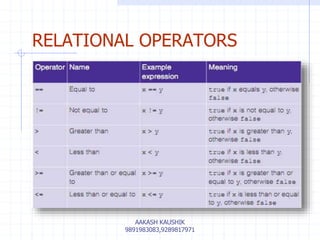
This document discusses operators in C++. It describes different types of operators - unary, binary, and ternary - and provides examples of common operators like arithmetic, relational, and logical operators. Specifically, it explains that operators operate on operands to produce results, and classifications of operators are based on the number of operands needed.