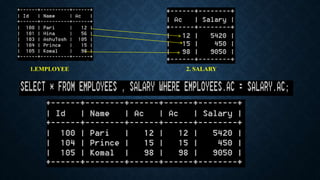
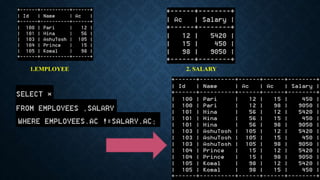
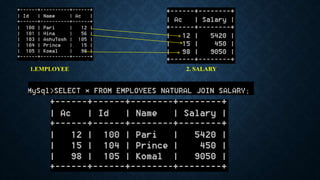
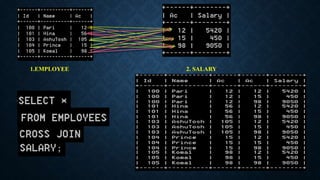
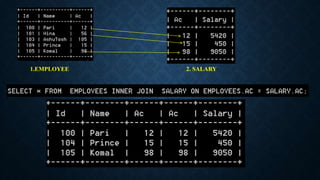
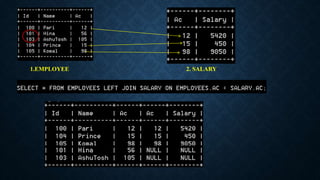
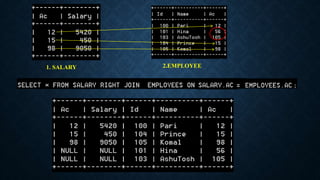
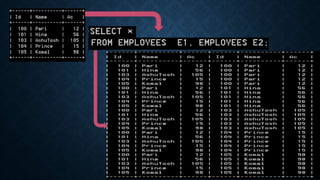
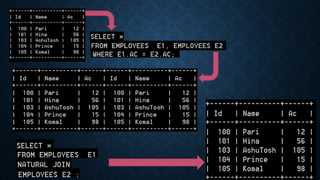
Joins are used to combine data from multiple tables and come in several types. The main types are inner joins, left joins, right joins, full joins, and self joins. Inner joins return rows where there are matches in both tables, left joins return all rows from the left table even if no match exists in the right table, and right joins are the opposite of left joins. Full joins are not directly supported in MySQL and require a combination of joins and unions. Self joins match a table to itself.