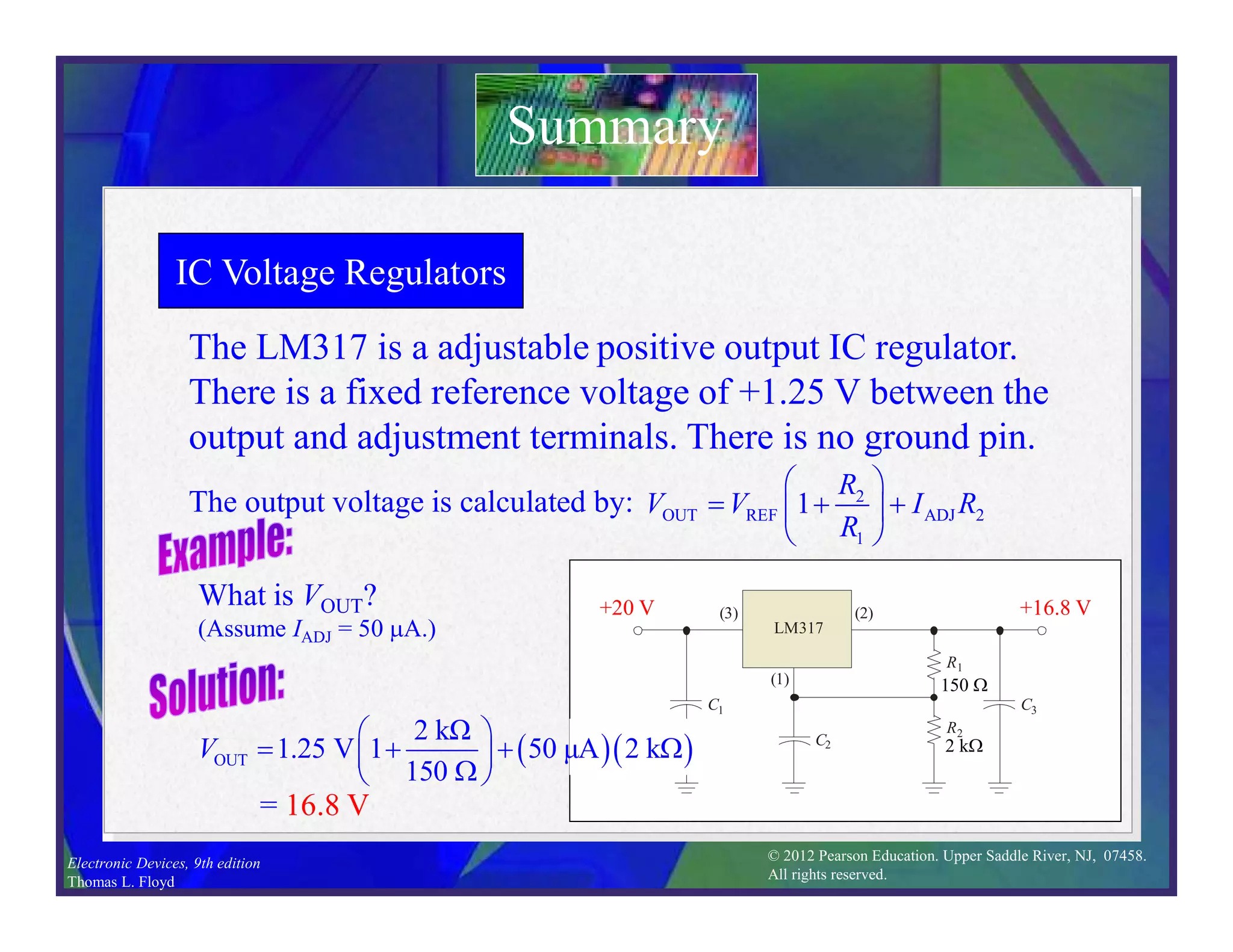
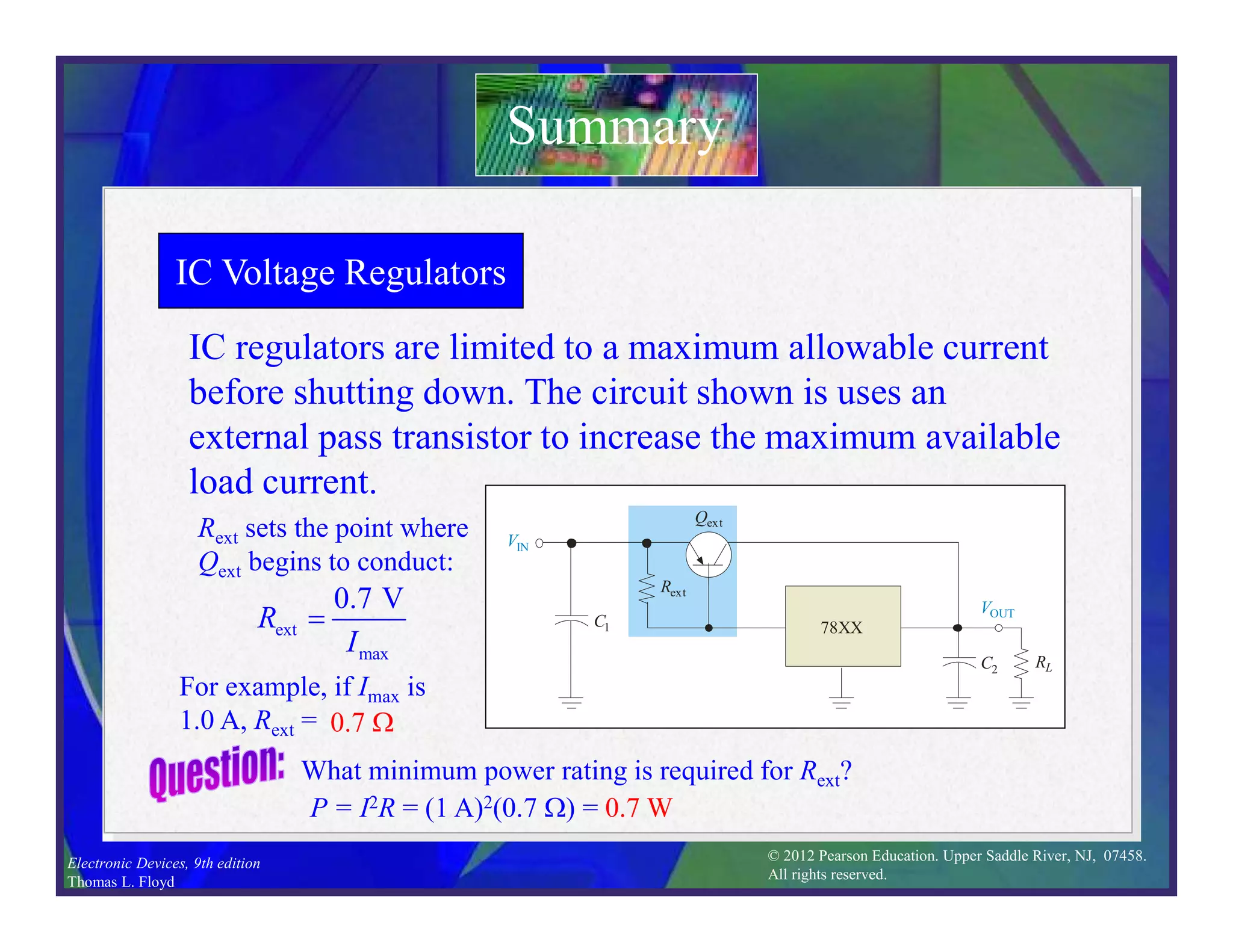
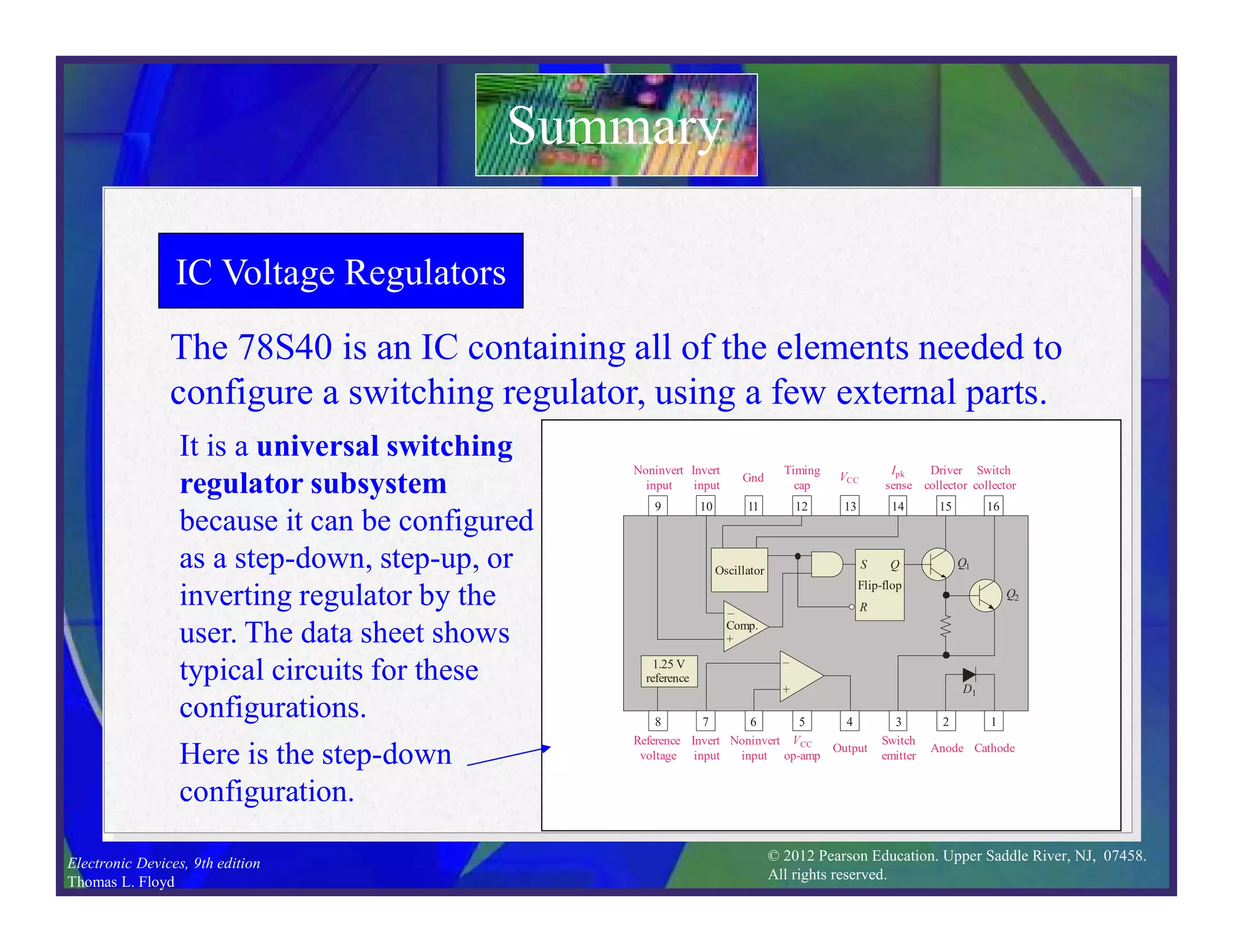
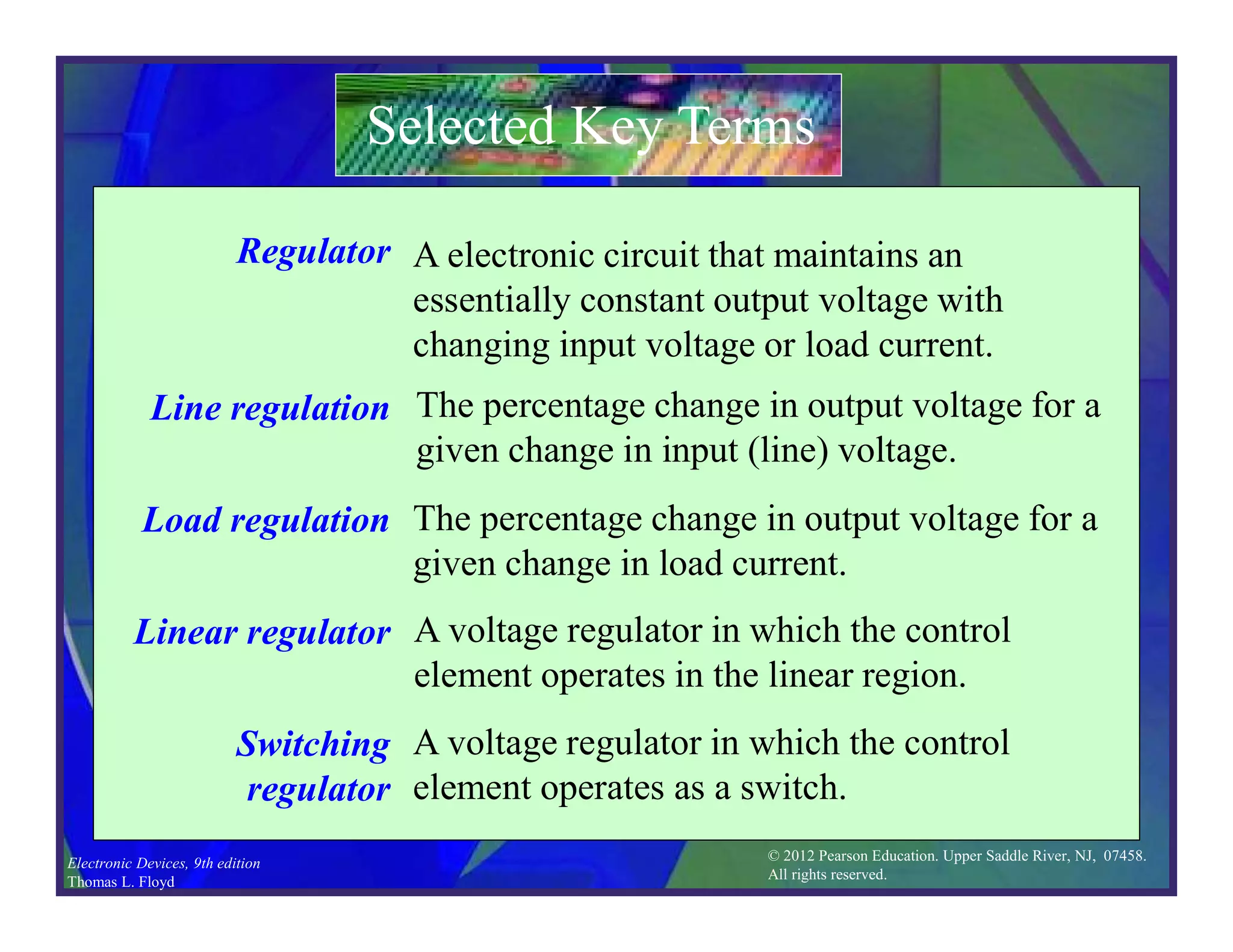
This document discusses various types of voltage regulators including series, shunt, switching, and integrated circuit regulators. Series regulators use a control transistor to maintain a constant output voltage. Shunt regulators operate similarly but are less efficient with inherent short circuit protection. Switching regulators rapidly switch the input voltage on and off at a duty cycle controlled by the load to regulate the output. IC voltage regulators integrate the control circuitry onto a single chip and are available as series or switching designs.