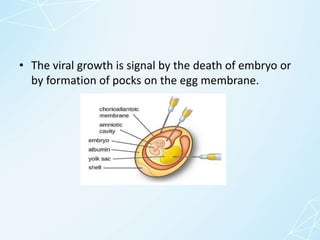
This presentation provides an overview of viruses including:
1) It defines viruses as ultra-microscopic agents consisting of nucleic acid and protein that can only replicate inside host cells.
2) It discusses the history of virus discovery and key figures like Ivanovsky, Beijerinck, and Stanley.
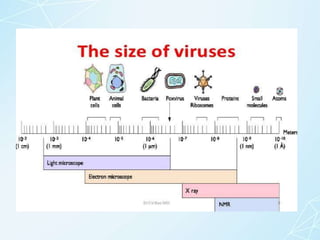
3) It describes the typical characteristics of viruses like their acellular and obligate parasitic nature, composition of nucleic acid and protein capsids, small size, and inability to metabolize.
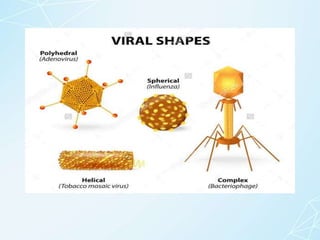
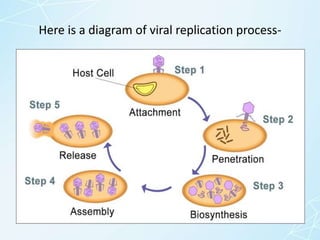
4) It covers virus morphology, classification based on shape, size, nucleic acid, and host range, and the multi-step process of viral replication within host cells.
5) It discusses common