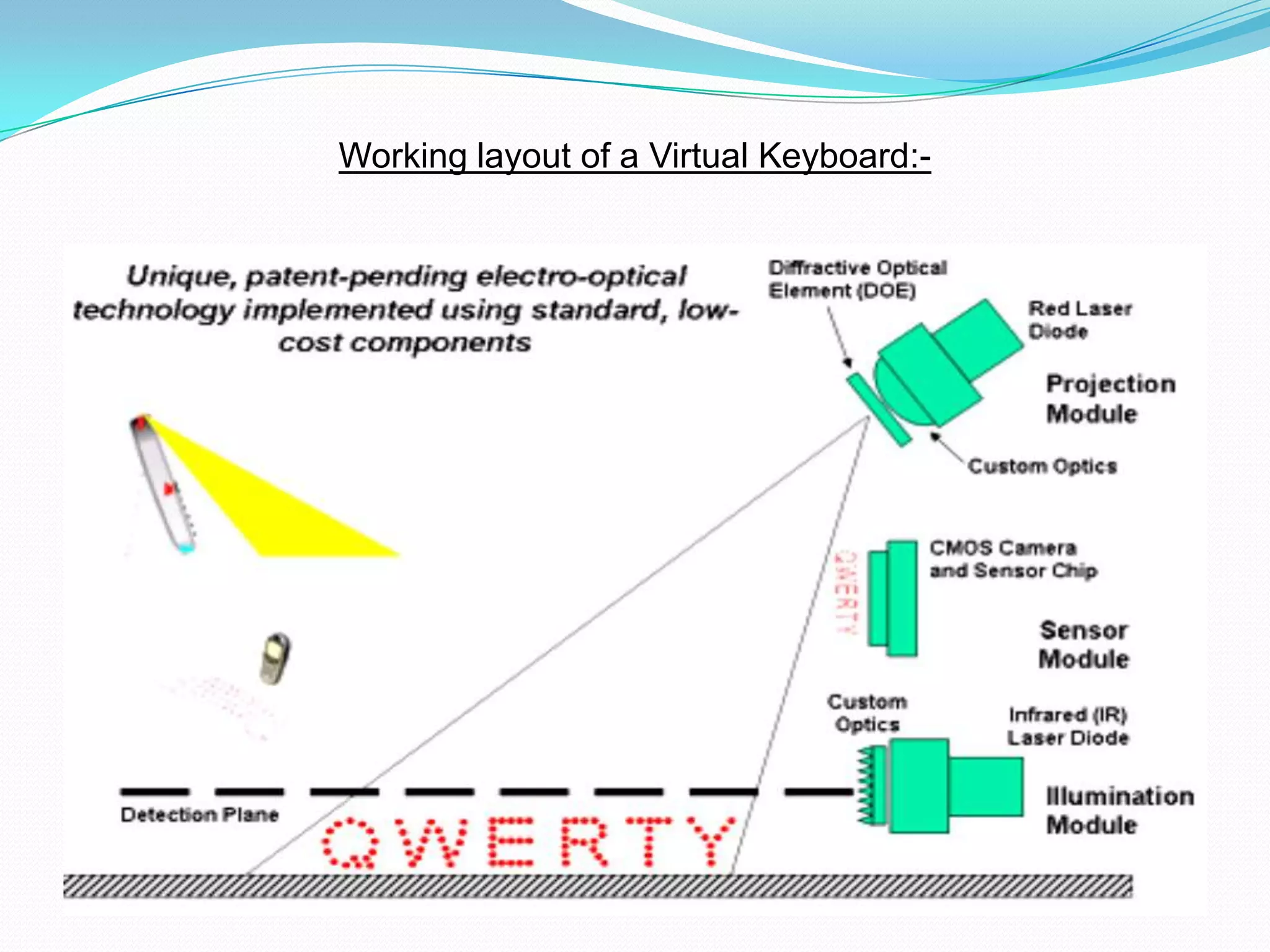
This document presents information on virtual keyboard technology. It discusses how a virtual keyboard works using camera tracking of finger movements rather than physical keys. The key components are an infrared light source, sensor module, and pattern projector. It provides advantages like portability and not needing a flat surface, though drawbacks include higher costs and needing practice. Virtual keyboards can be used with devices like phones and as an input for computers and games.