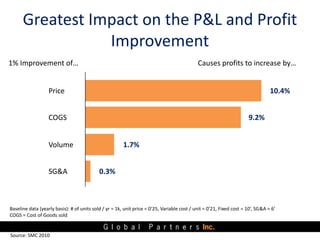
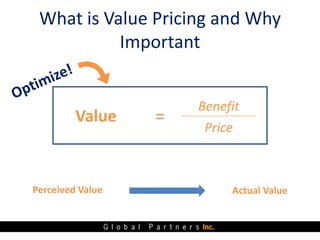
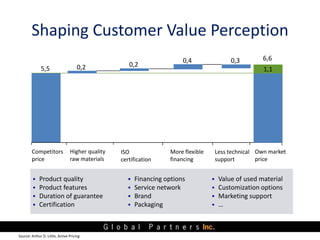
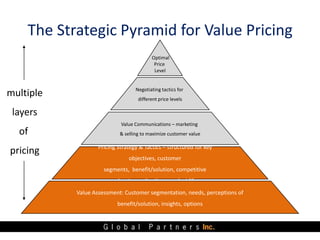
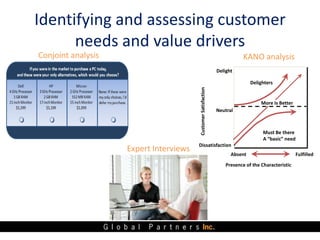
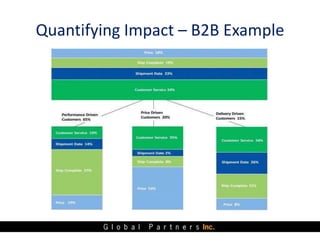
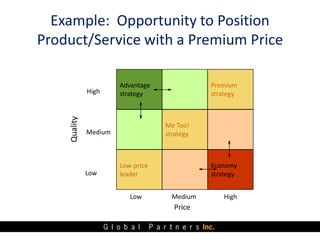
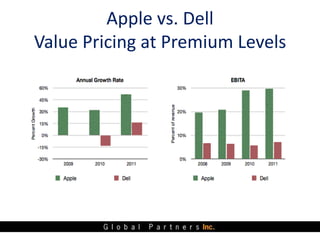
The document presents an overview of value pricing by Global Partners Inc., emphasizing its importance for businesses to accurately price their products based on customer perceived value. It outlines various pricing approaches, their strengths and weaknesses, and provides a framework for optimizing pricing strategies through customer insights and segmentation. Additionally, the document highlights the need for companies to improve their pricing power and research to enhance profitability.