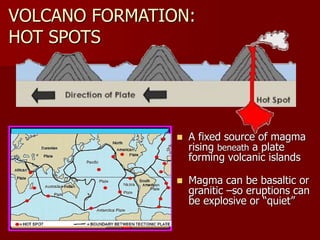
This document describes three main types of volcanoes: shield volcanoes, composite volcanoes, and cinder cone volcanoes. Shield volcanoes such as Mauna Loa have fluid basaltic lava that flows great distances, building wide gentle slopes. Composite volcanoes like Mount Fuji have thicker more explosive eruptions from trapped gases, forming alternating layers of ash and lava. Cinder cone volcanoes contain high gas levels that cause short, violent eruptions depositing ash in cone shapes.