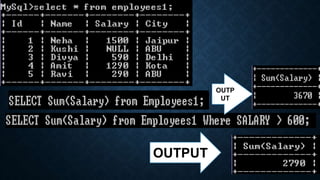
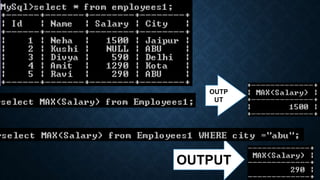
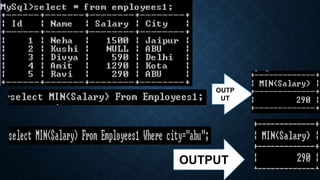
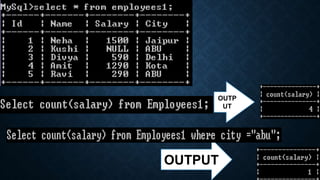
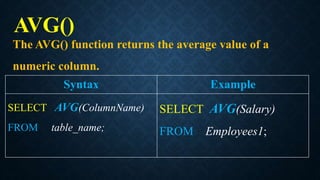
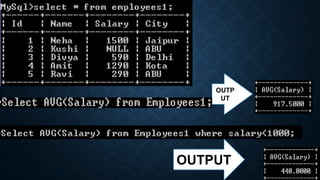
The document discusses several aggregate functions in SQL including SUM(), MAX(), MIN(), COUNT(), AVG(). It provides the syntax and examples of using each function with and without conditions to get the total sum, largest value, smallest value, number of rows, and average value from columns in tables.