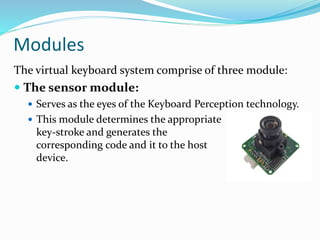
The document discusses virtual keyboards, which allow users to communicate with computers through a projected image of a keyboard on a flat surface. It outlines the technology's invention, components, working mechanism, as well as its advantages and disadvantages. The document highlights various types of virtual keyboards, including their applications and challenges in usage.