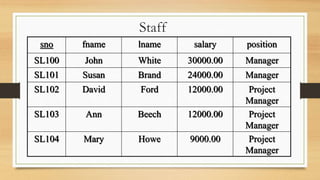
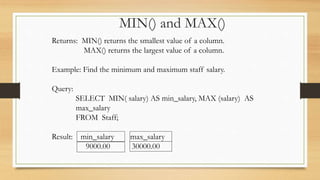
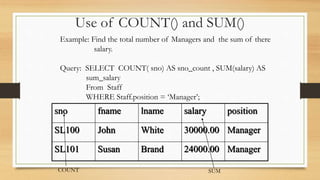
Shahadat Hossain presented on aggregate functions in SQL. Aggregate functions take a collection of values as input and return a single value. Common aggregate functions include MAX(), MIN(), AVG(), SUM(), and COUNT(). Each function operates on a single column and returns a single value. SUM() and AVG() operate on numeric data, while MIN(), MAX(), and COUNT() can operate on numeric or non-numeric data. Examples demonstrated how to use each function to return values like the total salary, average salary, minimum salary, and number of records that meet a condition.