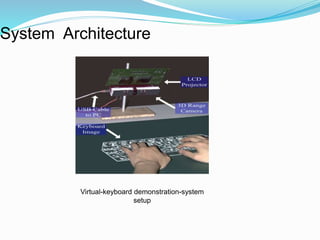
The document discusses virtual keyboards, which project a keyboard onto any surface that can be typed on. It describes the components of a virtual keyboard system, including a pattern projector, IR light source, and sensor module. Virtual keyboards allow users to type on small devices like phones or wearable computers. While costly and requiring practice, virtual keyboards are portable and can benefit injured users. They are used in industrial, smartphone, computer and gaming applications.