1. The document discusses an online class on cloud computing technologies held by D. Shunmuga Kumari on August 11, 2020.
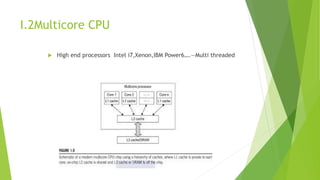
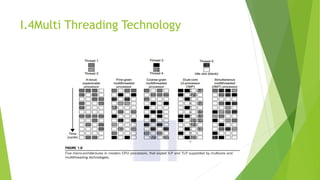
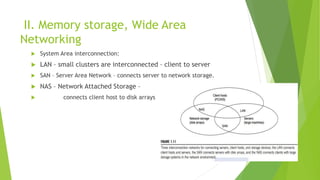
2. It covers key technologies for network-based systems including multicore CPUs, memory/storage, virtual machines, and data center virtualization for cloud computing.
3. Data center virtualization allows large data centers with thousands of servers to efficiently utilize resources through software-based network traffic balancing, fault tolerance, and expandability.