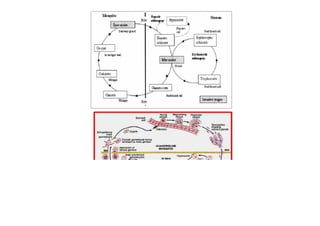
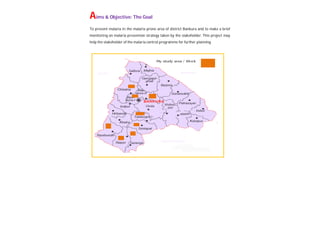
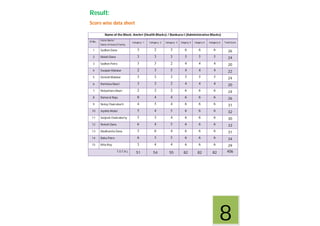
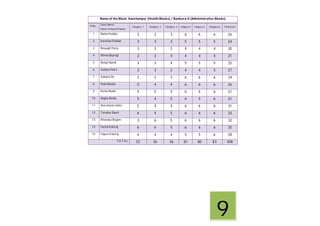
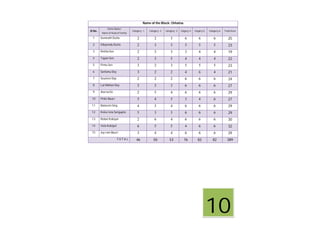
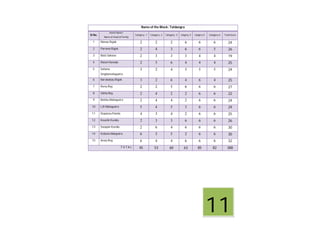
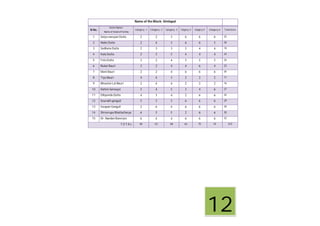
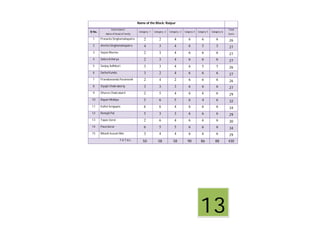
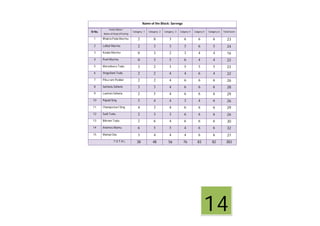
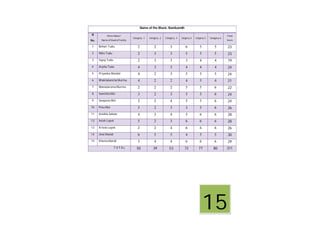
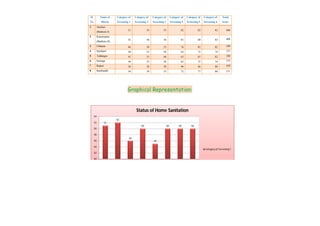
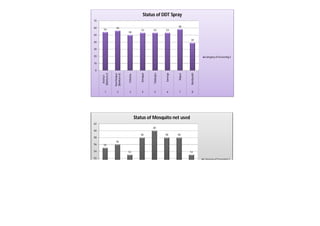
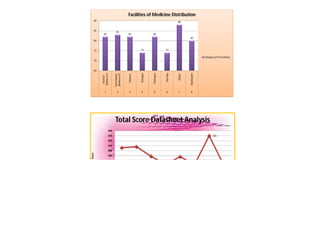
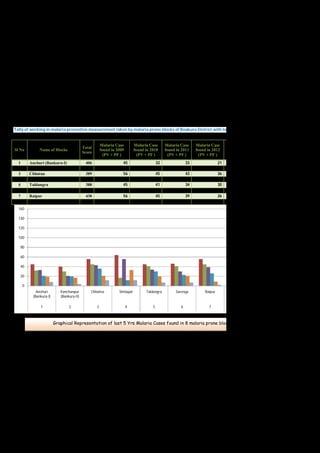
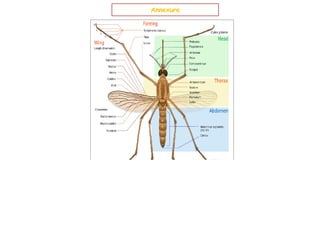
This document contains a certificate and project work from a student named Sourav De from Narrah High School in Bankura, India. The project is about developing a malaria prevention strategy for the malaria prone areas of Bankura District. It includes an introduction to malaria, its symptoms, life cycle and transmission. The aims and objectives are to prevent malaria in the area and monitor prevention strategies. The methods section describes using questionnaires and collecting malaria case data. The results section shows a scoring system used to analyze prevention work done in different categories like home sanitation, IRS spraying, mosquito net use and medicine availability.