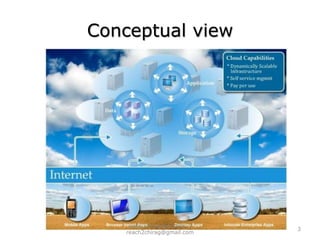
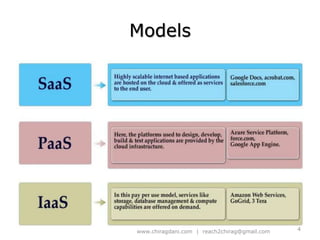
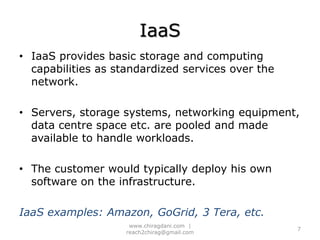
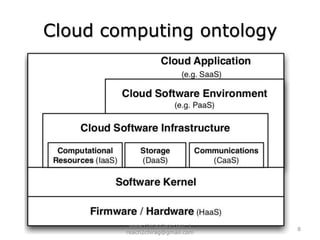
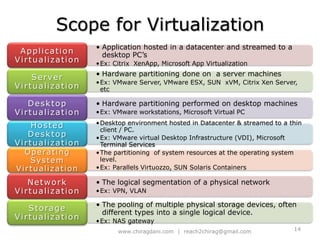
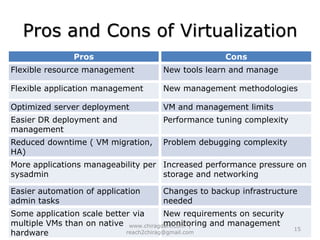
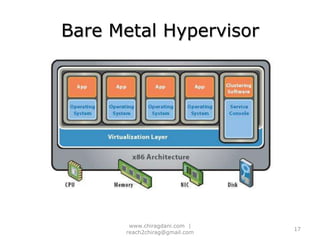
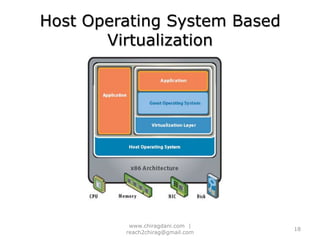
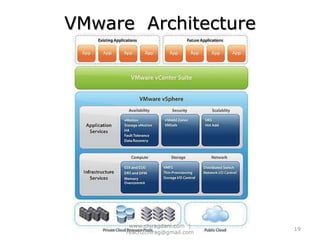
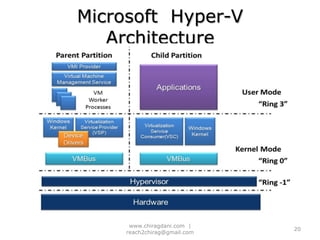
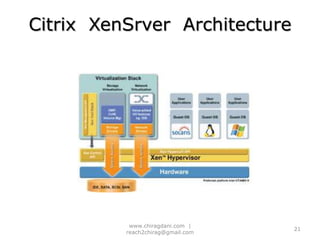
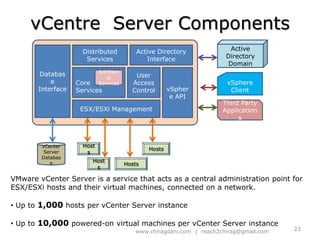
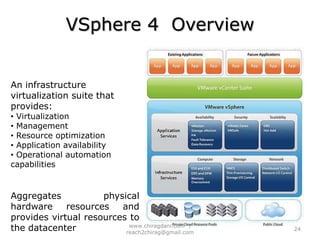
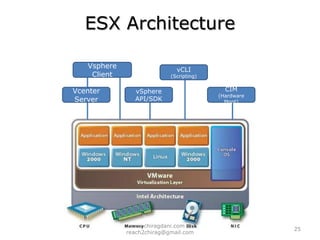
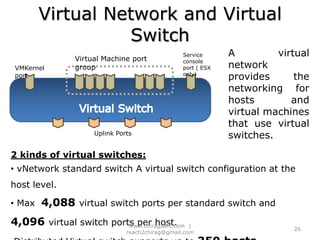
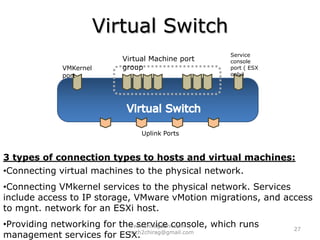
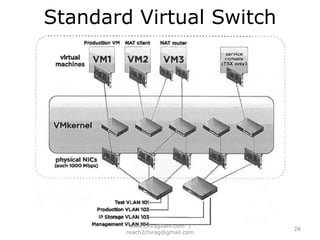
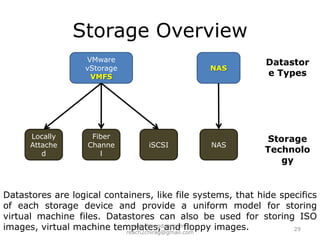
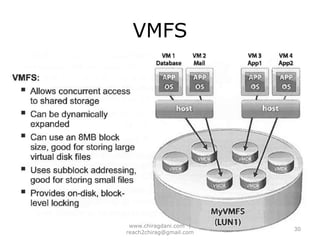
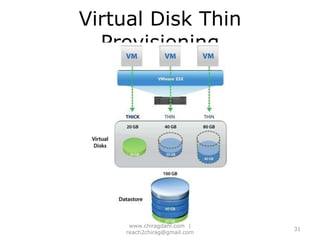
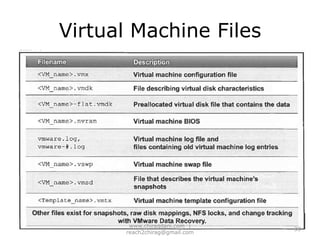
