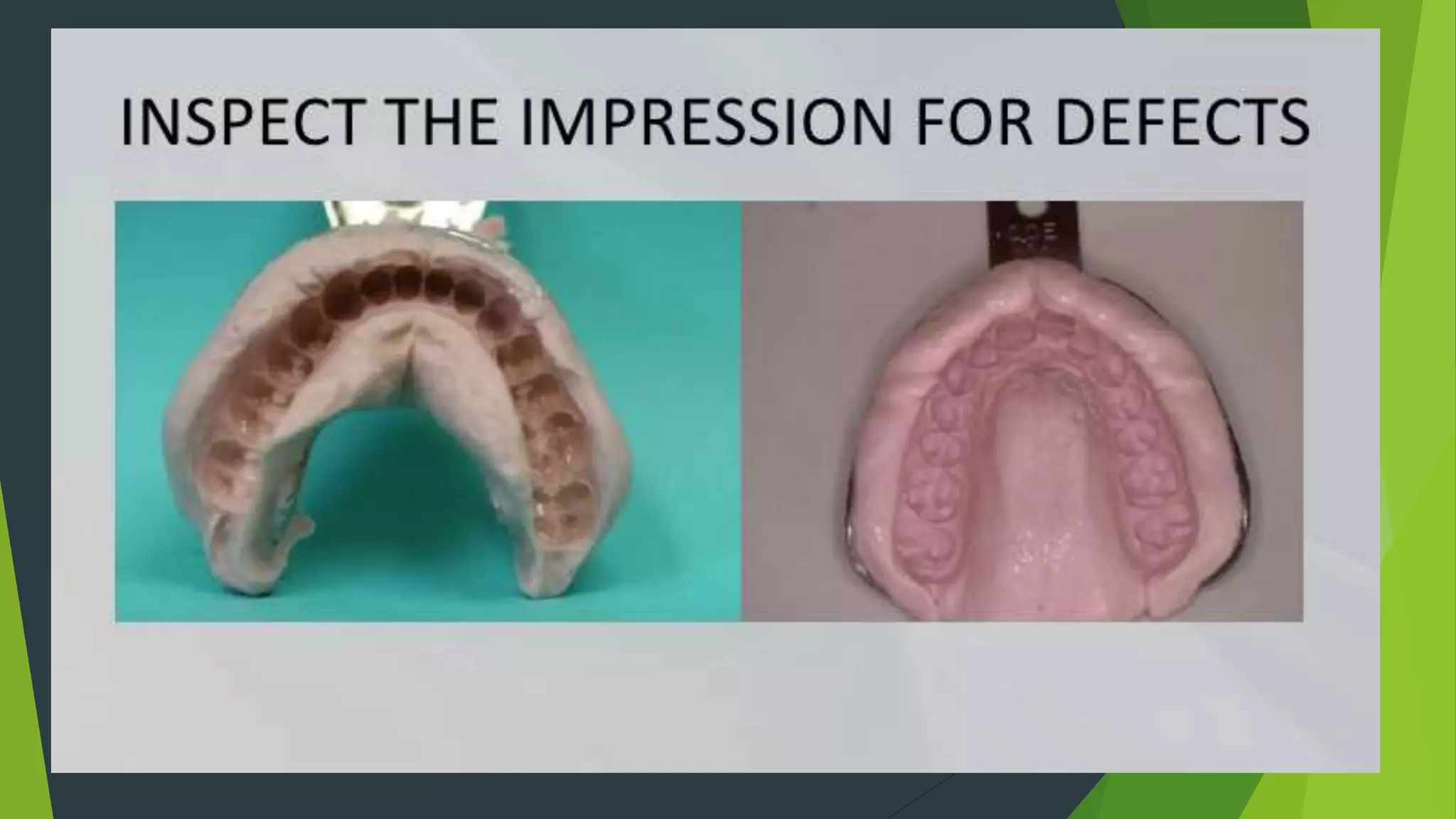
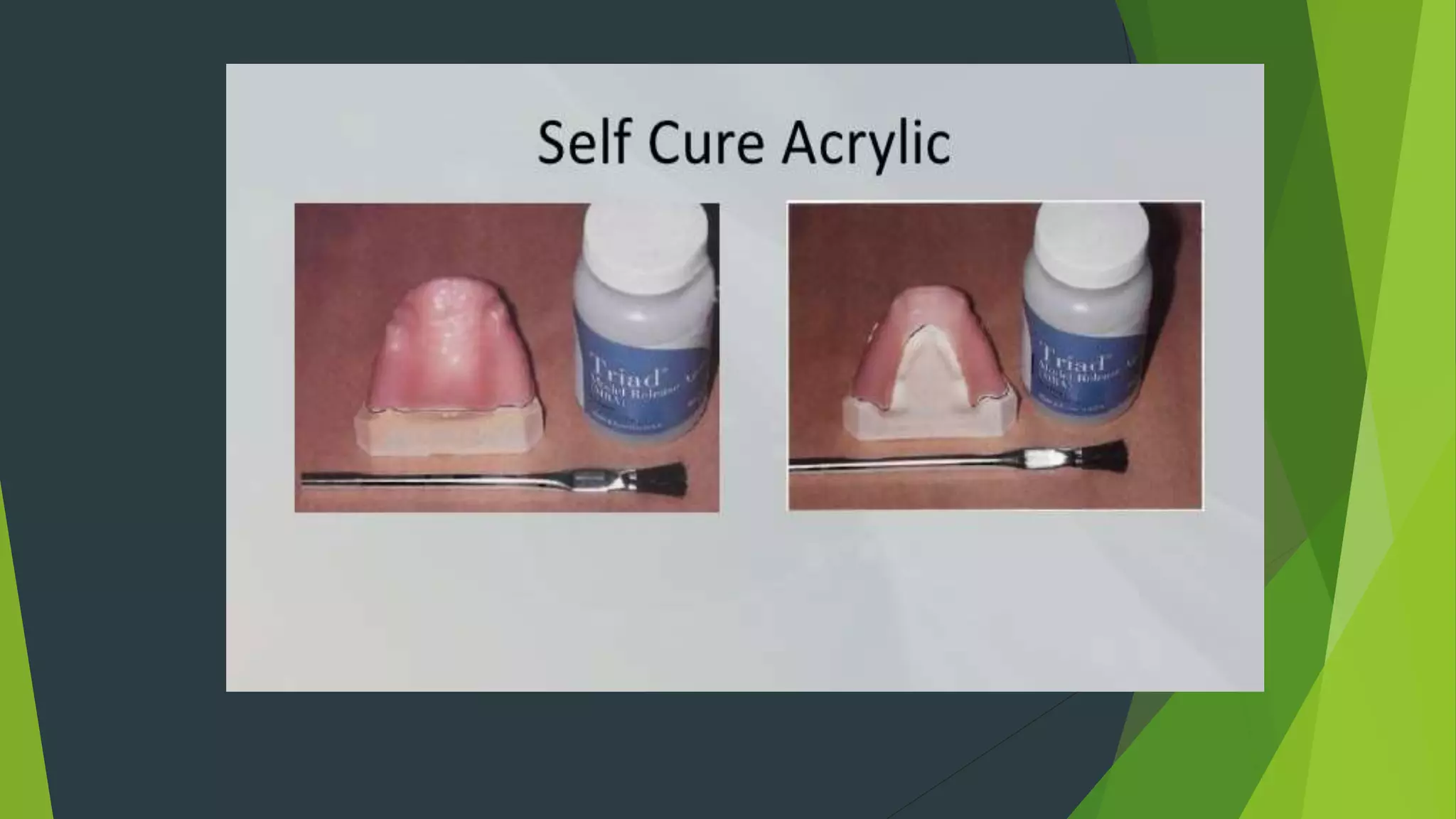
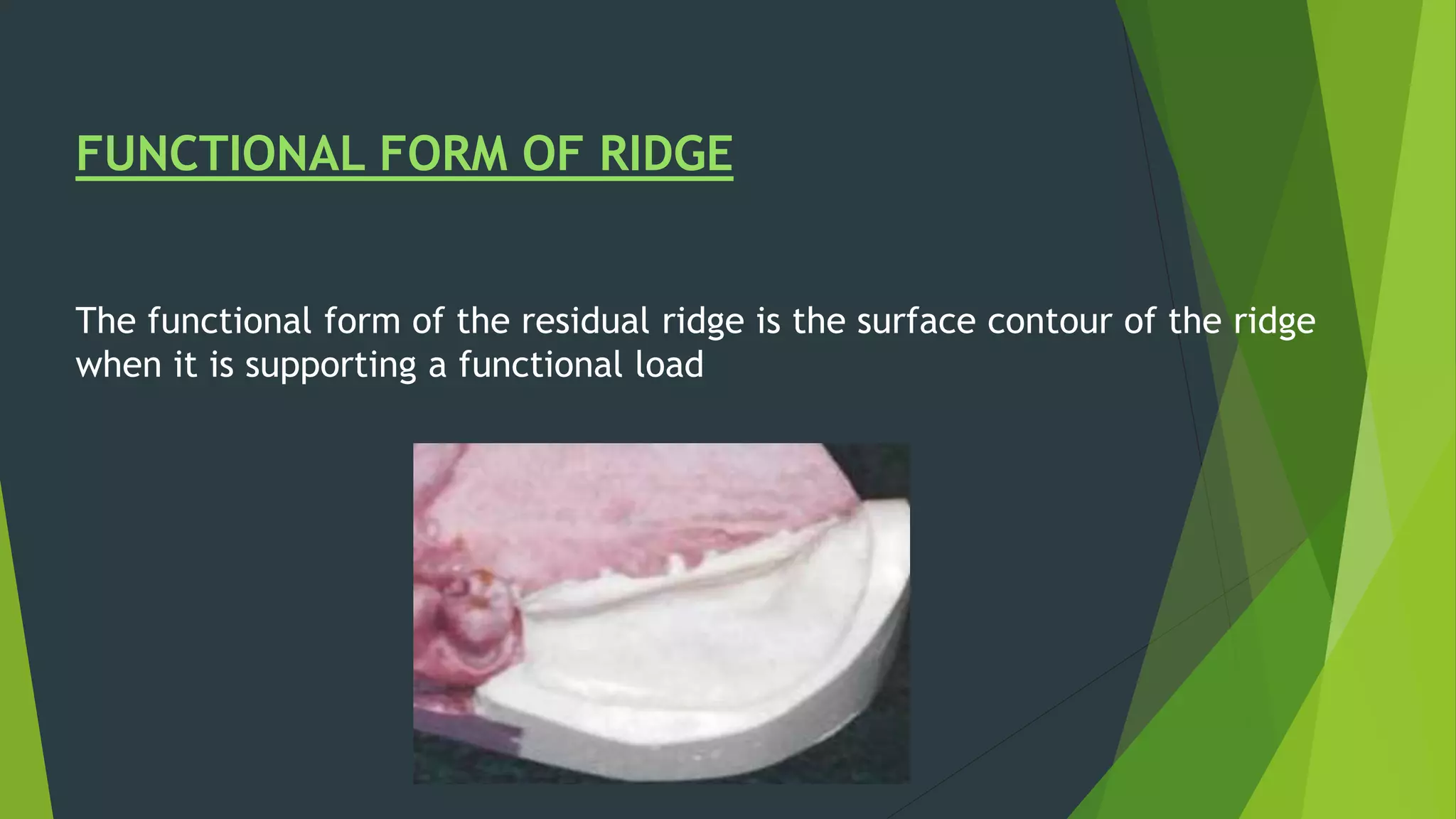
