Cloud Foundry is an open source cloud platform that provides developers with choice in frameworks, services, and deployment locations. It allows for high developer agility and optimized software delivery across public, private and hybrid clouds. Cloud Foundry supports various programming languages and frameworks. Developers can access services like databases through the VCAP_SERVICES environment variable. While auto-scaling is not built-in, third parties provide dynamic scaling options. Cloud Foundry can be run locally through Micro Cloud Foundry for development and testing purposes.

![Introduction
1. Cloud Foundry is an open source cloud
computing platform as a service (PaaS) [1].
2. Developed by VMware [1].
3. Apache License 2.0 [1].
4. The industry’s first open platform as a
service [2]
5. Derek Collison and Mark Lucovsky - Two of
the Super Coders Behind Cloud Foundry when
it was initially started in April 2011 [3].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-2-320.jpg)
![The Magic Triangle
It’s all about CHOICE! [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-3-320.jpg)
![Why Cloud Foundry?
● Developers Agility - No one between you and your
application [5]
● Optimized Software Delivery - Portability without
changes – Dev/Test/Production, Private/Public clouds
[5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-4-320.jpg)
![Why Cloud Foundry?
● Open System - The freedom to choose [5]
○ Choice of clouds for deployment, across public,
private and hybrid clouds
■ CloudFoundry.com – VMware's operated Cloud
Service
■ Micro Cloud Foundry™
○ Choice of industry standard frameworks. Spring for
Java, Scala etc.
○ Choice of application services. RabbitMQ, MySQL,
MongoDB etc
○ Extensible architecture
○ A Community open-source project](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-5-320.jpg)
![Choice of Developer Frameworks
(The Top of the Triangle)
Cloud Foundry supports the following
application development frameworks [6]:
1. Spring/Java
2. Ruby on Rails
3. Ruby and Sinatra
4. Node.js
5. Grails](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-6-320.jpg)

![Choice of Application Services (The
Left Side of the Triangle)
Cloud Foundry services [7]:
1. MySQL, the open source relational database.
2. vFabric Postgres, relational database based on
PostgreSQL.
3. MongoDB, the scalable, open, document-based
database.
4. Redis, the open key-value data structure server.
5. RabbitMQ, for reliable, scalable, and portable
messaging.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-8-320.jpg)
![Services
● To access Cloud Foundry services from your
application, you first create a service, and
then bind it to your application [7].
● When your application runs on Cloud
Foundry, the environment contains a
VCAP_SERVICES variable that has
information about all the services bound to
the application. The content of this variable
is a JSON document [7].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-9-320.jpg)
![Eg: VCAP_SERVICES variable
(JSON)
{ "mysql-5.1" : [ { "credentials" : { "host" : "172.30.48.28",
"hostname" : "172.30.48.28",
"name" : "dd6c83789383c421287bdb25b63eca1a6",
"password" : "pYS3fjgQTmO7I",
"port" : 3306,
"user" : "uTdRF0y1H2R9r",
"username" : "uTdRF0y1H2R9r"
},
"label" : "mysql-5.1",
"name" : "mysql-service",
"plan" : "free",
"tags" : [ "relational",
"mysql-5.1",
"mysql"
]
}]}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-10-320.jpg)
![Choice of Clouds (The Right Side of
the Triangle)
● Public, Private, VMware based and non-
VMware based it up to the developer and
organization as to where they want to run
Cloud Foundry [4].
● Cloud Foundry can run on top of vSphere
and vCloud Infrastructure [4].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-11-320.jpg)

