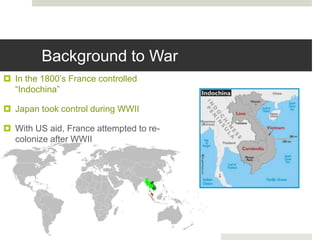
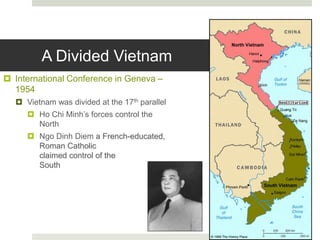
This document provides background information on the Vietnam War. It describes how the US became involved to prevent the spread of communism under the Truman Doctrine. It discusses key events like the Tet Offensive and the Kent State protests against the war. The war ended in 1975 with South Vietnam falling to communist forces from the North.