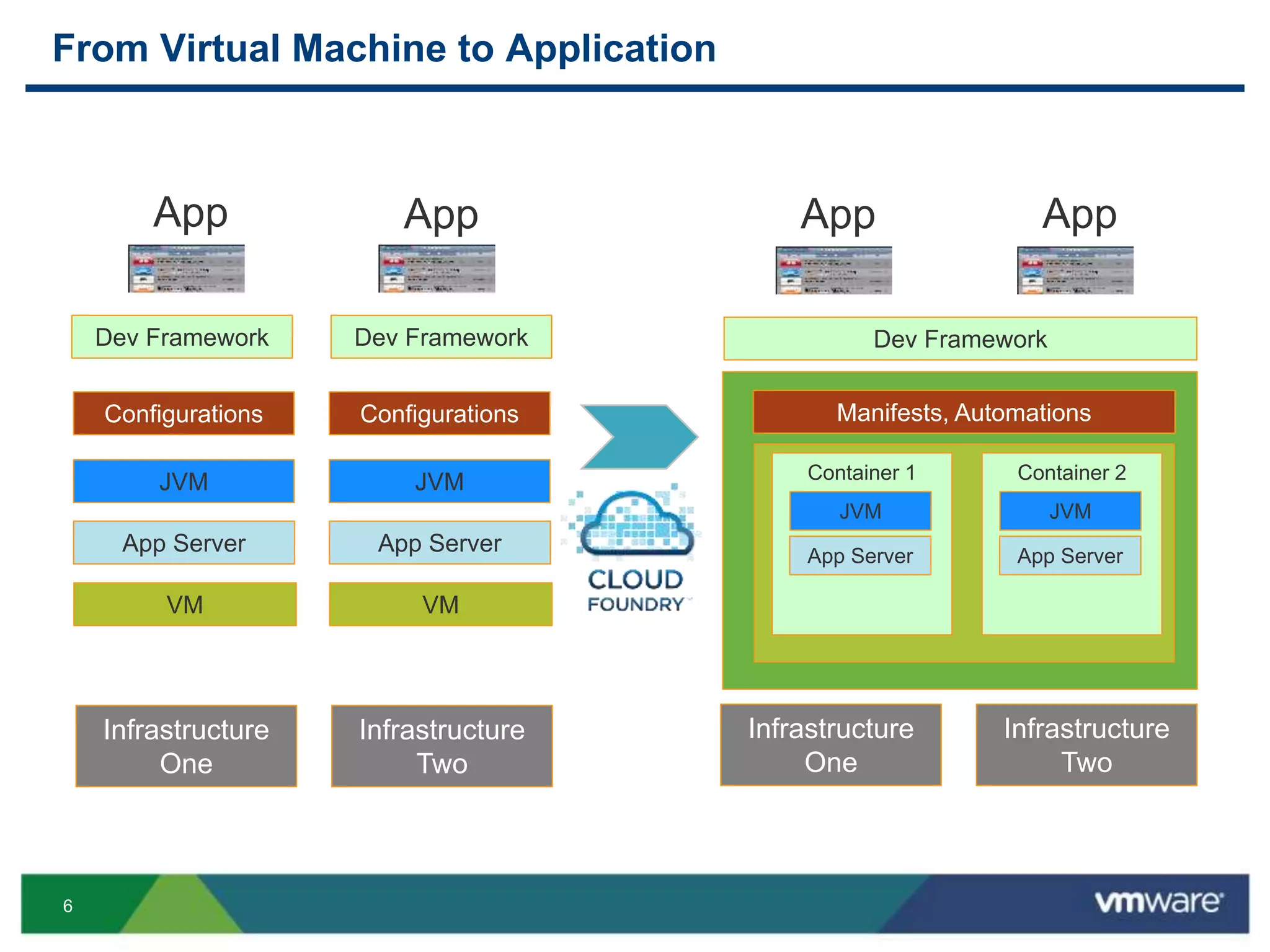
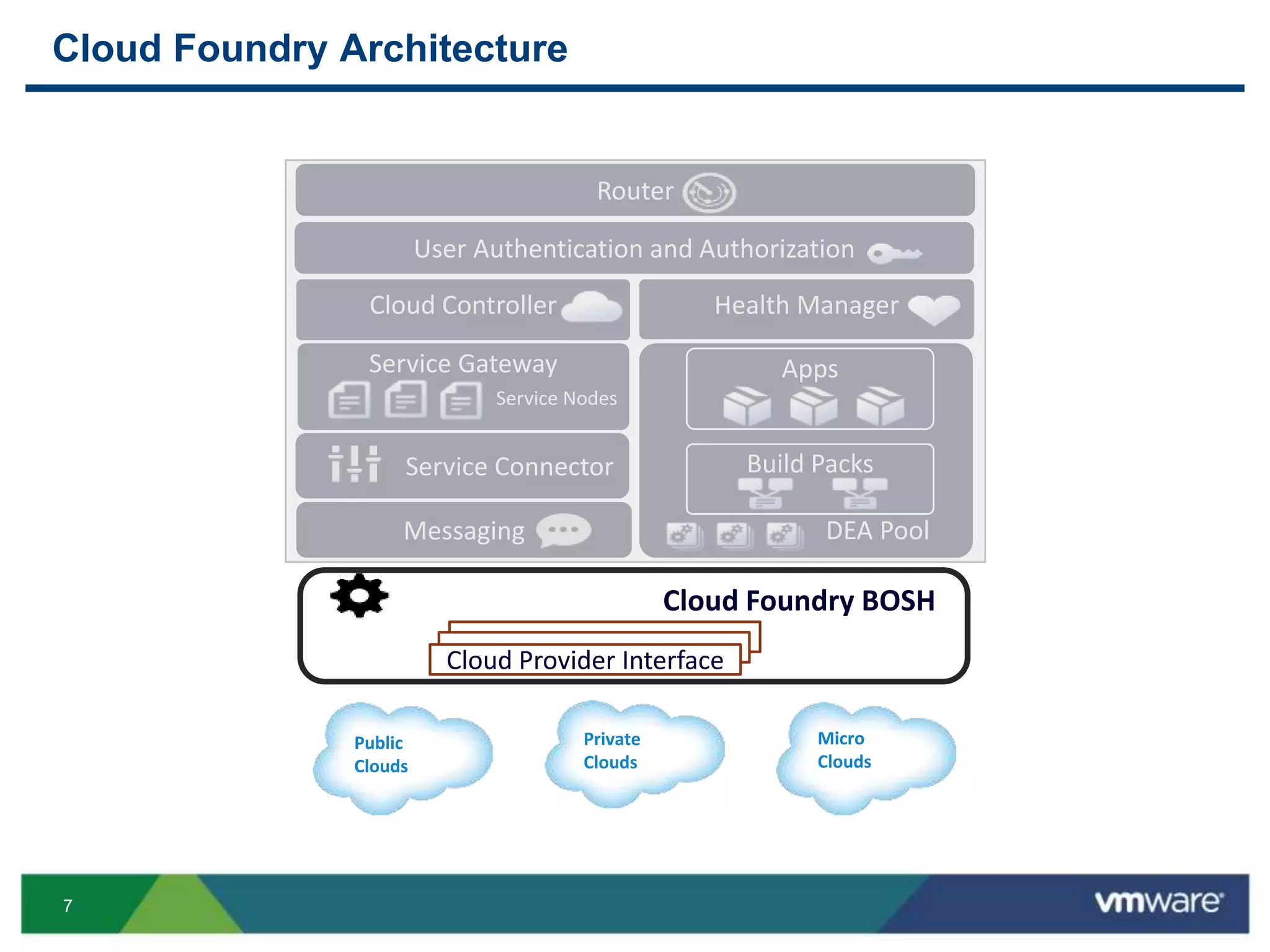
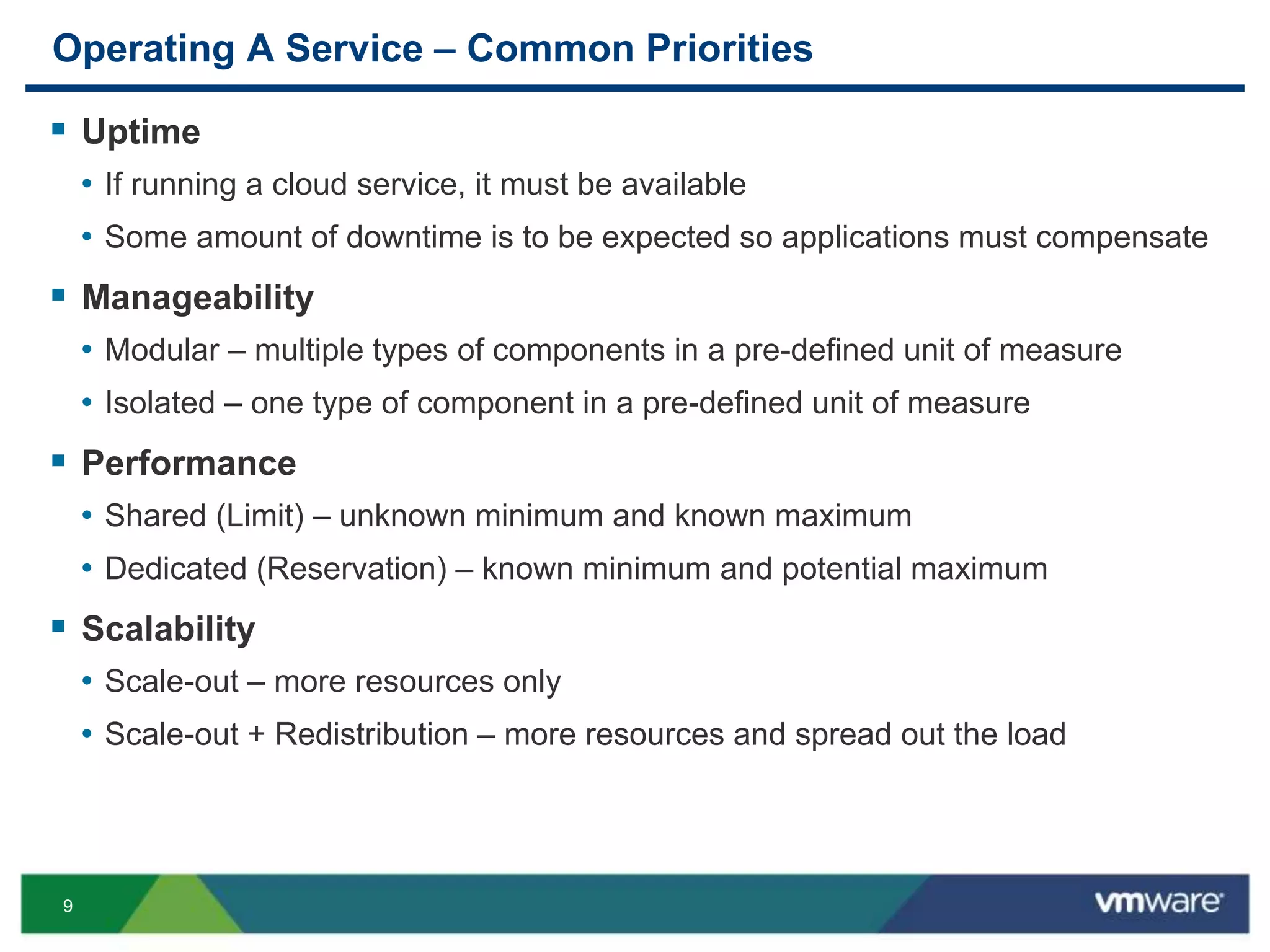
