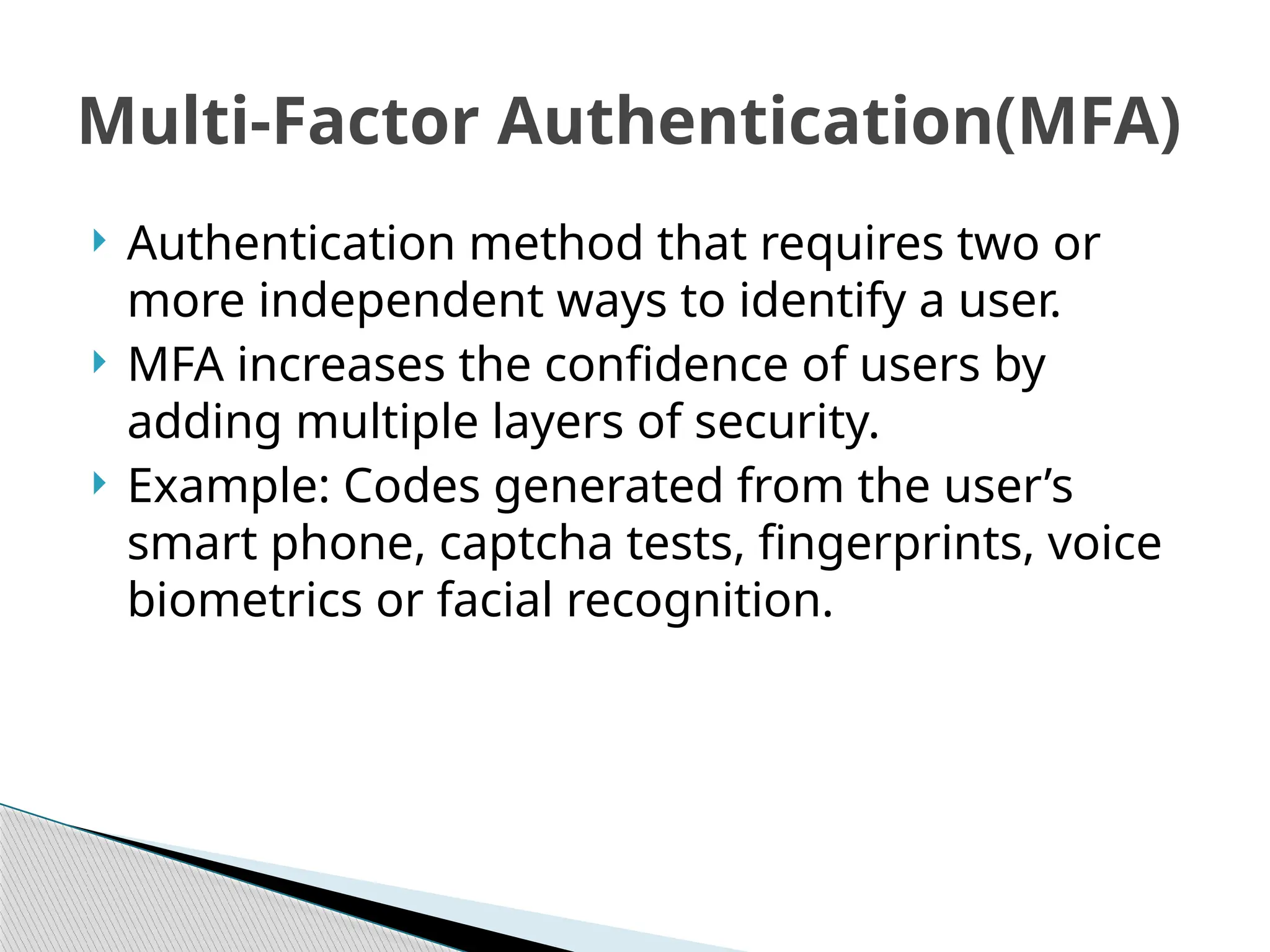
User authentication is the process of verifying a user's identity before granting access to computing resources. It involves three key tasks: identification, authentication, and authorization, with methods ranging from single-factor to multi-factor authentication. Best practices include strong password policies, implementing multi-factor authentication, and user education to address security challenges like phishing and brute force attacks.