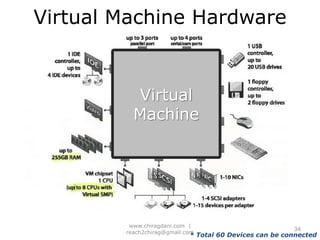
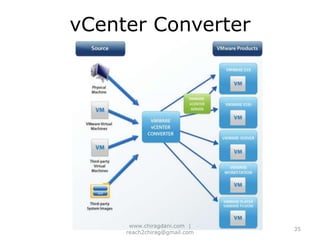
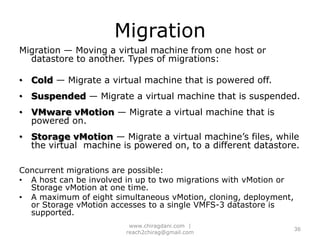
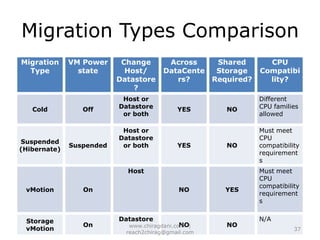
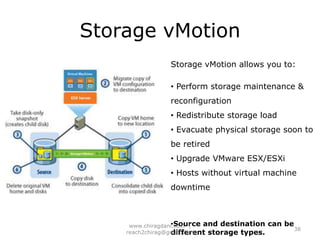
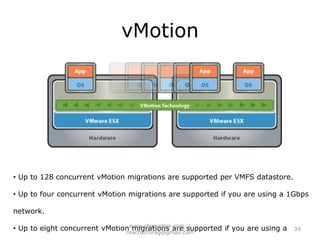
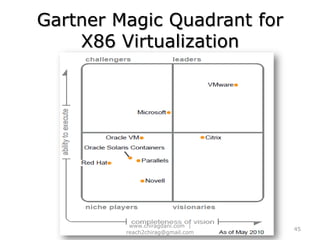
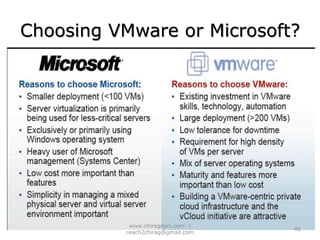
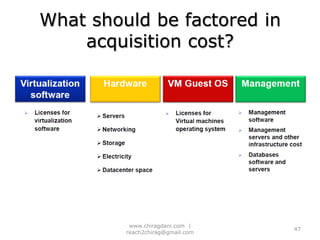
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, including definitions, models like SaaS, PaaS and IaaS, and concepts like public and private clouds. It discusses benefits of cloud computing like reduced costs and increased flexibility, as well as challenges around data protection, availability and regulatory compliance. The document also covers virtualization topics such as types of virtualization, virtual machine architecture, and virtual networking and storage components in VMware.