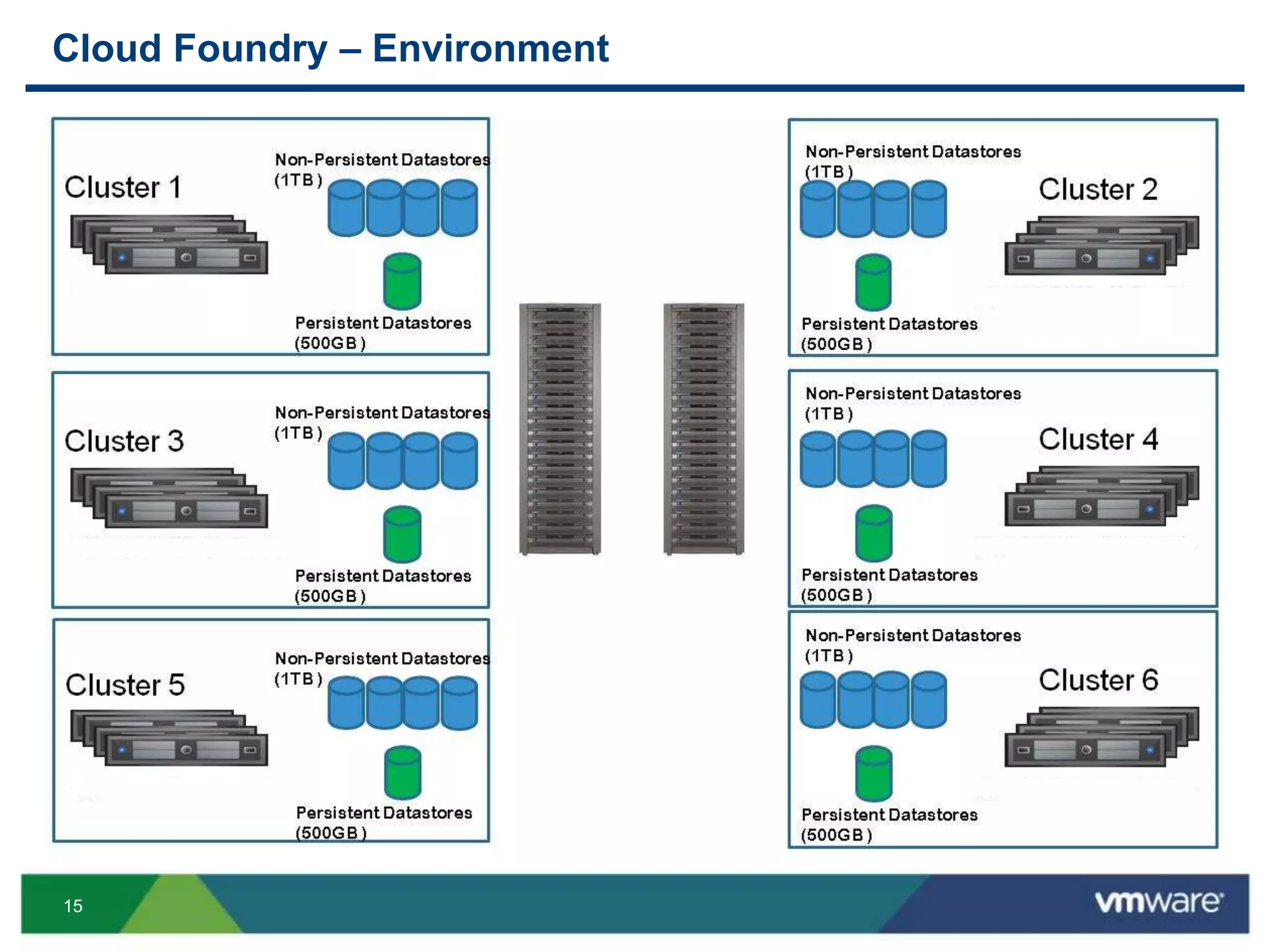
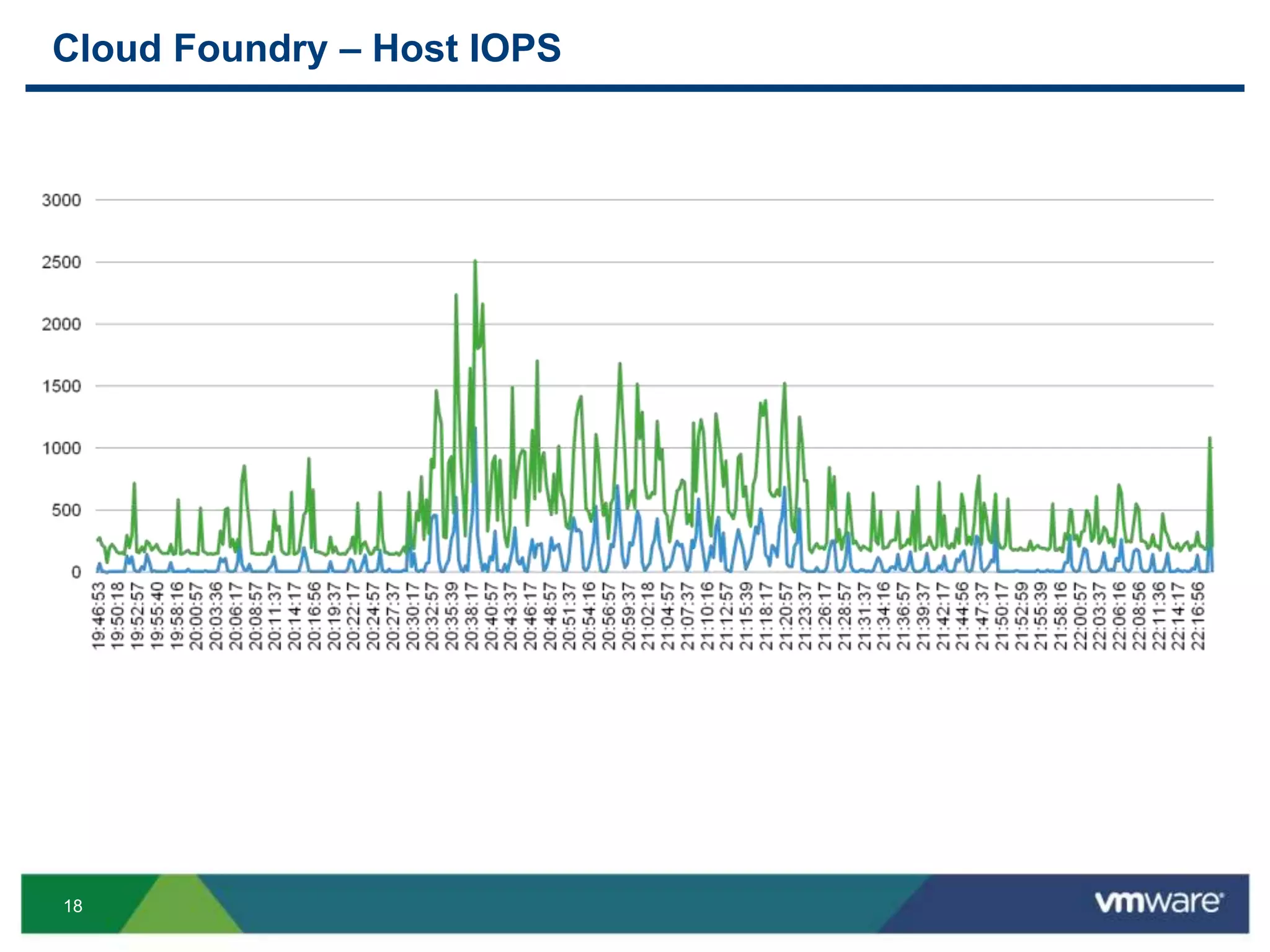
