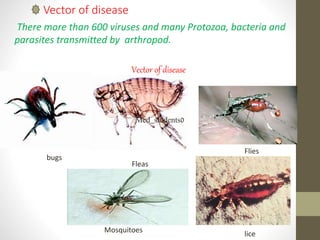
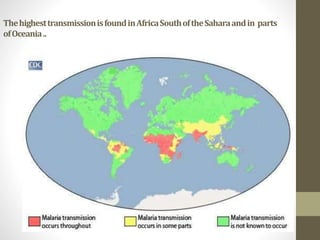
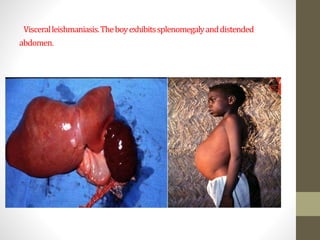
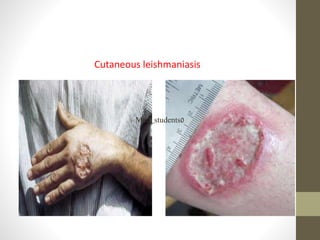
This document discusses several important vector-borne diseases including malaria, dengue fever, leishmaniasis, lymphatic filariasis (elephantiasis), African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness), and others. It describes the parasites and pathogens that cause each disease, their methods of transmission typically via arthropod vectors like mosquitoes and flies, characteristic symptoms, and global epidemiology. Malaria in particular is discussed in depth, outlining the four main plasmodium species that infect humans and how transmission is dependent on environmental factors like temperature. The clinical presentations of different forms of leishmaniasis are also reviewed.