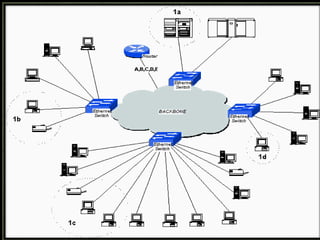
A VLAN allows hosts to communicate as if on the same broadcast domain regardless of physical location. It groups devices logically instead of relocating them physically. Network changes can be done through software. A WAP connects wired devices to a wireless network using Wi-Fi or Bluetooth standards. It relays data between wireless and wired devices on a network. WAPs are managed by wireless LAN controllers and provide wireless access in public hotspots. Security features like encryption and authentication servers help secure wireless traffic on WAPs.