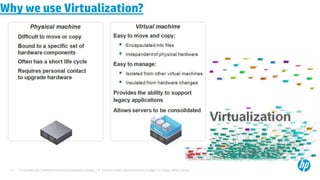
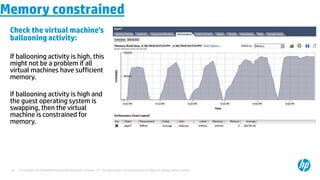
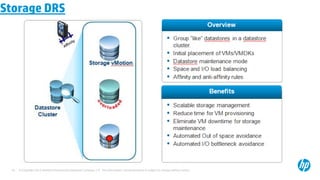
The document provides an overview of virtualization concepts using VMware vSphere 5.0. It discusses key components of vSphere including ESXi hosts, the vCenter Server, and the vSphere Client. The document outlines the installation and configuration of ESXi hosts, including requirements, and provides screenshots of installing and configuring the vCenter Server. It also discusses navigating and managing the vSphere environment and virtual machines.