![Micro Cloud Foundry
● Micro Cloud Foundry™ - now you can run a
complete instance of Cloud Foundry on your
own computer [8].
● It is a full instance of Cloud Foundry that
provides the flexibility of local development
while preserving your options for future
deployment and scaling of your applications
[9].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-13-320.jpg)
![Micro Cloud Foundry
Just 3 steps [8]:
1. Install - VMware Player (free)
2. Login using CloudFoundry.com credentials
3. Download Micro Cloud Foundry virtual
machine image (It's about 1.4GB)
prompt$ du -h micro-v119-20121113.000224.zip
1.4G micro-v119-20121113.000224.zip](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-14-320.jpg)
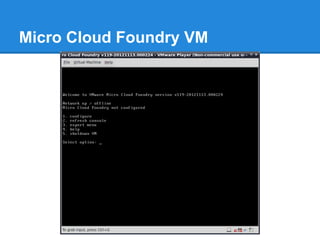
![Micro Cloud Foundry Configuration
● When you first start the VM, it will prompt to configure
the Micro Cloud Foundry instance.
● Set password for the ‘root’ and ‘vcap’
● The ‘root’ and ‘vcap’ users are the administrative/control
accounts for your Micro Cloud Foundry VM [9].
● Micro Cloud Foundry networking is also configured.
● Enter DNS configuration token, which is received on the
page where you downloaded the Micro Cloud VM. (This
is very important to work in offline mode as we are
relying on DNS lookup)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-16-320.jpg)
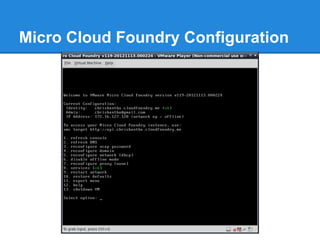
![Micro Cloud Foundry Configuration
Can use SSH tunnel to access the Micro Cloud
Foundry VM [10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-18-320.jpg)


![Command-Line Interface (vmc)
Cloud Foundry command-line interface can be
used to execute all the Cloud Foundry
operations, such as configuring your
applications and deploying them to Cloud
Foundry [11].
Prerequisite: Ruby and RubyGems
prompt$ sudo gem install vmc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-21-320.jpg)
![vmc target
Execute the vmc target command to specify the
Cloud Foundry target to which you will deploy
your applications [11].
1. To deploy on the PaaS Cloud Foundry,
specify https://api.cloudfoundry.com
2. To deploy on your local Micro Cloud
Foundry, specify http://api.<appname>.
cloudfoundry.me, where appname is the
domain you registered for your application at
the Micro Cloud Foundry Web site.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-22-320.jpg)
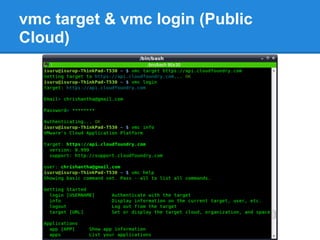
![VMC Basic Commands
The following command targets the PaaS
Cloud Foundry [11]:
prompt$ vmc target https://api.cloudfoundry.
com
To determine your current target:
prompt$ vmc target
Login:
prompt$ vmc login](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-23-320.jpg)


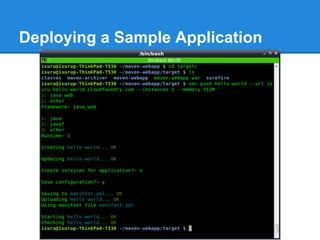
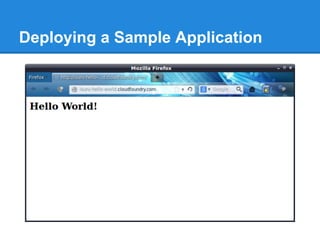
![Deploying a Sample Application
You can specify one or all of the following options to pass
deployment values; if you do not specify an option, vmc
push will interactively prompt you for it [12]:
prompt$ vmc push <appname> --path <directory> --url
<deploymentURL> --instances <instance-number> --
memory <MB> --no-start](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-28-320.jpg)
![Getting Information about the Cloud
Foundry Target
Display the instances of these service types
created [12]:
prompt$ vmc services](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-31-320.jpg)
![Getting Information about
Applications
Display the list of applications that are currently
deployed for your account, along with
instances, health, and associated service
instances [12]:
prompt$ vmc apps
Display the standard output log entries for an
application [12]:
prompt$ vmc logs <appname>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-32-320.jpg)
![Debugging Problems With Your
Applications
Viewing Log Files:
Use the "vmc files" command to get a list of
available log files [13]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-33-320.jpg)
![Does Cloud Foundry Auto Scale?
According to Collison [14], Cloud Foundry
provides all the mechanisms to allow auto-
scaling, however auto-scaling at its simplest
form is not directly builtin.
Thorsten [15] answers to this question by
saying “no, but trivially so”
RightScale [16] provides dynamic server
configuration for Cloud Foundry with their All-
In-One Cloud Foundry ServerTemplate™.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-34-320.jpg)
![Simplified Application Deployment
With Cloud Foundry “Manifest”
● Automates application deployments [17].
● The manifests feature uses a YAML
document, "manifest.yml" [17].
Ways to create manifest
● The manifest can be created by hand
● It can be created after a "vmc push"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-35-320.jpg)

