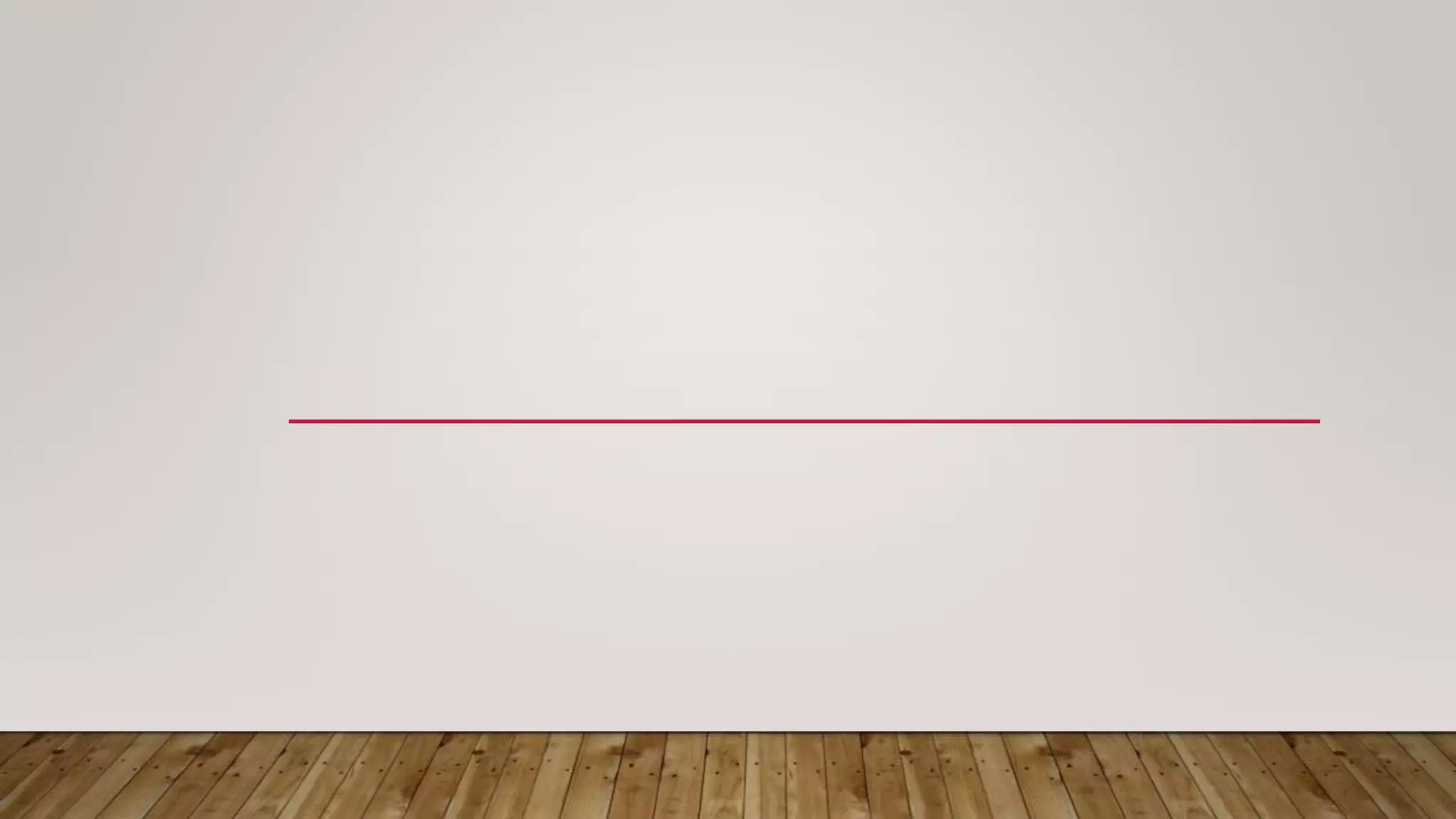
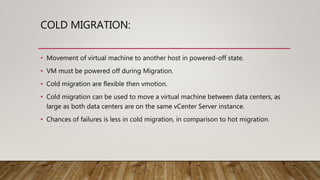
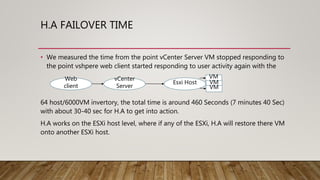
Migration involves moving virtual machines between hosts or datastores. There are different types of migration including cold migration, vMotion, suspended migration, and physical to virtual (P2V) or virtual to virtual (V2V) conversions. High availability (HA) ensures virtual machines restart on another host if the original host fails, providing continuous availability with little downtime.