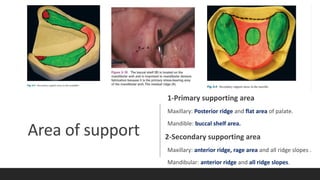
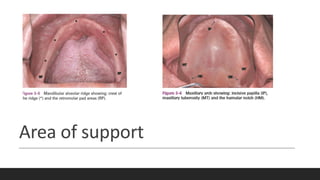
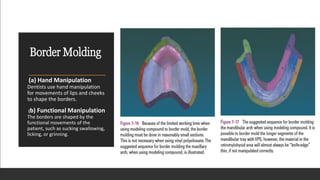
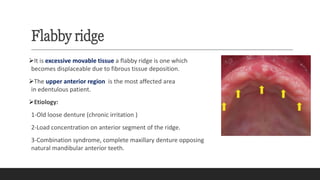
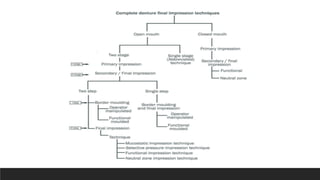
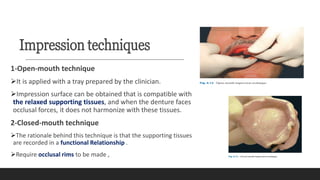
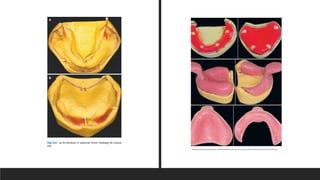
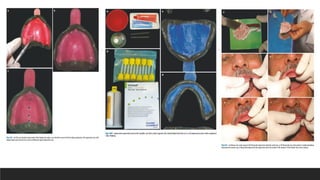
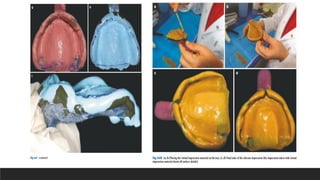
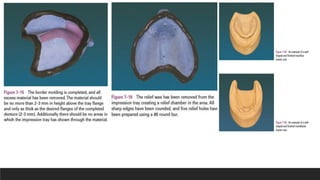
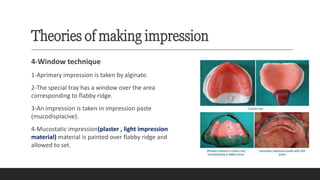
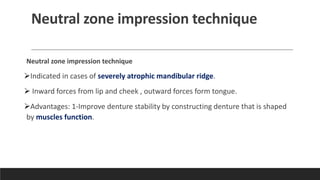
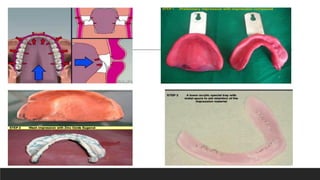
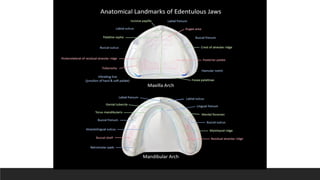
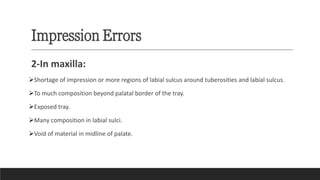
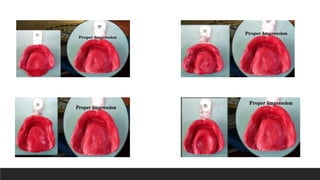
This document discusses impression techniques for complete dentures. It begins by defining an impression and primary and secondary impressions. The objectives of a good impression are outlined as retention, support, stability, aesthetics, and tissue preservation. Key areas of support in the maxilla and mandible are described. Border molding techniques including hand and functional manipulation are explained. Standard and special impression trays are discussed. Common impression materials like impression compound, alginate, zinc oxide eugenol, and elastomers are described. Open and closed mouth impression techniques as well as various theories of impression making like mucostatic, pressure, selective pressure, and neutral zone techniques are summarized. Finally, common errors in maxillary and mandibular impressions