![References
[1] Wikipedia, “Cloud Foundry,” Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, 2012.
[Online]. Available: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_Foundry. [Accessed: 09-
Jan-2013].
[2] VMware, “Cloud Foundry — Delivering on VMware’s ‘Open PaaS’ Strategy,”
The Console Blog - VMware Blogs, 2011. [Online]. Available: http://blogs.
vmware.com/console/2011/04/cloud-foundry-delivering-on-vmwares-open-
paas-strategy.html. [Accessed: 09-Jan-2013].
[3] VMware, “Two of the Super Coders Behind Cloud Foundry,” CloudFoundry.
com Blog, 2011. [Online]. Available: http://blog.cloudfoundry.
com/2011/04/12/two-of-the-super-coders-behind-cloud-foundry/. [Accessed: 09-
Jan-2013].
[4] VMware, “Explaining The Magic Triangle,” CloudFoundry.com Blog, 2011.
[Online]. Available: http://blog.cloudfoundry.com/2011/04/14/explaining-the-
magic-triangle/. [Accessed: 09-Jan-2013].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-37-320.jpg)
![References
[5] VMware, “About Cloud Foundry,” 2013. [Online]. Available: http://www.
cloudfoundry.com/about. [Accessed: 09-Jan-2013].
[6] VMware, “Frameworks Overview,” Documentation, 2012. [Online]. Available:
http://docs.cloudfoundry.com/frameworks.html. [Accessed: 09-Jan-2013].
[7] VMware, “Services Overview,” Documentation, 2012. [Online]. Available:
http://docs.cloudfoundry.com/services.html. [Accessed: 09-Jan-2013].
[8] VMware, “Micro Cloud Foundry,” 2012. [Online]. Available: https://micro.
cloudfoundry.com/. [Accessed: 09-Jan-2013].
[9] VMware, “‘We Shrunk the Cloud’ – Introducing Micro Cloud Foundry for
Developers,” CloudFoundry.com Blog, 2011. [Online]. Available: http://blog.
cloudfoundry.com/2011/08/24/we-shrunk-the-cloud-introducing-micro-cloud-
foundry-for-developers/. [Accessed: 09-Jan-2013].
[10] VMware, “Working Offline with Micro Cloud Foundry,” CloudFoundry.com
Blog, 2011. [Online]. Available: http://blog.cloudfoundry.
com/2011/09/08/working-offline-with-micro-cloud-foundry/. [Accessed: 09-Jan-
2013].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-38-320.jpg)
![References
[11] VMware, “VMC Installation,” Documentation, 2012. [Online]. Available:
http://docs.cloudfoundry.com/tools/vmc/installing-vmc.html. [Accessed: 09-Jan-
2013].
[12] VMware, “VMC Quick Reference,” Documentation, 2012. [Online].
Available: http://docs.cloudfoundry.com/tools/vmc/vmc-quick-ref.html.
[Accessed: 09-Jan-2013].
[13] VMware, “Debugging with VMC,” Documentation, 2012. [Online]. Available:
http://docs.cloudfoundry.com/tools/vmc/debugging.html. [Accessed: 09-Jan-
2013].
[14] D. Collison, “auto scaling in cloud foundry : CloudFoundry.com Support,”
2011. [Online]. Available: http://support.cloudfoundry.com/entries/20273738-
auto-scaling-in-cloud-foundry. [Accessed: 10-Jan-2013].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-39-320.jpg)
![References
[15] Thorsten, “Cloud Foundry Architecture and Auto-Scaling,” RightScale Blog,
2011. [Online]. Available: http://blog.rightscale.com/2011/04/14/cloud-foundry-
architecture-and-auto-scaling/. [Accessed: 10-Jan-2013].
[16] RightScale, “RightScale Free Edition | RightScale Cloud Management
Platform,” 2013. [Online]. Available: https://www.rightscale.com/s/vmware-
cloud-foundry.php. [Accessed: 10-Jan-2013].
[17] VMware, “Simplified Application Deployment With Cloud Foundry
‘Manifest’,” CloudFoundry.com Blog, 2012. [Online]. Available: http://blog.
cloudfoundry.com/2012/01/10/simplified-application-deployment-with-cloud-
foundry-manifest/. [Accessed: 10-Jan-2013].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudfoundry-130308022944-phpapp02/85/Cloud-foundry-40-320.jpg)