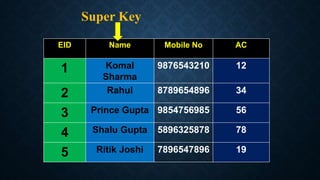
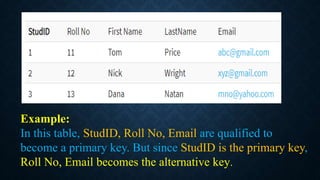
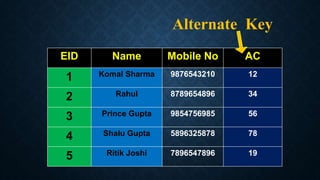
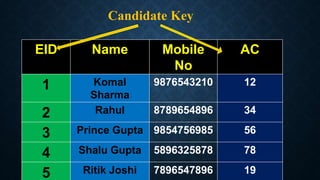
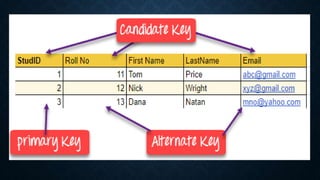
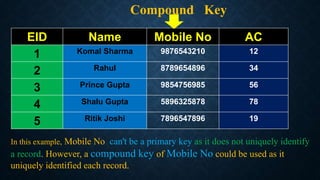
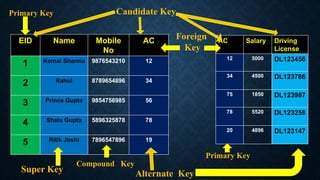
Keys in databases help uniquely identify rows in tables. The main types of keys are:
1. Primary keys uniquely identify each row and cannot contain duplicate values.
2. Foreign keys link rows between tables and must match the primary key of another table.
3. Composite/compound keys combine two or more columns to uniquely identify rows, since the columns individually may not be unique.
Surrogate keys are artificial primary keys used when the table lacks a natural candidate key to uniquely identify rows. Other keys include unique keys, alternate keys, candidate keys, and super keys. Keys are important for maintaining data integrity and relationships between tables.