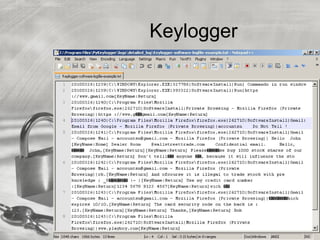
The document provides an overview of electronic authentication, including its importance, definitions, and various types of authentication factors such as something you know (passwords), something you have (one-time password devices), and something you are (biometrics). It discusses the benefits and drawbacks of these authentication methods, emphasizing that while passwords are widely used, they are the weakest form of authentication, whereas biometrics is considered the strongest. The document also highlights the implementation of dual-factor authentication at UW-Madison to protect sensitive information in their systems.