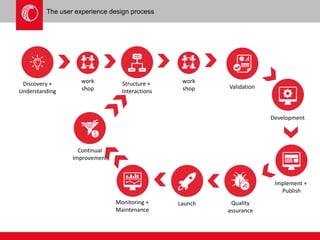
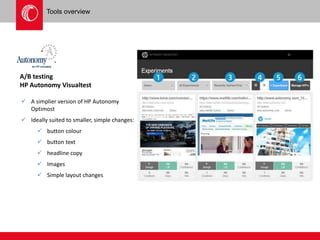
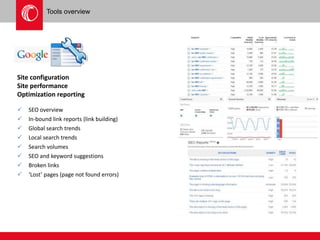
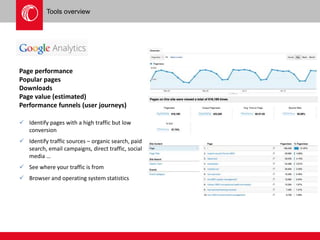
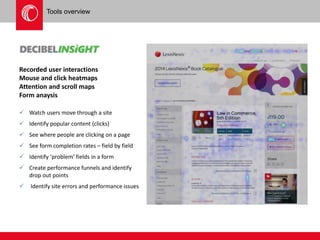
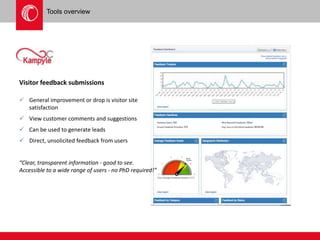
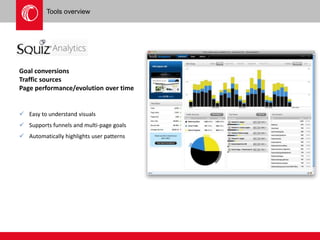
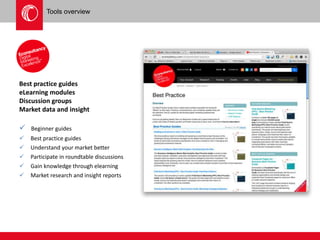
The document provides an overview of user experience (UX) design, emphasizing the importance of understanding user motivations and business goals to create effective web design. It outlines the UX design process, which includes phases such as discovery, content strategy, development, implementation, and continual improvement, highlighting the roles of various teams and tools involved. Additionally, the necessity of ongoing evaluation and optimization based on user feedback and performance metrics is underscored.