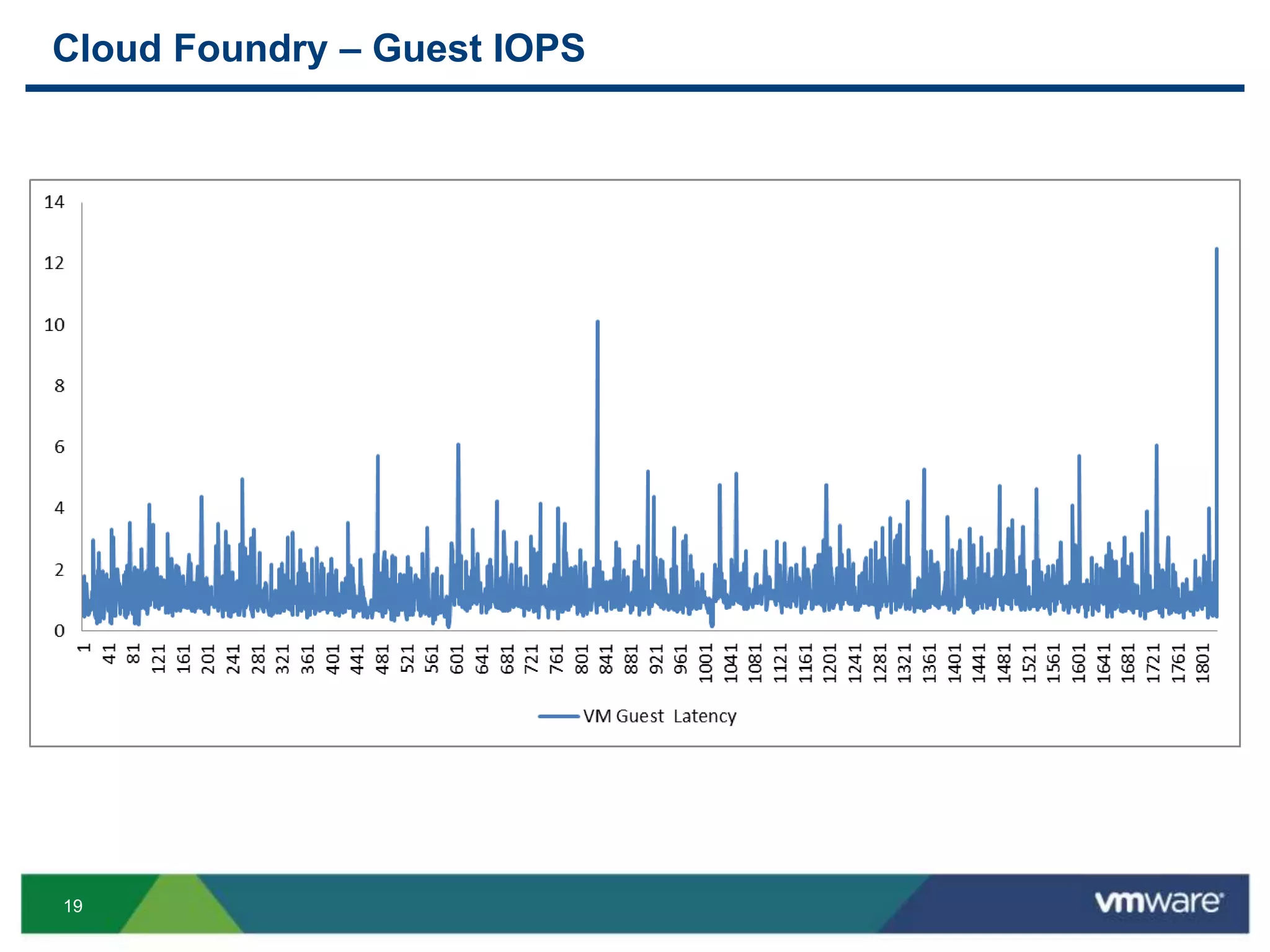
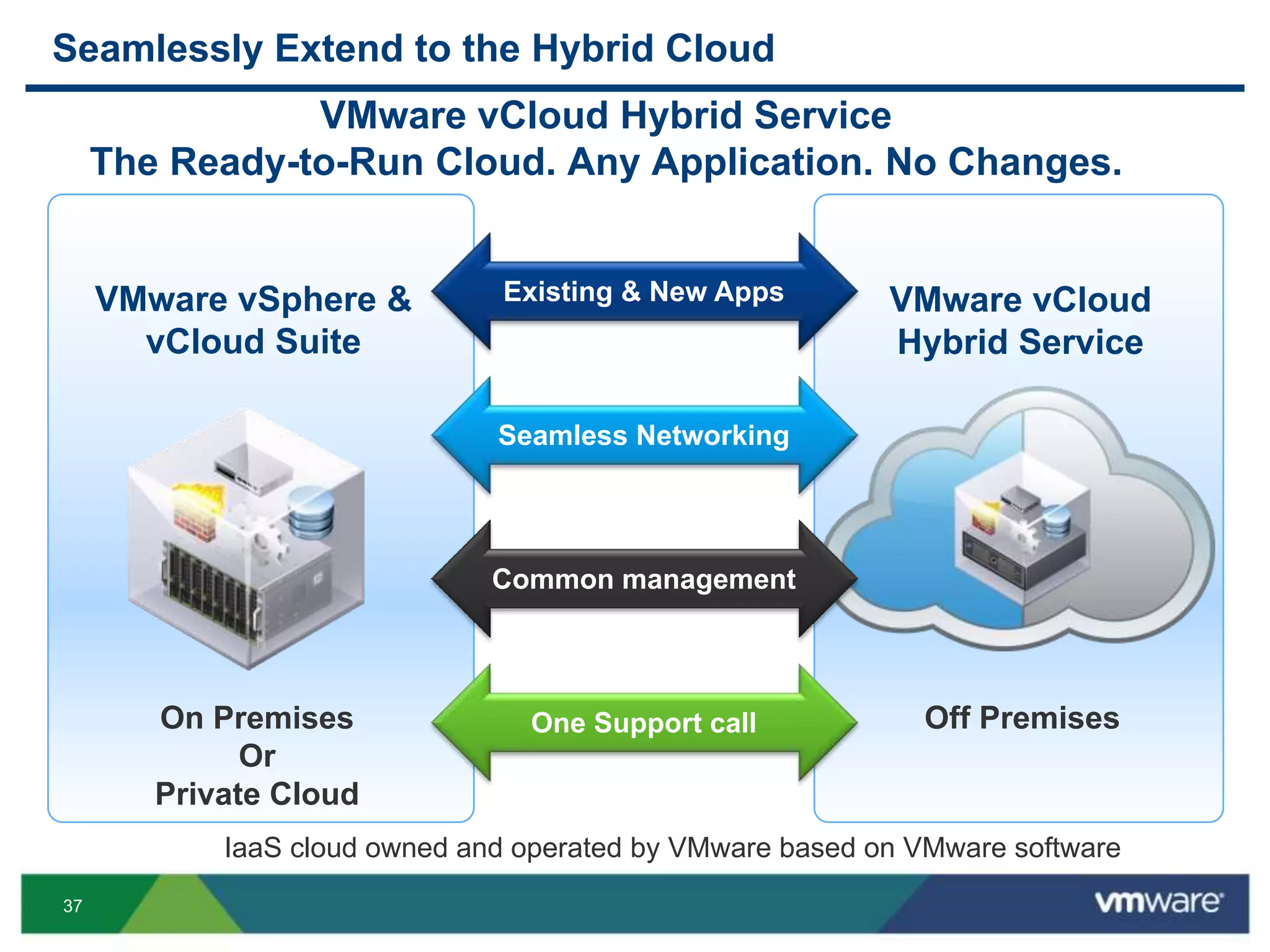
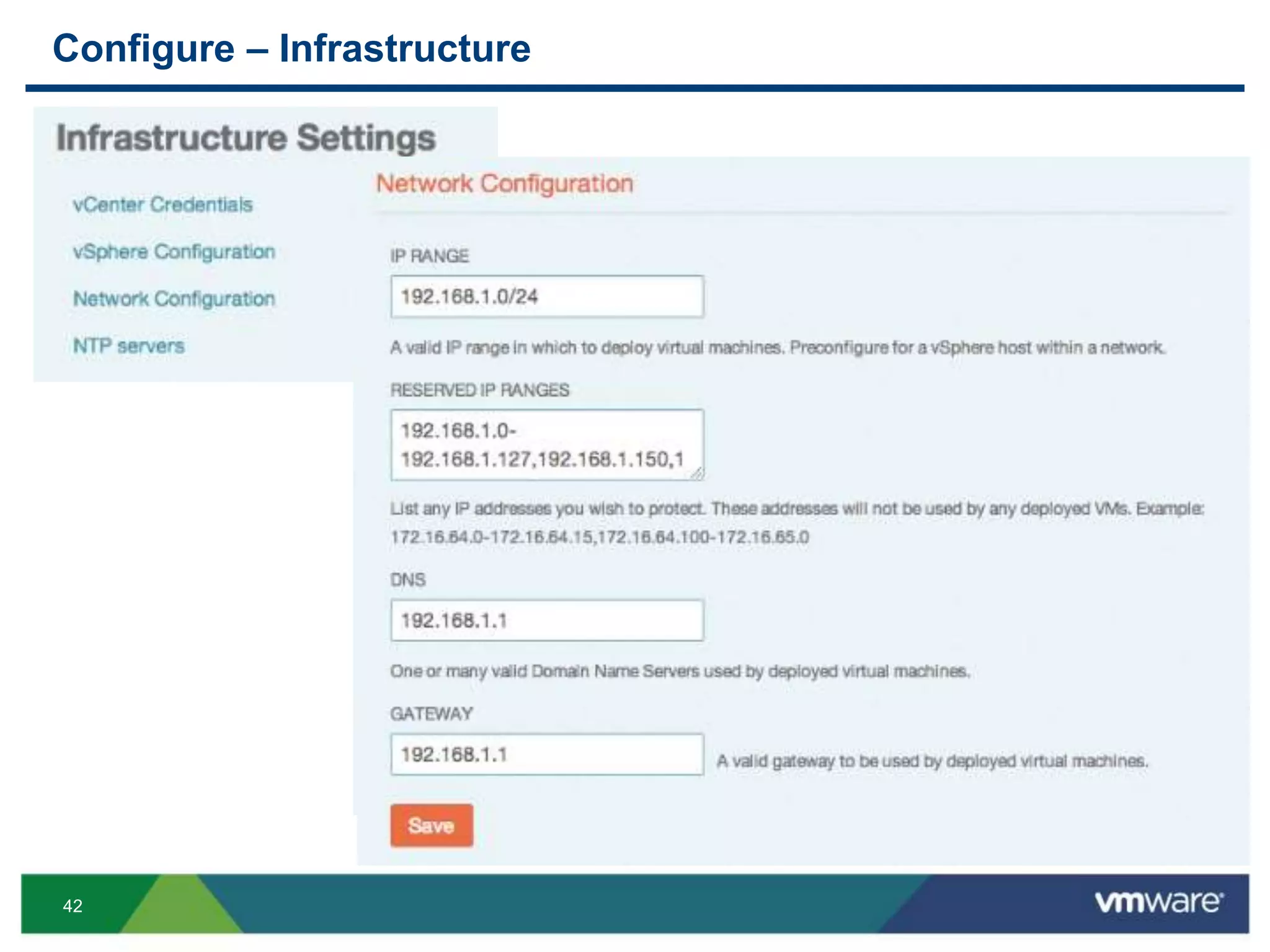
