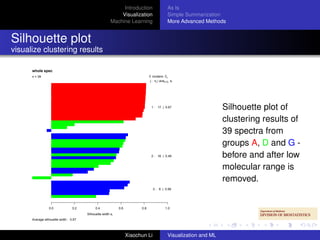
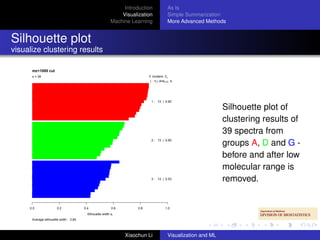
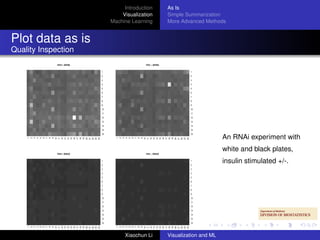
This document discusses visualization and machine learning techniques for exploratory data analysis. It begins with an introduction on how these methods can help search for patterns in large datasets and present data structures succinctly. It then covers visualizing data in its raw form, after simple summarization, and using more advanced techniques like clustering and dimensionality reduction. Machine learning methods like supervised learning, unsupervised learning, random forests and support vector machines are also briefly introduced. Specific examples shown include quality inspection plots of gene chips and cumulative expression plots along genomic coordinates.









![Introduction As Is
Visualization Simple Summarization
Machine Learning More Advanced Methods
Mass Spec
Example
40
30
One spectrum from
x[1, ]
20
group A
10
0
0e+00 2e+04 4e+04 6e+04 8e+04 1e+05
mz
Xiaochun Li Visualization and ML](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/visualization-and-machine-learning-for-exploratory-data1557/85/Visualization-and-Machine-Learning-for-exploratory-data-14-320.jpg)