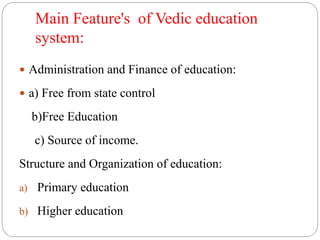
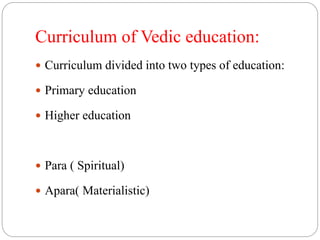
Vedic education during the Vedic period was both narrow and extensive. Students received education initially at home and then attended gurukuls for further study. Education focused on religious texts like the Vedas as well as subjects like arts. Students lived a disciplined life at gurukuls under the guidance of gurus for many years depending on how many Vedas they studied. The education system was free from state control and aimed at spiritual and religious learning as well as the preservation of culture and development of knowledge and social duties. Medium of instruction was Sanskrit and teaching methods included memorization under the tutelage of gurus.