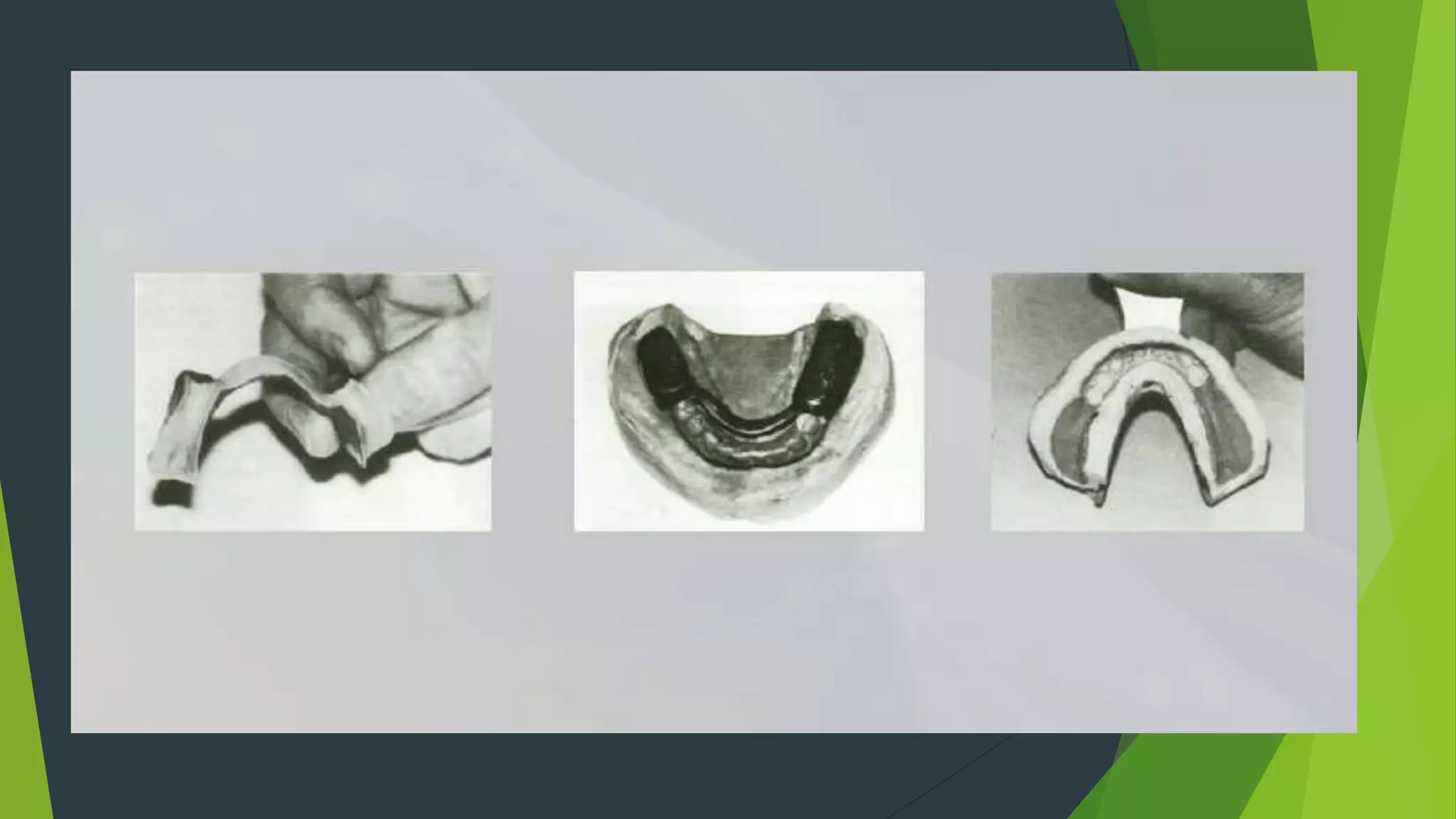
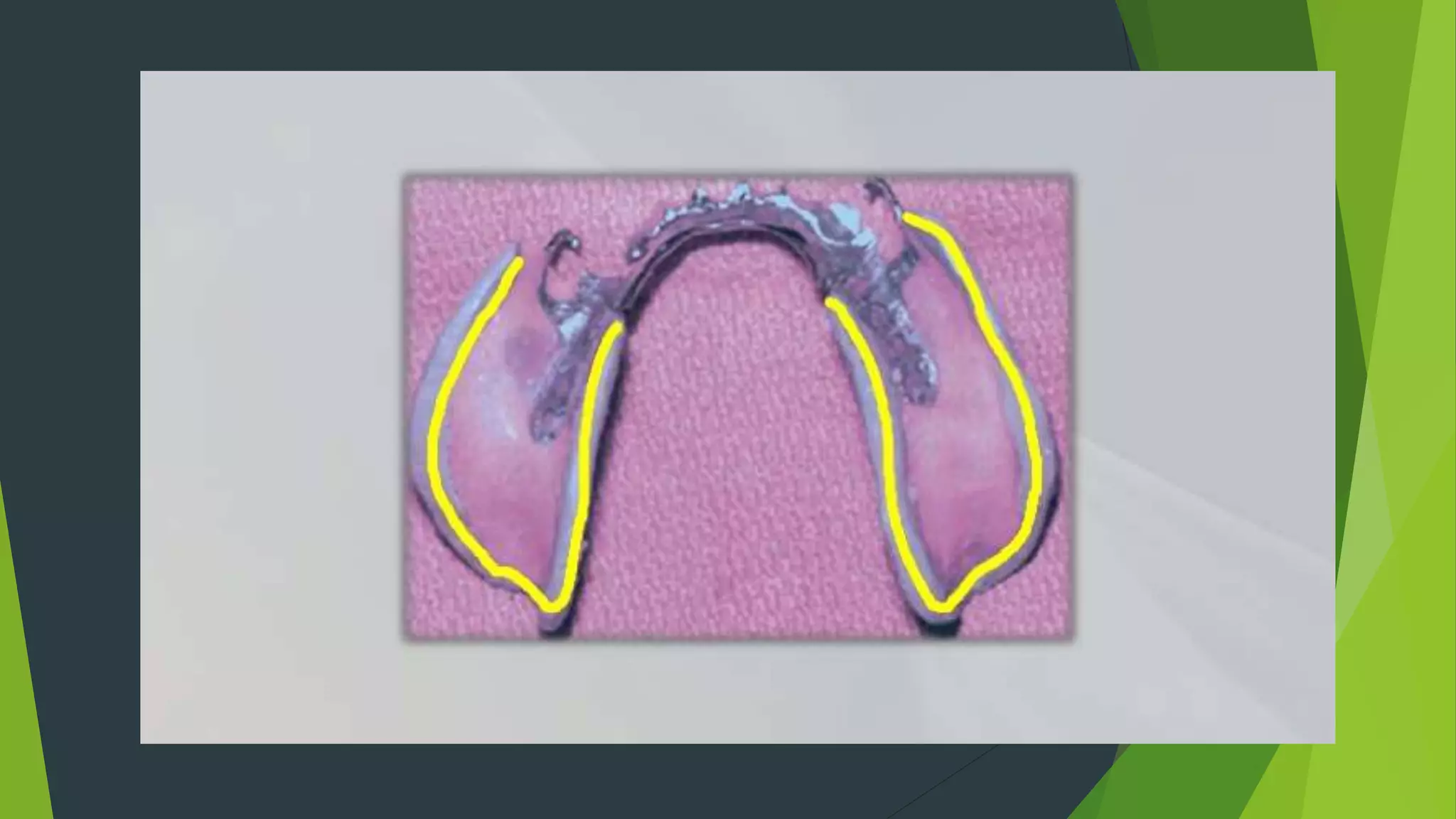
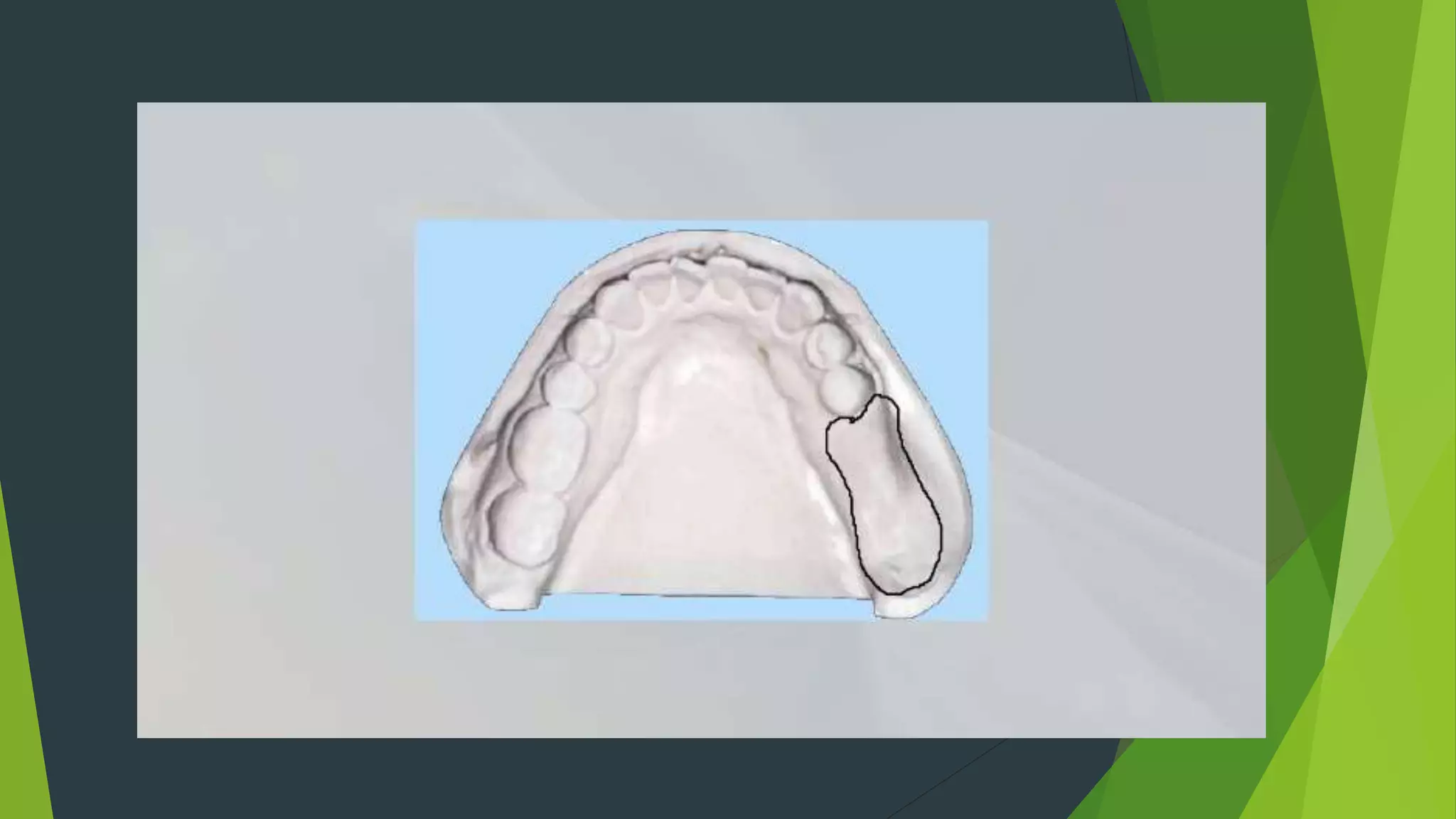
