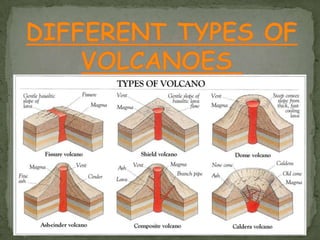
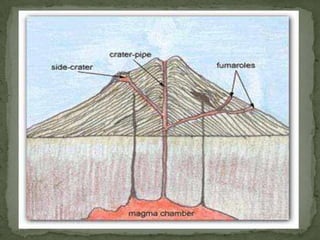
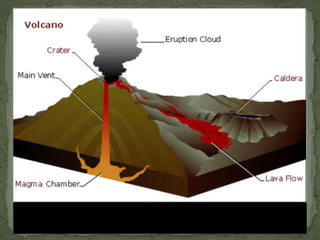
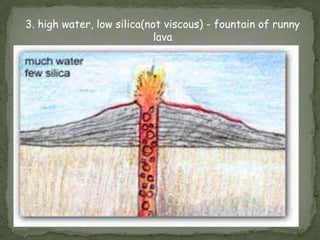
Composite volcanoes, also called stratovolcanoes, are formed from layers of lava and rock fragments ejected from a central vent. They often form tall, steep conical peaks over 1000 meters high and can erupt explosively when viscous magma builds up pressure in the vent. Stratovolcanoes display a variety of shapes including concave, pyramidal, and those with multiple summits. Shield volcanoes are broad, gently sloping cones produced by fluid basaltic lava flows over a large area from a central vent. Cinder cones are small, steep hills formed from accumulation of ejected volcanic cinder around a vent.