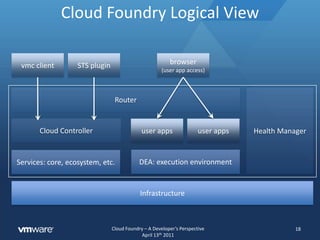
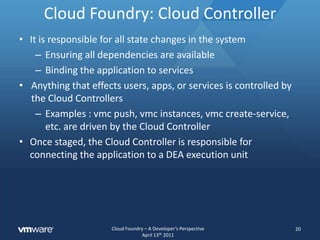
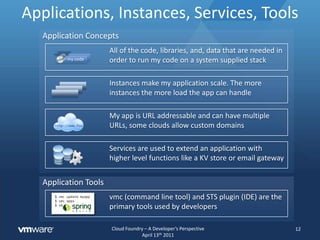
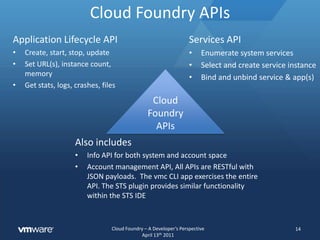
The document discusses Cloud Foundry from a developer's perspective, highlighting its capabilities as a multi-language, multi-framework platform as a service (PaaS) that facilitates application scaling and deployment. It outlines the developer's expectations for seamless deployment, the architecture of typical web applications, and the lifecycle management provided through Cloud Foundry's APIs and command line tools. The platform abstracts infrastructure management to allow developers to focus on writing code rather than configuring environments.




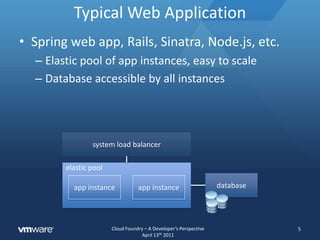
![Deploying Web App the Old Way6[mysqld]user = foobarport = 3306basedir = /usrbind-address = 172.58.77.101key_buffer = 16Mthread_stack = 128Kthread_cache_size = 8…[nginx]http.includemime.types;default_type: application/octet-stream;log_format: main ‘$remote_addr - $remote_user []…’keepalive_timeout 65;[tomcat]<Connector redirectPort=“8443” emptySessionPath…/><bean id=“sessionFactory” class=“org.springframework…/>[frontend]dependencies:mysqlclient](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-developerrev4-110416153322-phpapp02/85/Cloud-Foundry-a-Developer-s-Perspective-6-320.jpg)
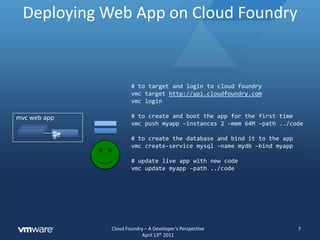
![core/common/**/*[blah]- blah blah blahmvc web app](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-developerrev4-110416153322-phpapp02/85/Cloud-Foundry-a-Developer-s-Perspective-8-320.jpg)






![The vmc CLI15Create app, update app, control appvmc push [appname] [--path] [--url] [--instances N] [--mem] [--no-start]vmc update <appname> [--path PATH]vmc stop <appname>vmc start <appname>vmc target [url]Update app settings, get app informationvmcmem <appname> [memsize]vmc map <appname> <url>vmc instances <appname> <num | delta>vmc {crashes, crashlogs, logs} <appname>vmc files <appname> [path]Deal with services, users, and informationvmc create-service <service> [--name servicename] [--bind appname]vmc bind-service <servicename> <appname>vmc unbind-service <servicename> <appname>vmc delete-service <servicename>vmc user, vmcpasswd, vmc login, vmc logout, vmc add-uservmc services, vmc apps, vmc info](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-developerrev4-110416153322-phpapp02/85/Cloud-Foundry-a-Developer-s-Perspective-17-320.jpg)