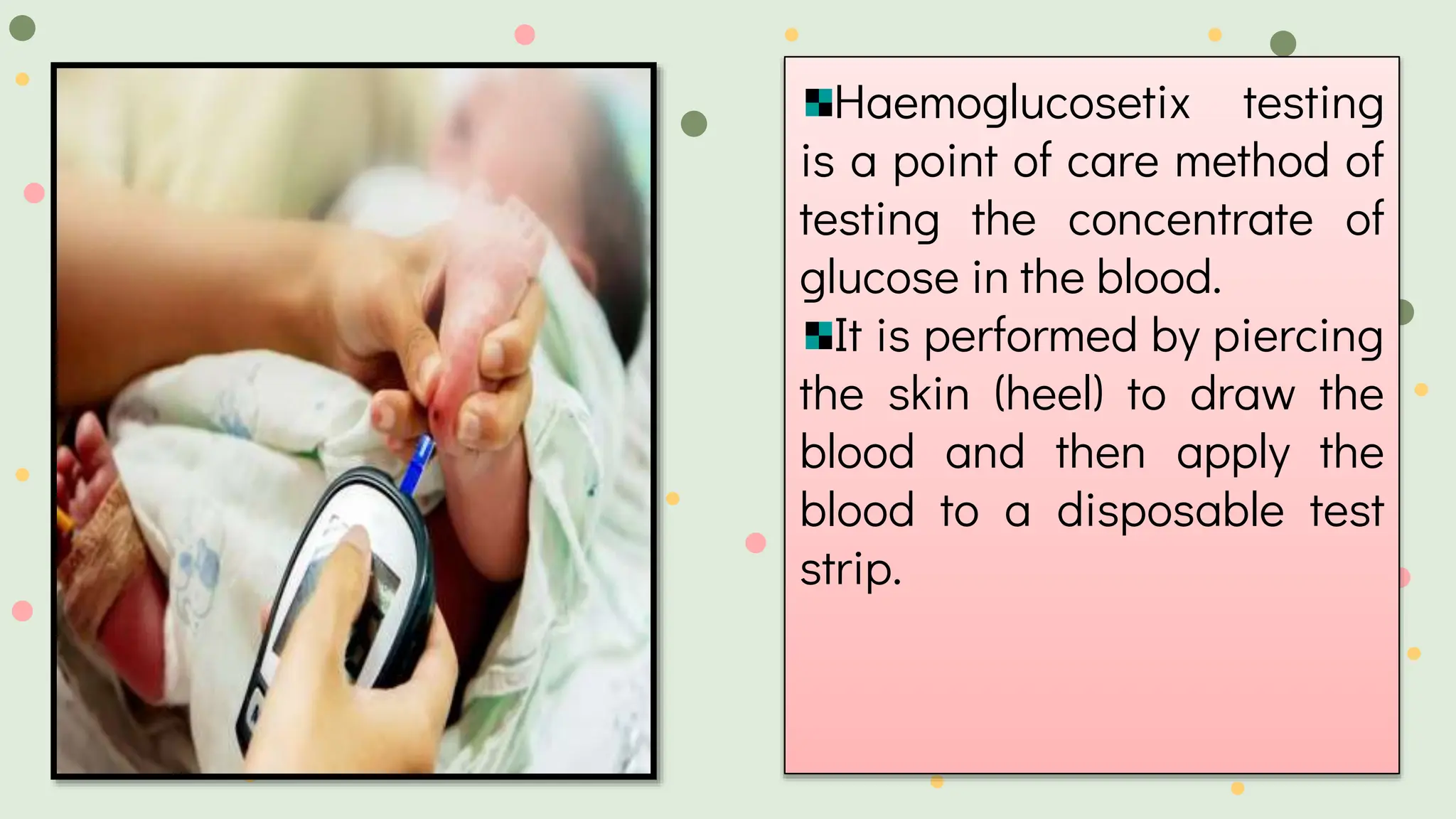
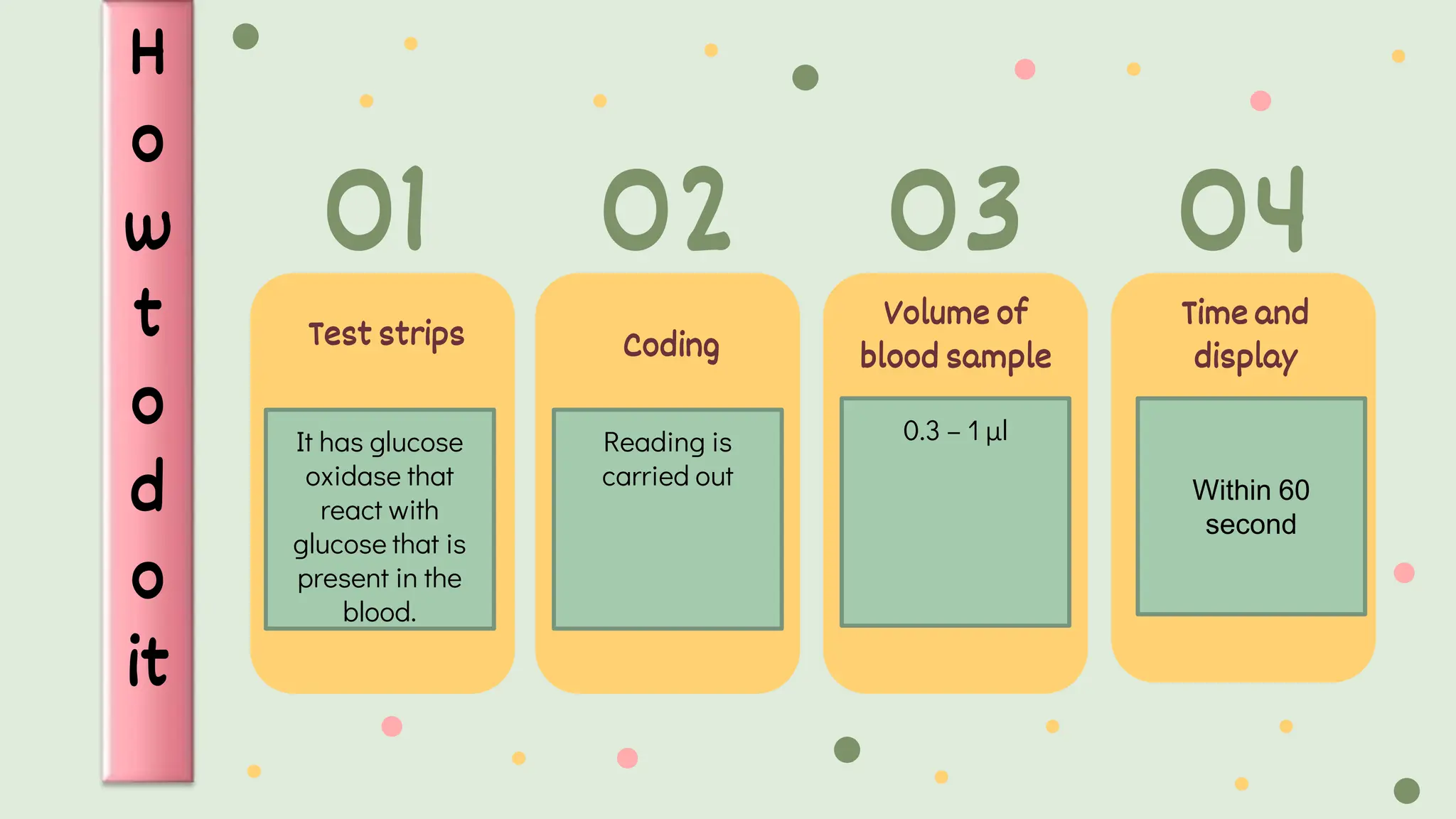
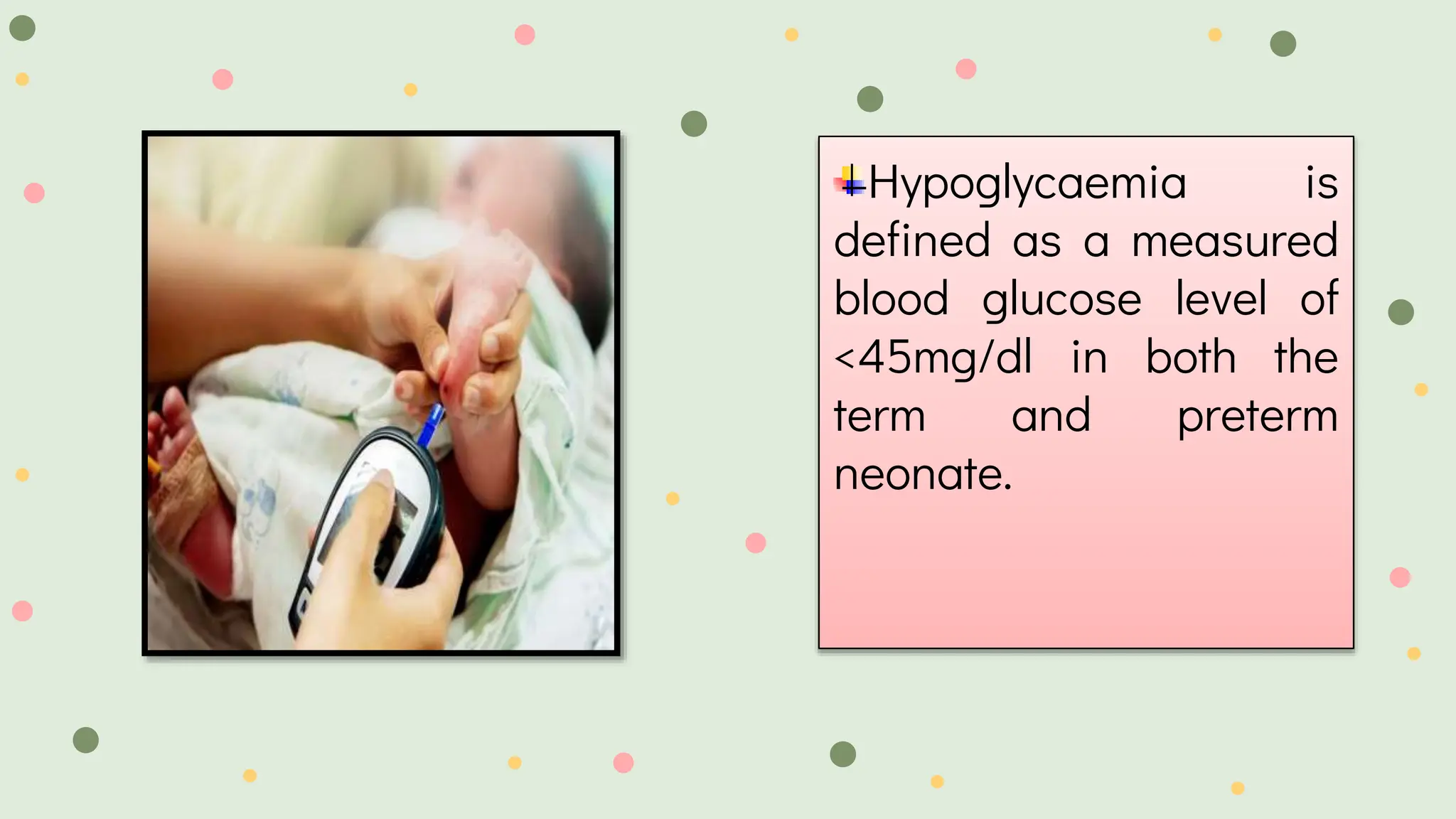
This document provides information on haemoglucosetix testing, which is a point-of-care method to test blood glucose levels. It involves pricking the skin, usually the heel, to draw a small amount of blood, which is then applied to a disposable test strip. The test can help monitor blood glucose fluctuations in sick infants and guide interventions if needed. Factors like temperature, sample size, and test strip accuracy can influence readings. Hypoglycemia is defined as a blood glucose level below 45mg/dl in neonates and should be treated by increasing oral feeds or intravenous glucose depending on the severity of symptoms. Nursing considerations include ensuring continuous glucose infusion to prevent rebound hypoglycemia.