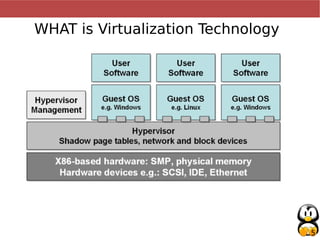
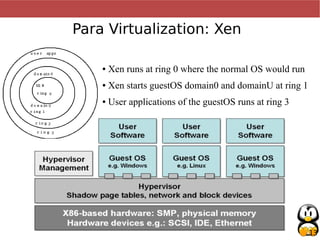
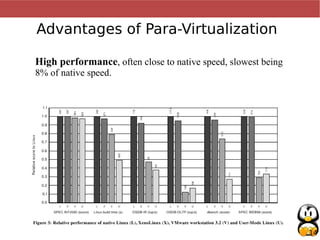
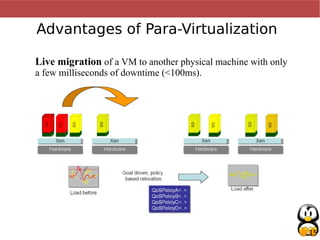
Virtualization allows multiple operating systems, called virtual machines, to run simultaneously on a single physical computer. It works by emulating or partially emulating the processor, BIOS, and other hardware for the virtual machines. This provides benefits like better hardware utilization, scalability, fault tolerance, and easier deployment (paragraphs 1-4). Popular virtualization technologies include Qemu, KVM, VirtualBox, and VMWare, which emulate x86, ARM, and PowerPC architectures using native CPU instructions or full emulation (paragraphs 5-7). Virtualization saves costs by improving hardware utilization and allowing dynamic scalability. It also improves maintainability, availability, and deployment times (paragraphs 8-10). Para-virtualization requires modifying