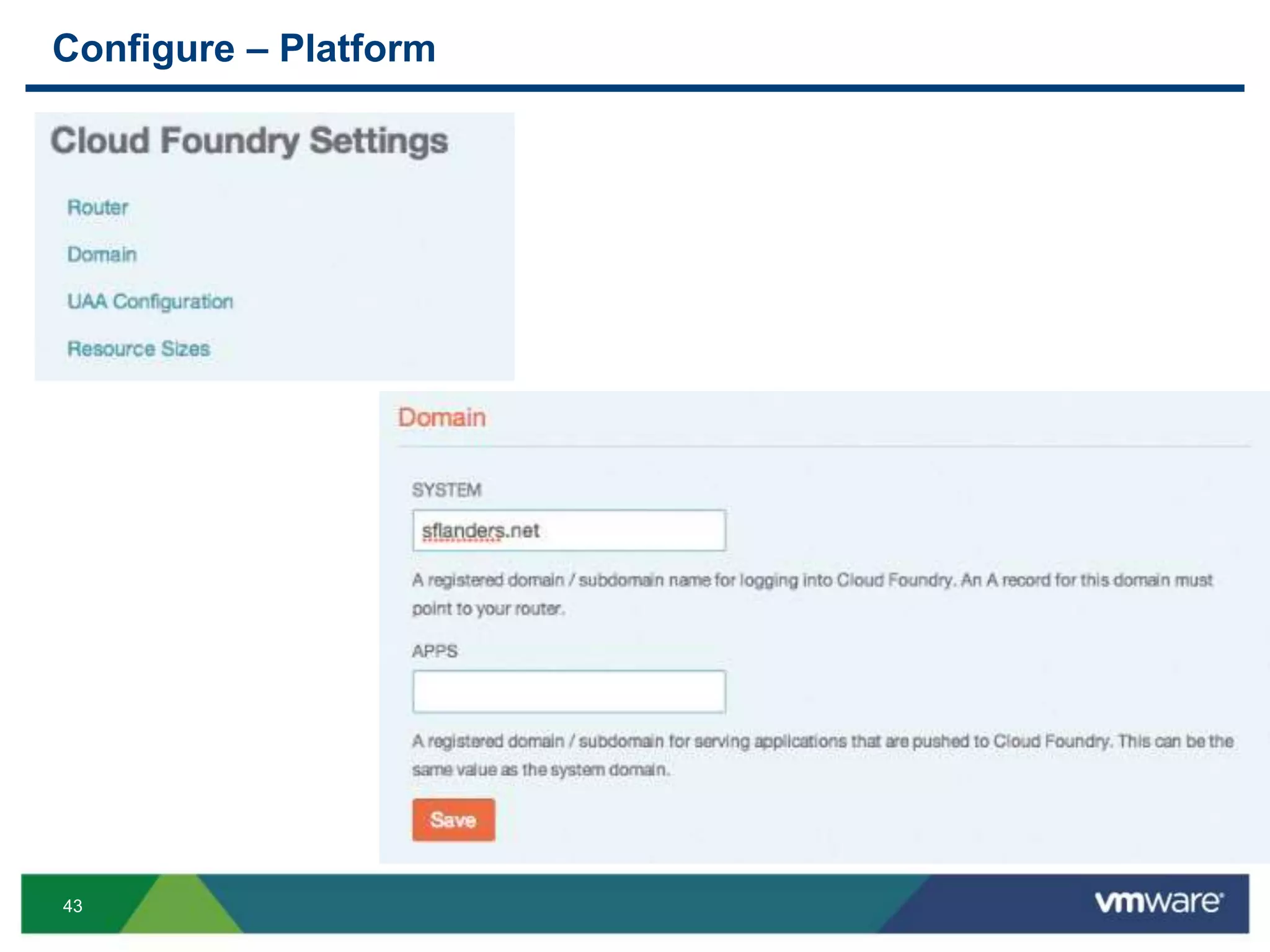
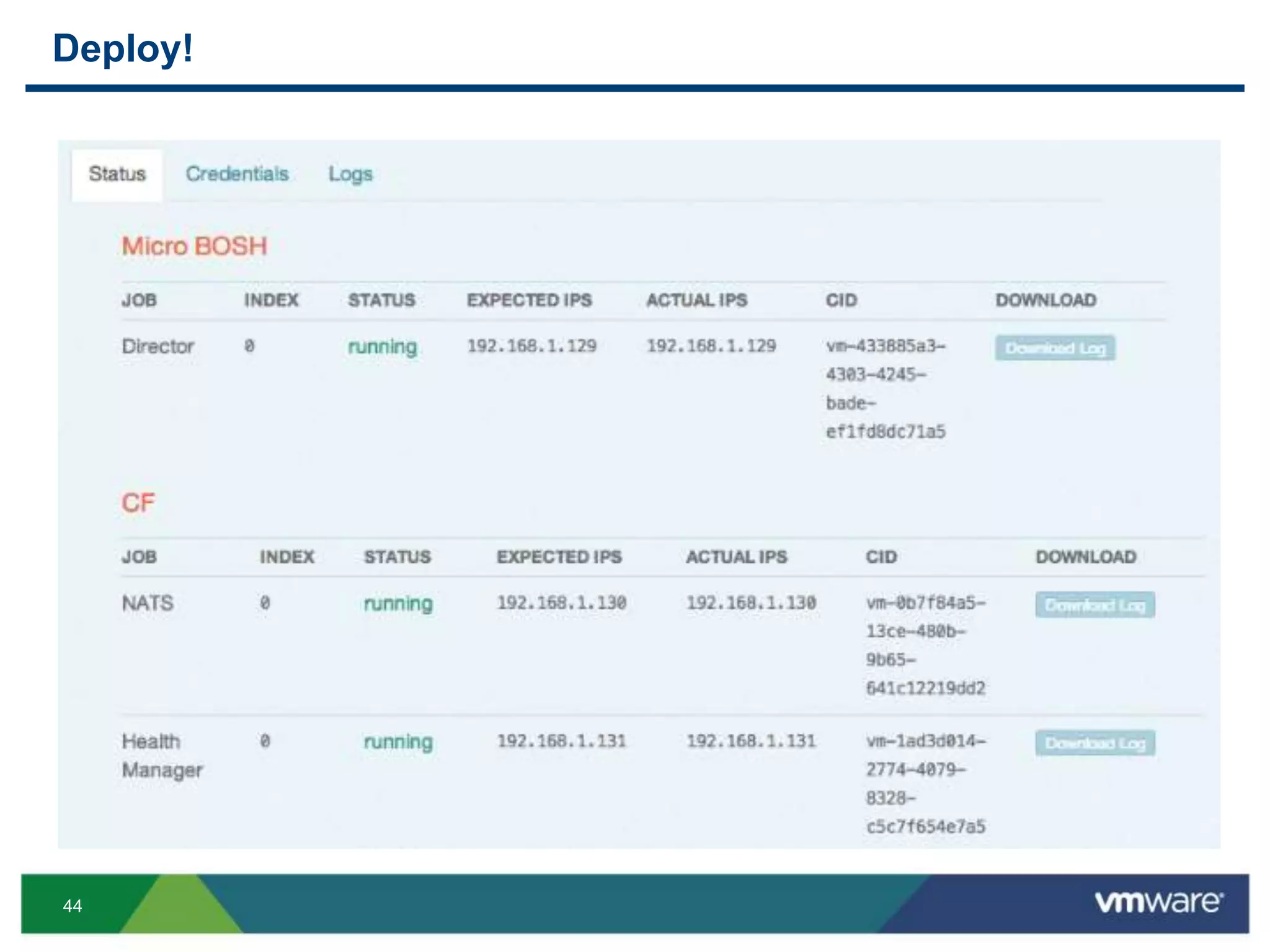
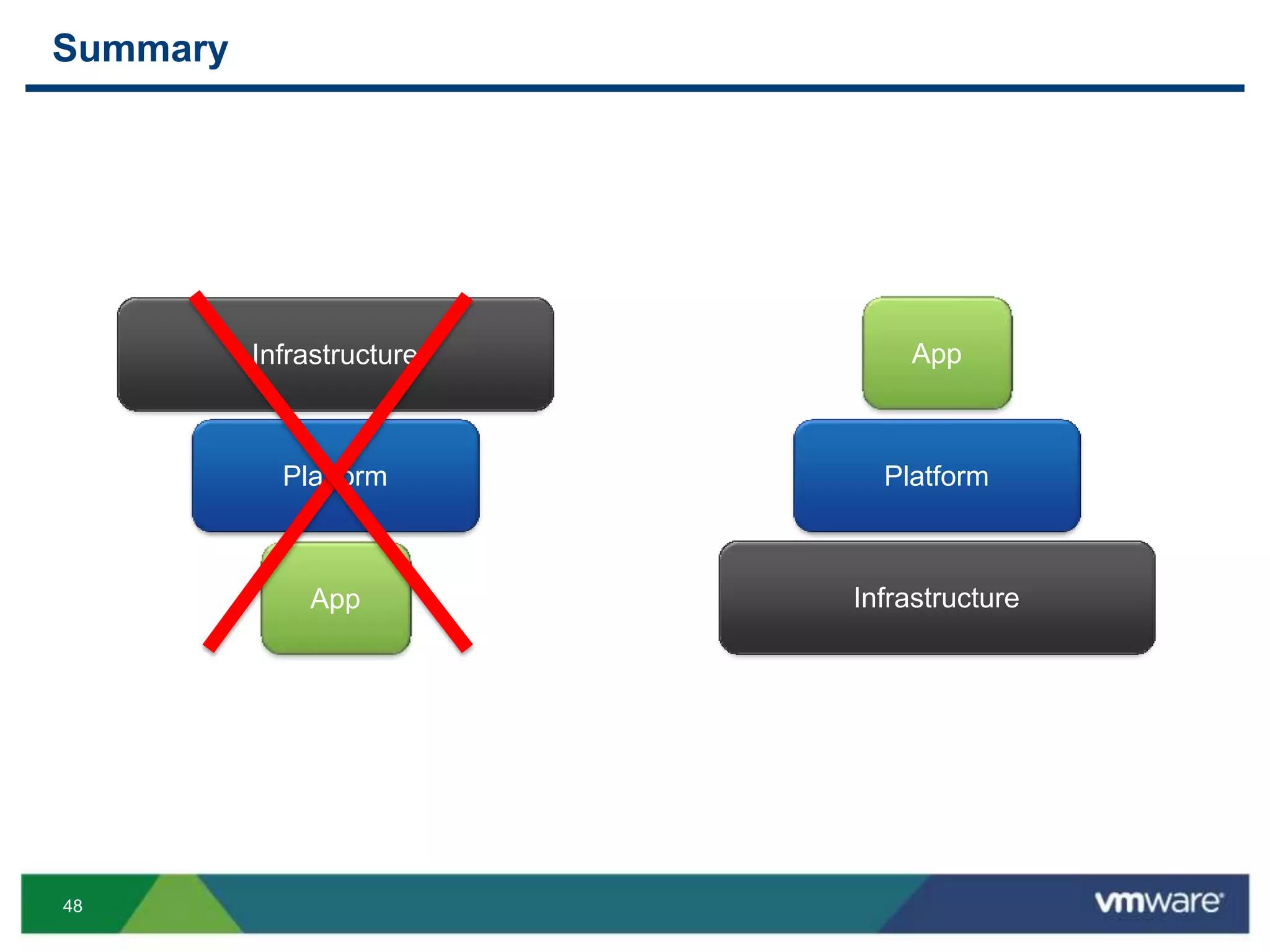
The document outlines three primary advantages of running Cloud Foundry in a VMware private cloud: high availability and disaster recovery, performance and scalability, and predictable IaaS operations. It emphasizes the importance of infrastructure in managing cloud services and addresses the benefits of hybrid cloud. The presentation concludes with a roadmap for integrating Cloud Foundry with VMware products.