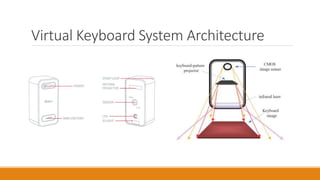
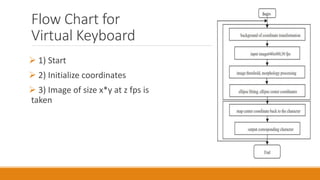
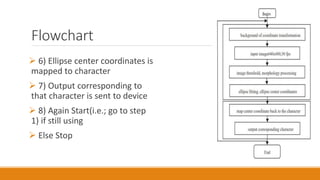
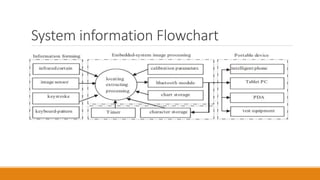
The document discusses a seminar on virtual keyboards, detailing their functionality and components such as sensor modules, IR light sources, and pattern projectors. It outlines the operational flow of the virtual keyboard system, emphasizing its advantages like portability and low maintenance, while also noting disadvantages like high cost and visibility issues. The conclusion highlights the practicality of virtual keyboards as a replacement for traditional keyboards, enhancing typing convenience and speed.