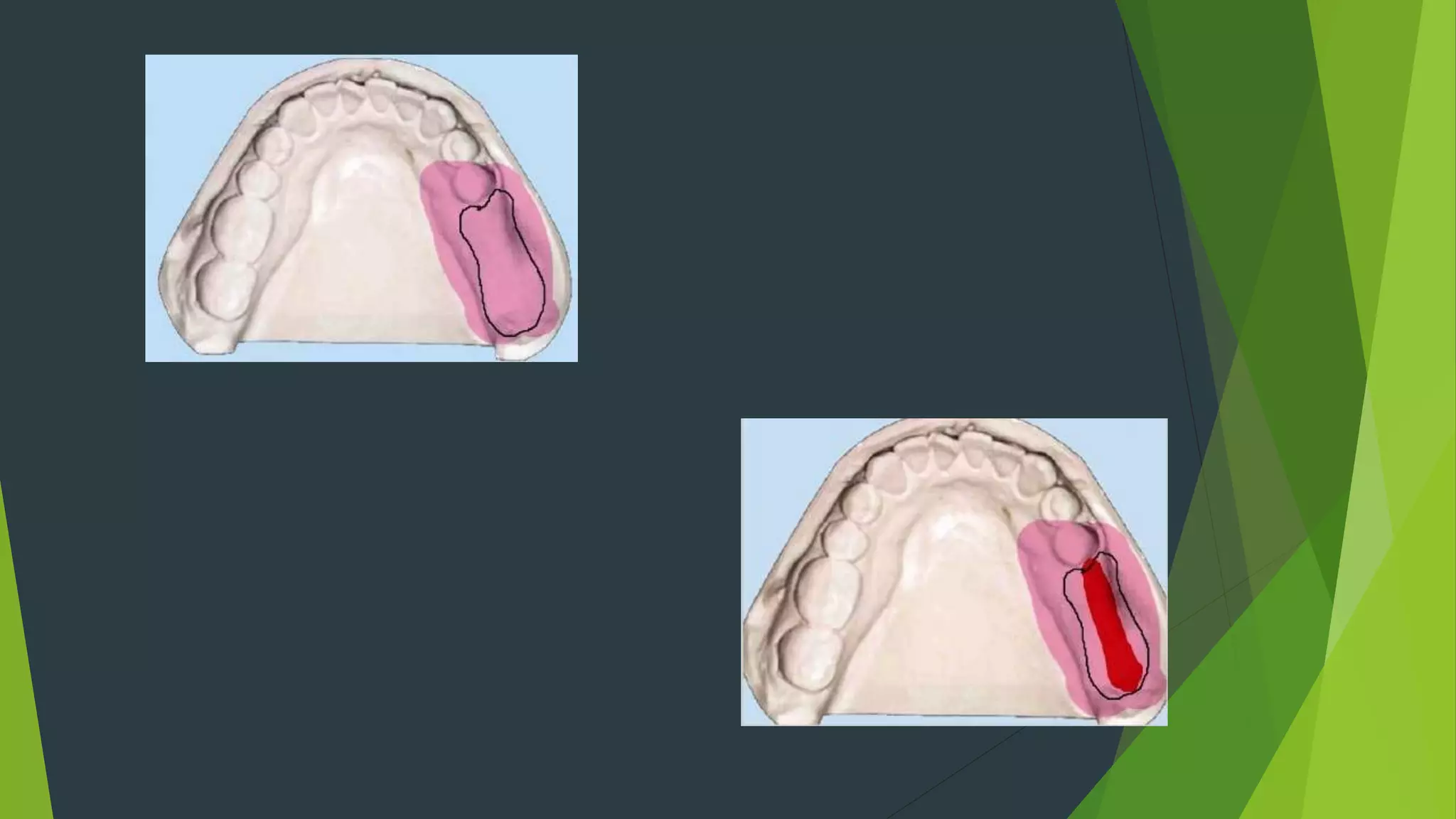
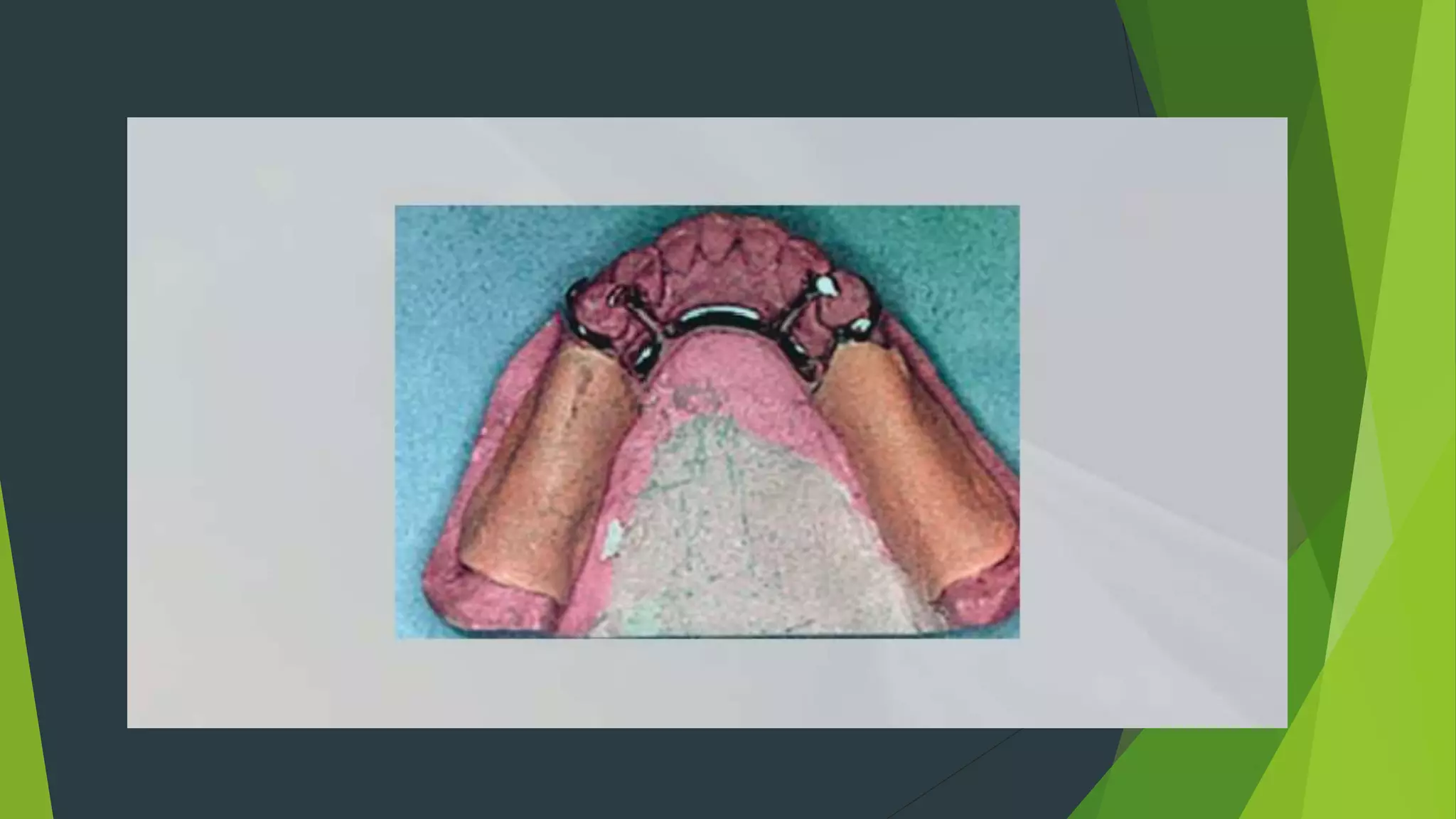
Vibhor Tyagi presented on impression materials and procedures for removable partial dentures. The presentation covered classification of impression materials including rigid, thermoplastic and elastic materials. Specific elastic materials discussed included reversible and irreversible hydrocolloids, polysulfide and polyether impressions. Techniques for maxillary and mandibular impressions were outlined. Special impression procedures for edentulous ridges including functional, McLean's, Hindel's and fluid wax methods were also presented. The importance of custom trays, border molding and selective pressure techniques were emphasized for accurate impressions.