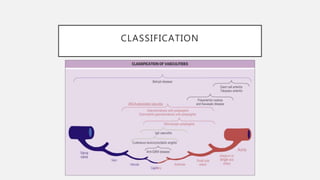
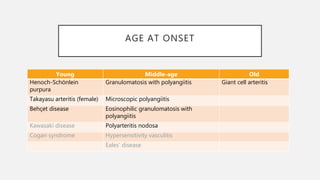
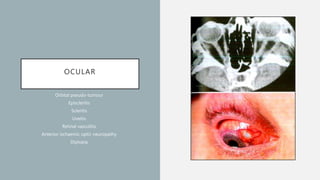
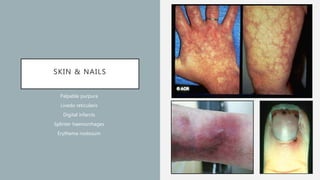
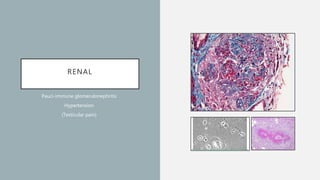
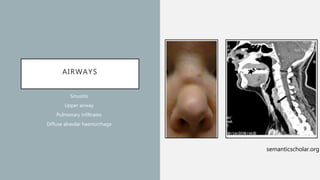
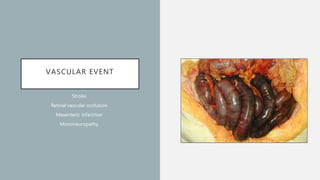
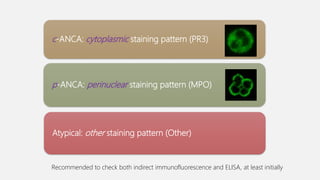
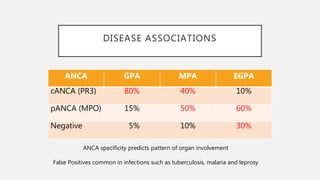
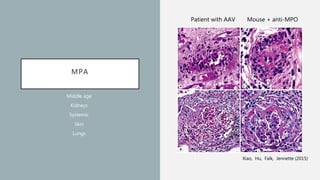
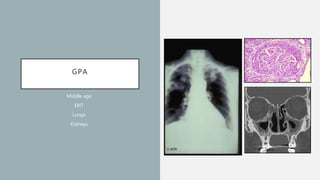
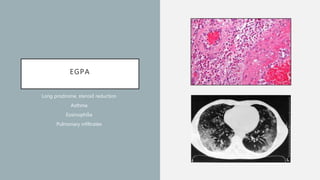
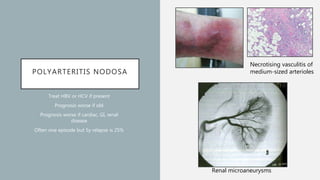
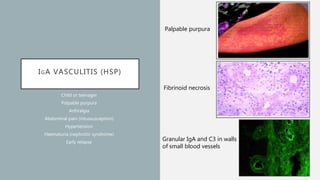
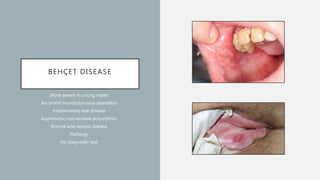
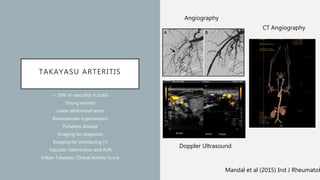
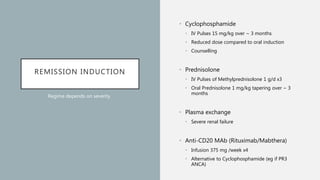
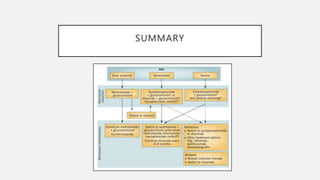
Vasculitis refers to inflammation of blood vessels which can be primary or secondary. It presents in different ways depending on the age of onset and type, affecting various organs like skin, kidneys, lungs and eyes. Diagnosis involves assessing clinical features, labs, imaging and biopsy. Treatment focuses on inducing remission with steroids and immunosuppressants like cyclophosphamide. Maintenance involves steroids, azathioprine or biologics to prevent relapse while monitoring for complications. Outcomes have improved but morbidity and mortality remain high without treatment.