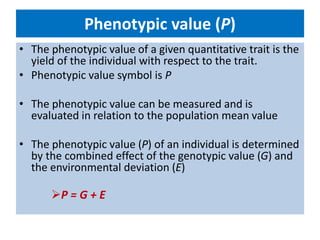
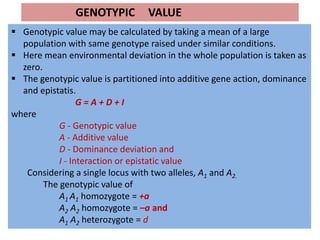
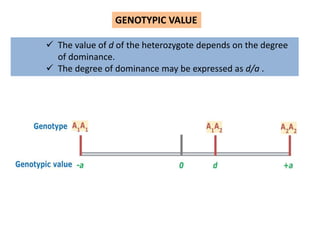
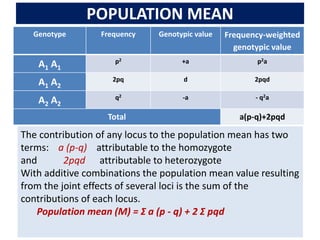
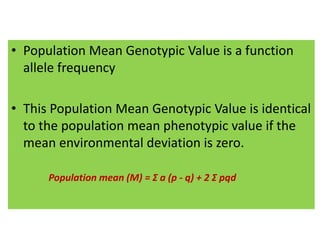
This document discusses quantitative genetics and the concepts of phenotypic value, genotypic value, environmental deviation, and population mean. It explains that quantitative traits are controlled by multiple genes and their inheritance is called quantitative or polygenic inheritance. The phenotypic value of an individual is determined by the sum of their genotypic value and environmental deviation. The population mean genotypic value, which is equal to the population mean phenotypic value if environmental deviations average to zero, can be calculated based on allele frequencies at loci and their additive and dominance effects.