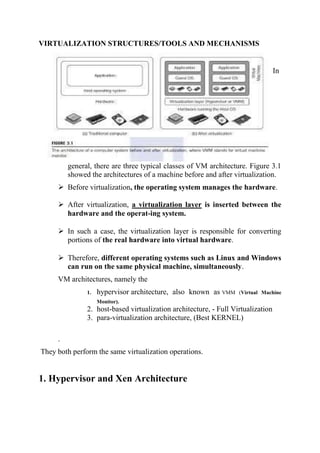
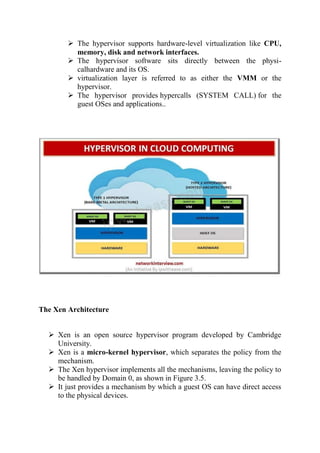
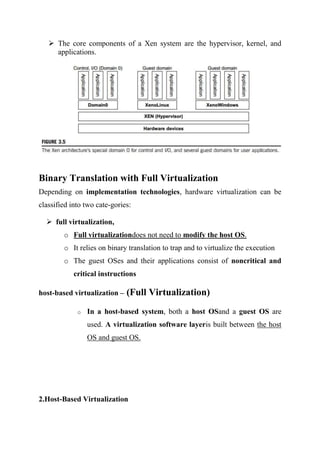
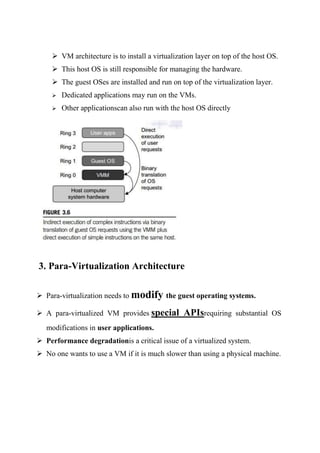
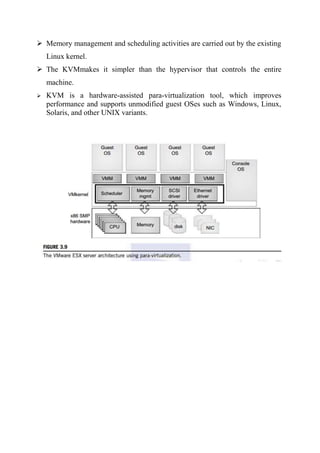
There are three main virtual machine architectures: hypervisor/VMM architecture, host-based virtualization, and para-virtualization. The hypervisor/VMM architecture inserts a virtualization layer between the hardware and operating system to allow multiple operating systems to run simultaneously on the same physical machine. Host-based virtualization builds a virtualization layer on top of the host operating system, which still manages the hardware. Para-virtualization requires modifying guest operating systems and provides APIs for improved performance over full virtualization. KVM is an example of para-virtualization that uses the existing Linux kernel for scheduling and memory management.